P=V 2 /R

Parallel Circuit
• A parallel circuit is one that has two or more paths for the electricity to flow – similar to a fork in a river
• In other words, the loads are parallel to each other.
• If the loads in this circuit were light bulbs and one blew out there is still current flowing to the others.
Electric Current
• Current is the rate at which electric charges move through a given area.
• SI unit is the Ampere or Amp.
• 1 A = 1 C/s
• I = ΔQ/t
• Current = charge / time
Example problem
• The current in a light bulb is 0.835 A. How long does it take for a total charge of 1.67 C to pass a point in the wire?
ΔQ = 1.6 C I = 0.835 A t= ?
I = ΔQ/t t = ΔQ/I t= 1.6C/0.835A
t= 2.00s
Potential Difference
• The potential difference between the positive and negative ends of batteries:
• All AA, AAA, C, D Cell Batteries = 1.5 V
• The only difference is how long they produce the 1.5 V.
• Car battery = 12 V
• Positive and Negative slots of an electrical outlet = 120 V
Resistance
• Resistance- The opposition to the flow of current in a conductor
• R = V/I
• Resistance = Potential difference/Current
• SI unit – ohm Symbol-
(omega)
Example Problem
• The resistance of a steam iron is 19.0 Ω. What is the current in the iron when it is connected across a potential difference of 120V?
• R= 19.0 Ω V= 120V I= ?
• R=V/I
• I=V/R
• I=120V/19.0 Ω
• I= 6.32 A
Ohm’s Law
• Relates electric current, voltage and resistance.
• • Current = Voltage/Resistance (I=V/R)
• Current (I)
• flow of e-
• I = Q/t
• I = V/R
• Ampere (Amps)
• A
• Resistance (R)
• opposition to the flow of e-
• R = V/I
• Ohms
• Ω
• Voltage (V)
• push of e-
• V = PE/Q
• V = IR
• Volts
• V
Electric Power
• Electric power is the rate of conversion of electrical energy
• Formula for Electric Power:
P = IV
Electric power = current X potential difference
Electric Power
Because P= IV and V=IR we can also say;
P= IV = I(IR) = I 2 R
P = I 2 R
Or, because I = V/R, we can also say:
P = IV = (V/R)V = V 2 /R
P=V 2 /R
Electric Power
• An electric space heater is connected across a 120 V outlet. The heater dissipates 1320 W of power in the form of electromagnetic radiation and heat. Calculate the resistance of the heater.
• P = V 2 /R R = V 2 /P
• R = 120 2 /1320
• R = 10.9 Ω
Electric Power
• Power companies measure energy not power, using the kilowatt-
hour as the unit
• One kilowatt-hour = the energy delivered in 1 hour at the constant rate of 1 kW.
• To convert between kWh and the SI unit of Joule:
• 1 kWh = 3.6 X 10 6 J
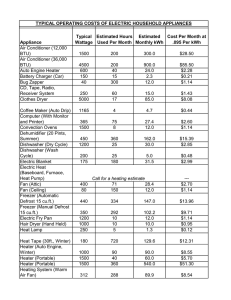
Energy Usage Cost
• Power (P)
• • meas. of the rate at which electricity does work.
• • P = V x I
• • Watts (W)
• Energy (E)
• •meas. By electric meter.
• • E = P x t
• • kilowatt-hour
• (kWh)
• Cost ($)
• •cost of electricity
• • Cost = energy x kwh
• ($.07)
Example Problem
• How much does it cost to operate a 100.0 W light bulb for 24 h if electrical energy costs $0.080 per kWh?
• P= 100W = 0.100 kW; t= 24 h
• Energy = Pt = 0.100 kW*24 h = 2.4 kWh
• Cost = 2.4 kWh*$0.080 = $0.19