Unit 7 Ch.23
advertisement

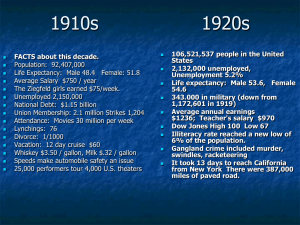
The Modern Era of the 1920s Unit 7 Ch.23 1920-1929 Business-Government Partnership Republicans believed that the economy would prosper if business took the lead Warren G. Harding became president in 1921 with Calvin Coolidge as his vice president Harding assembled a cabinet of progressives, conservatives, and friends The “Associated” State Sec. of Commerce Hoover directed the creation of two thousand trade associations to work with businesses Hoover wanted to achieve through voluntary cooperation what the Progressives had tried to legislate Scandal in the Administration Charles Forbes (Veterans Bureau) caught selling government and hospital supplies to private companies Thomas Miller (Office of Alien Property) took bribes Albert Fall (Sec. of Interior) arranged to have oil-rich land transferred to his department and then secretly leased it to his friends in the oil industryTeapot Dome Scandal Harding died in 1923 as the news was breaking Election of 1924 Republicans- Calvin Coolidge Democrats- divided between North and South Taciturn and moral John Davis was the compromise Candidate Progressive party- Robert La Follette Coolidge won handily low voter turnout Women in Politics Influential as lobbyists The Women’s Joint Congressional Committee Sheppard-Towner Maternity and Infancy Act First federally funded health-care legislation Conservatives attacked it as a Communist plot and an attempt to socialize America Corporate Capitalism Business Consolidation Accelerated rapidly during the 1920s in major industries Chemicals (DuPont), electrical appliances and machinery (Westinghouse and General Electric), and automobiles (General Motors) Oligopolies dominated major industries 1920s Economy 1919-inflation, 2 years of recession, 1922-1929 steady growth Abundance of new consumer products Agriculture, coal, textiles, and railroads were the “sick industries” Welfare Capitalism Labor relations that stressed management’s responsibility for employees’ wellbeing. Large corporations offered health insurance, pension plans, and the opportunity to buy stock Goals were to create a loyal workforce and deter unionization Economic Expansion Abroad American business spread to Europe, Asia, and south America Fordney-McCumber Tariff (1922) Raised tariffs on foreign-made goods Made it difficult European nations to pay their war debts Dawes Plan (1924) Reduced German reparations while providing them with loans Success depended on American loans to Germany and Allied payments to America Foreign Policy in the 1920s Combination of isolationism and internationalism Washington Naval Arms Conference Placed strict limits on naval expansion to deter excessive spending and limit Japanese naval power in SEA Kellogg-Briand Pact Agreement condemn war for the “solution of international controversies, and to renounce it as an instrument of national policy.” National Culture Consumer Society New electrical conveniences started to become necessities instead of luxuries Modern Advertising Irons, refrigerators, cooking ranges, and toasters Hired psychologists to study how to appeal to people’s desires The Automobile Paved roads, homes with garages, gas stations, repair shops, motels, shopping centers, traffic signals People could live farther from work (urban sprawl) and vacation far from home Symbolized freedom and success Mass Culture Movies Jazz Began in New Orleans and spread to the major cities Journalism Early stars included Buster Keaton, Charlie Chaplain, Mary Pickford, and Clara Bow (who became the icon of flappers) Mass circulation magazines, tabloid newspapers, Associated Press spread mass culture Radio Became the primary form of entertainment for many households Mass Culture Leisure Driving, playing tennis or golf, swimming Sports Baseball and boxing were the primary professional sports of the 1920s Rise of Nativism Nativism- prejudice against foreign-born people Immigration Restriction Emergency Quota Act (1921) and the National Origins Act (1924) severely restricted immigration from Europe Immigration from the Western Hemisphere continued The New Klan 4.5 million members by 1924 Prohibitionists, anti-Catholic, anti-Semitic, anti-Union, anti-immigration, anti-black Appealed to most American sentiments at the time Legislating Values Protestant Fundamentalism A movement grounded in the literal interpretation of the Bible The Scopes Trial (1925) Tennessee science teacher John Scopes was put on trial for teaching about evolution ACLU provided Clarence Darrow as defense attorney William Jennings Bryan served as special prosecutor and Bible expert Scopes was found guilty, but it was overturned by the Tenn. Supreme court Legislating Values The “Noble Experiment” Eighteenth Amendment took effect in 1920 Some urban ethnic groups made their own beer or distilled bathtub gin (bootleggers) Organized crime increased Speakeasies sprang up across the country Twenty-first Amendment in 1933 ended prohibition Intellectual Crosscurrents “Lost Generation” A group of writers and artists who lashed out against war and the pursuit of excess material wealth Harlem Renaissance Championed racial pride among Black Americans Writers, musicians, and other artists went to Harlem to be part of the experience Ernest Hemingway, F. Scott Fitzgerald, T.S. Eliot , Sinclair Lewis Claude McKay, Zora Neale Hurston, Langston Hughes Marcus Garvey and UNIA Universal Negro Improvement Association Jamaican immigrant who encouraged black separatism and started a back to Africa movement Election of 1928 Campaign issues: Prohibition, Protestant Fundamentalism, nativism Democrat- Alfred Smith 4 terms as governor of New York Tammany Hall political machine Irish Catholic Opponent of prohibition Republicans- Herbert Hoover Secretary of Commerce Food Administration (WWI) Wins election (only elected office Hoover ever wins)