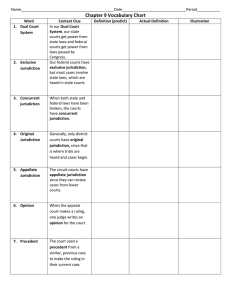
Goal 5/6 Notes: The Federal Court System Name: Why do we have
advertisement

Goal 5/6 Notes: The Federal Court System Name: __________________________________________________ Why do we have courts? “_________________________________________________________________________________________________.” To settle disputes (civil cases – 3 types: lawsuits, family law, contract law) and hold trials for those accused of a crime (felonies or misdemeanors). Judges act as a neutral 3rd party (arbitration) to decide issues, based on the law & precedent – not their own opinion. The Federal Court System: ____________________________ of the Constitution established a national Supreme Court and gave Congress the power to establish lower federal courts. Over the years, Congress set up three levels in the federal court system–district courts at the bottom, appeals courts in the middle, and the Supreme Court at the top. Each state also has its __________________________________________________________________________. Jurisdiction is a court’s authority to _______________________________________________________________________________. Original Jurisdiction: authority to hear a case first. Appellate Jurisdiction: authority to review the decisions of a court having original jurisdiction. Concurrent Jurisdiction: two courts _____________________________________________________________ to hear the case. Exclusive Jurisdiction: only federal courts may hear the case. The Constitution gives federal courts jurisdiction over eight kinds of cases. 1. If the law in question applies to the US ______________________________ 2. Cases involving violation of federal laws. 3. Any disagreement between 2 state governments. 4. Lawsuits between citizens of different states. 5. If the US government sues someone or someone sues the U.S. government 6. Disputes between a ________________________________________________ and either the U.S. government or an American private party. 7. Admiralty and maritime laws concern accidents or crimes on the high seas. 8. Cases involving ___________________________________. Levels of Federal Courts: ________________________________________ - are the federal courts where trials are held and lawsuits are begun (Original Jurisdiction in these cases). _____________________________________________________ - review decisions made in lower district courts. (Appellate Jurisdiction). ____________________________________________ – highest court in the US and hears cases of significance (Appellate [after US Court of Appeals] and Exclusive in cases involving the Constitution) U.S. District Courts: All states have at least one. For all federal cases, district courts have original jurisdiction, the authority to ___________________________________________________________________________. District courts hear both civil and criminal cases. They are the only federal courts that involve witnesses and juries. _____________________________: jury that is unable to decide a verdict. _________________________________: trial with no jury – only a judge U.S. Court of Appeals: People who lose in a district court often _______________________________________________________ ____________________–a U.S. court of appeals. This is appellate jurisdiction–the authority to hear a case appealed from a lower court. There are no juries. Guilt/innocence is not decided here – only if due process was followed. They can make 3 choices: ___________________________________________________________. Remand the case to a lower court (to have another trial). _____________________________________________ of the district court. Most appeals court decisions are final. A few cases are appealed to the ___________________________________________. One appellate judge writes an opinion that explains the legal thinking behind the court’s decision in the case. The opinion sets a precedent or model for other judges to follow in making their own decisions on similar cases. A judge may write a dissenting opinion if they ________________________________________________________________________________. US Supreme Court: Highest court of the United States. Part of the Judicial Branch – _________________________________ Has power of judicial review of federal laws. Marbury v. Madison (1803) gave them this power. 9 Supreme Court justices appointed for life by the President (_____________________________________________________________). Can be removed only through impeachment North Carolina State Courts NC District Court: original jurisdiction - Hears ___________________________________ and civil cases of less than $10,00 NC Superior Court: original jurisdiction - Hears cases in which felony crimes have been committed and civil cases of __________________________________________________ NC Court of Appeals: appellate jurisdiction - Reviews cases from lower courts NC Supreme Court: Appellate jurisdiction – hears appeals cases after NC Court of Appeals; exclusive jurisdiction for cases involving the _____________________________________________________. Jurisdiction Practice – Which court would these cases go to? Be specific. Federal – US District, US Court of Appeals, or US Supreme Court. State – NC District, NC Superior, NC Court of Appeals, NC Supreme. ____________________________________ 1. Martin sues Wake County public schools for $250,000 after he suffered 3 rd degree burns in a fire at Knightdale High School. ____________________________________ 2. Brooke is found guilty of killing three people in three different states and want to appeal her verdict. ____________________________________ 3. Renee sues the US government for her husband’s death in the Iraq War. ____________________________________ 4. Parents press charges against North Carolina in the Leandro cases because they are concerned that NC is not giving their children the education guaranteed to them in the NC Constitution. ____________________________________ 5. Miranda arguesd that he did not know what his rights were that were listed in the US Constitution, so he appeals his case. ____________________________________ 6. Robert commits a felony by kidnapping his little sister. ____________________________________ 7. Caroline steals a sweater from a local Raleigh store. ____________________________________ 8. Caroline appeals her case after she is found guilty of stealing a sweater from a local Raleigh store. ____________________________________ 9. Two US diplomats are accused of abusing their power and are put on trial. ____________________________________ 10. Parents sue a local Knightdale restaurant for $9,000 for making their children fat. Create a poster outlining the Judicial Branch. Top ½ of the poster – Federal Courts: Include the 3 levels of federal courts, what their jurisdiction is, and an example of a case each court might hear. Bottom ½ of the poster – NC Courts: Include the 4 levels of NC courts, what their jurisdiction is, and an example of a case each court might hear. Also label each court (federal and NC) as a trial court or an appeals court. Turn in the poster when you finish!