module specification template
advertisement

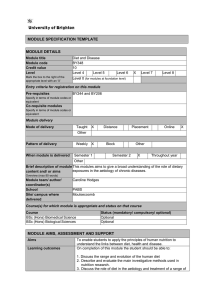
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Basic Human Nutrition BY244 10 Level 4 Level 5 X Level 6 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 7 Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites BY130; BY116 or BY104 Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other X Distance Placement Pattern of delivery Weekly X Block Other Online When module is delivered Semester 1 Semester 2 X Throughout year Other Brief description of module This module will build on level one physiology and cell biology and biochemistry extending the student’s knowledge into clinical and medical content and/ or aims applications. The main emphasis will be on the importance and Overview (max 80 words) significance of diet and nutrition. Module team/ author/ Caroline Hodges; Imogen Rogers coordinator(s) School PABS Site/ campus where Moulsecoomb delivered Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course BSc (Hons) Biomedical Science BSc (Hons) Biological Sciences BSc (Hons) Chemistry Other BY routes MChem Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) Optional Optional Optional Optional Compulsory (BY pathway) MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims To provide the student with a broad understanding of human food and nutrition and the physiological and biochemical processes involved in nourishment. Learning outcomes By the end of the module the student should be able to: Discuss the evolution and range of the human diet. (1) Content Learning support Describe in detail the nature and function of micronutrients. (2) Describe in detail the nature and function of macronutrients (3) Explain the concept of dietary reference values and their limitations.(4) To distinguish between the changing nutrient requirements throughout the lifetime.(5) To appreciate the importance of nutritional status and body composition.(6) To appreciate dietary problems in industrialised and developing countries.(7) Whilst covering nutrition in its broadest sense, the course pays particular attention to modern areas of concern both to the general public and medical profession. Macronutrients and micronutrients function and sources. Recommended daily amounts of the above – their determination and limitations. Nutritional changes at different stages in life such as during childhood, pregnancy, and old age. Methods used to assess nutritional status and body composition. The evolution and range of the human diet. Latest editions of : Smolin LA, Introduction to Human Nutrition – Science and Applications, Wiley. Mann J and Truswell AS, Essentials of Human Nutrition, Oxford University Press. Geissler C and Powers H, Human Nutrition and Dietetics, Churchill Livingstone. Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities The module will be delivered via lectures (approximately 24 hours), personal study (approximately 66 hours) assessment: case studies/workshop (10 hours). Allocation of study hours (indicative) Study hours Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. 34 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 66 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not work-based learning or a year abroad. TOTAL STUDY HOURS 100 Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module 60% exam : (LO 1, 2, 3, and 5) 40% coursework: worksheet/case study (40%, LO 4, 6 and 7) Types of assessment task1 % weighting Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN Written exam 60 1 Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task. COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise 40 EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board Biology and Biomedical Sciences External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Dr P Nicholls Senior Lecturer, University of Kent 01/10/09 30/09/13 QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval 2008 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision n/a Only complete where this is not the first version Date of approval for this version 2013 Version number 2 Modules replaced BY246 Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Yes No X