Tort Law
advertisement

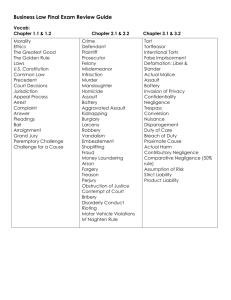
HOT D E BAT E Where do you stand? Your neighbor Shana is using a multipurpose woodcutting machine in her basement hobby shop. Suddenly, because of a defect in the two-year-old machine, a metal clamp from the machine breaks. The metal strikes Shana’s left eye, badly injuring it. The manufacturer had provided a one-year warranty against defects on the machine. 1.Do you think the manufacturer should be responsible for paying Shana’s medical expenses? 2.What defense(s) does the manufacturer have against a suit for damages for the injury. The Law of Torts One Person’s interference with another’s rights, either through intent, negligence, or strict liability. In other words, a private or civil wrong. What is a Tortfeasor? Your Rights….. To be free from bodily harm. To enjoy a good reputation. To conduct business without unwarranted interference. To have one’s property free from damage or trespass. Torts Are Classified As Being Intentional or Unintentional The elements of a tort are: 1. Duty 2. Breach 3. Injury 4. Causation We also have the duty to respect the rights of others. 1. The duty not to injure another. 2. The duty not to interfere with the property rights of others. 3. The duty not to interfere with the economic rights of others, such as the right to contract. Intentional Torts Intentional Torts Wrong that occurs when a person knows and desires the consequences of his or her act. Examples: Invasion of Privacy False Imprisonment Emotional Distress Assault Battery Defamation Deceit Nuisance Trespass Conversion Trespass Wrongful injury to or interference with the property of another. Nuisance Anything that interferes with the enjoyment of life or property. Defamation Wrongful act of injuring another’s reputation by making false statements. False Imprisonment Unlawful Physical Restraint Invasion of Privacy Interfering with a person’s right to be alone. Unintentional Torts *The most common tort. *Intent is not required for Negligence this tort, only carelessness. Failure to exercise the degree of care that a reasonable person would have exercised in the same circumstances. To succeed in a tort suit for negligence, you must prove all of the following: The defendant owed the plaintiff a duty of care. The defendant failed to act as a reasonable person would have and, therefore, did not use the degree of care required under the circumstances (breach of duty). The breach of duty defendant was the proximate cause of the injury to the plaintiff. The plaintiff suffered some actual harm or injury. Key Terms Duty of Care Each of us has certain rights--the rest of us have the duty not to violate those rights. Breach of Duty Not exercising the degree of care that a reasonable person would exercise in that same situation. Proximate Cause Something that produces a result, and without which, the result would not have occurred. Actual Harm Must show he or she suffered some sort of harm. Defenses to Negligence You Can Defend a Negligence Suit by Eliminating One of the Four Elements. Contributory Negligence Prove that the plaintiff’s own negligence helped cause the injuries. Comparative Negligence Compare each party, then the amount of the plaintiff’s recovery is reduced by the percent of their negligence. Defenses (cont.) Assumption of Risk Plaintiff new risk involved and still took the chance of being injured. Strict Liability Ultra-hazardous activities Injunction Court order issued by a judge ordering a person to do or not to do something. What’s your verdict? Mrs. Lamm went to a grocery store and placed a carton of a carbonated soft drink in her shopping cart. One of the bottles exploded and the broken glass cut her leg. Can she collect in tort from the grocery store or the bottler? What’s your verdict? Joan was a guest in Lane’s home. While leaving the house, Joan was injured when she slipped on some ice that had formed on the steps leading from the door. Lane had cautioned Joan about the possibility of the steps being slippery, and Joan admitted seeing the ice. In a legal action claiming negligence, would Lane be liable?