Chapter 16 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
advertisement

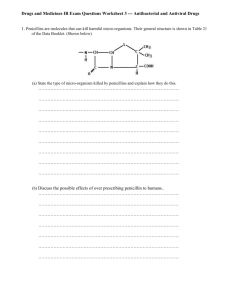
Chapter 84 Drugs That Weaken the Bacterial Cell Wall I: Penicillins Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Penicillins Active against a variety of bacteria Direct toxicity: low Principal adverse effect: allergic reaction Beta-lactam ring in their structure Beta-lactam family: also includes cephalosporins, aztreonam, imipenem, meropenem, and ertapenem Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 2 Penicillins Mechanism of action Weaken the cell wall, causing bacteria to take up excessive water and rupture Active only against bacteria that are undergoing growth and division Bactericidal Bacterial resistance • Inability of penicillins to reach their target • Inactivation of penicillins by bacterial enzymes Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 3 Mechanisms of Bacterial Resistance Three factors Inability of penicillins to reach their targets Inactivation of penicillins by bacterial enzymes Production of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) that have a low affinity for penicillins Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 4 Cell Envelope Gram-negative cell envelope Three layers Thin cell wall and an additional outer membrane that is hard to penetrate Gram-positive cell envelope Only two layers Relatively thick cell wall that is easily penetrated Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 5 Penicillinases Beta-lactamases Enzymes that render penicillin inactive Bacteria can produce a large variety of these enzymes specific for penicillins (and other beta-lactam antibiotics) Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 6 Classification of Penicillins Narrow-spectrum penicillins Narrow-spectrum penicillins Pencillinase-sensitive Pencillinase-resistant Broad-spectrum penicillins Extended-spectrum penicillins Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 7 Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin) Bactericidal to numerous gram-positive and some gram-negative organisms Adverse effects Least toxic of all antibiotics Penicillins are the most common cause of drug allergy Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 8 Penicillin Allergy Development of penicillin allergy Skin tests for penicillin allergy Management of patients with a history of penicillin allergy Assess for penicillin allergy in each patient who will be receiving penicillin If history of mild reaction, consider cephalosporin If history of anaphylaxis, avoid administration of penicillin or cephalosporins Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 9 Penicillin Allergy Types Immediate (reaction in 2–30 minutes) Accelerated (reaction in 1–72 hours) Late (reaction takes days or weeks to develop) Anaphylaxis Laryngeal edema Bronchoconstriction Severe hypotension Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 10 Penicillin Allergy Treatment Epinephrine Respiratory support Prevention: skin testing Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 11 Drug Interactions Aminoglycosides Penicillin V Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 12 Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins Available in the United States Nafcillin Oxacillin Dicloxacillin MRSA: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 13 Broad-Spectrum Penicillins Broad-spectrum penicillins (aminopenicillins) Ampicillin (Principen) Amoxicillin (Amoxil, DisperMox, Moxatag, Trimox) Adverse effects Rash Diarrhea Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 14 Extended-Spectrum Penicillins Extended-spectrum penicillins (antipseudomonal penicillins) Piperacillin • Broad-spectrum, but penicillinase-sensitive Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 15 Penicillin Combinations Beta-lactamase inhibitors Clavulanic acid, tazobactam, sulbactam Extends antimicrobial spectrum when combined with penicillinase-sensitive antibiotics Ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn) Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (Augmentin) Ticarcillin/clavulanic acid (Timentin) Piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn) Copyright © 2013, 2010 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 16