UNIT 4- Perception
advertisement

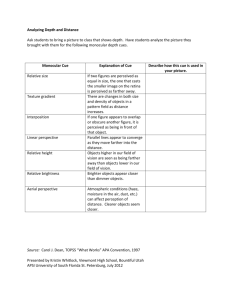
CHAPTER 6 PERCEPTION Perception Perception – organizing and interpreting our sensations. (aka Top –down processing) Selective Attention we focus our attention to only a limited aspect of all that we experience. We tend to focus on that which is important to us. * We only process about 40 bits of information per sec. (But our 5 senses take in 11 million bits per sec. – We must choose which parts to perceive. Butler student. Re bottom 238 driven to distraction: Q What recent traffic safety laws does research on selective attention support? Test Your Awareness: Do The Test – YouTube This was an example of Inattentive Blindness Cocktail Party Effect Re: 1st half of para after X p.232 The cocktail party effect – the ability to attend to only one voice among many. Ex. Many people are talking and someone across the room yells your name. Ex. Someone calls out FIRE while you are in a room full of people Study talking in each ear. Q At a Pep Rally Change blindness NOVA | Inside NOVA: Change Blindness YouTube The Invisible Gorilla: And Other Ways Our Intuitions Deceive Us Experimental Psychology - Change Blindness – Q Other examples from movies VIEW Saved list from movies. Illusions Muller-Lyer classic illusion PsychSim 5e - Online Edition More Illusions …. Examples on separate word document Ames Room (Philip Zimbardo) – YouTube The Best Optical Illusions Ever – YouTube The Best optical illusions ever!!! part 2 YouTube GESTALT Gestalt – German word meaning whole, perception of the whole exceeds the sum of its parts Figure Ground Grouping Proximity Similarity Continuity Connectedness Closure Figure Ground Figure Ground – the organization of the visual field into objects (the figures) that stand out from their surroundings (the ground) Live Psych Q Pep Rally? Grouping: Proximity Proximity – the tendency to group nearby objects together Grouping: Similarity Similarity – the tendency to group alike figures together Grouping: Continuity and Connectedness Continuity – the tendency to perceive a smooth pattern Connectedness – when objects are uniform and linked, the tendency to perceive spots, lines or areas as a single unit. Grouping: Closure Closure – the tendency to fill in the gaps to create a meaningful whole. Gestalt Grouping Review The Gestalt School of Learning Web.mp4 – YouTube (German cartoon) Depth Perception Depth Perception – the ability to see objects in three dimension, depth perception allows us to judge distance. Visual cliff – Eleanor Gibson used a glass-covered drop-off to test depth perception in infants and young animals. Most infants and young animals would refuse to crawl onto the glass – our capacity to understand depth is innate Our experience amplifies our wariness – the more children learn … the more they develop their understanding of depth. Binocular Cues Binocular Cues – depth cues that depend on the use of two eyes. Retinal disparity – using two eyes, the brain computes distance. The greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object. Convergence – the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object. (if the object is close, the eyes have a greater inward turn) http://www.google.com/url?q=http://www.prenhall.c om/livepsych/livepsych_ad/index.html&sa=U&ei=q M_DTrruIcK2tgfPlvXZDQ&ved=0CBIQFjAA&usg= Retinal Disparity Autostereograms - The physical autostereogram plane is located at the solid line. To view an autostereogram, the eyes do not converge at the plane of the screen image, but at some other point in space indicated by the intersection of the lines of sight at another location in space. Autostereograms An autostereogram is formed by superimposing two repeating patterns The two patterns are slightly offset, and when viewed properly, this offset is seen as a binocular disparity. Retinal Disparity Ex. Autostereograms Autostereogram Autostereogram Monocular Cues Monocular Cues – distance cues that can be used with either eye alone. Relative Size Interposition Relative Clarity Texture Gradient Relative height Relative motion Relative brightness (light and shadow) Linear perspective Monocular Cue: Relative Size Relative Size – smaller images are farther away Monocular Cue: Interposition Interposition – if one object blocks the view of another, it is perceived as closer Monocular Cue: Relative Clarity Relative Clarity – hazy objects are far away, clear objects are closer Monocular Cue: Texture Gradient Texture Gradient – coarse and distinct textures are close, fading textures are farther away Monocular Cue: Relative Height Relative height – objects in our higher field of vision are perceived as farther away. Monocular Cue: Relative Brightness Relative brightness (light and shadow) – nearby objects reflect more light Monocular Cue: Linear Perspective Linear perspective – parallel lines appear to converge with distance. Monocular Cue: Relative Motion Relative motion (aka Motion Parallax)– as we move, objects that are stable appear to move. Motion Perception Phi Phenomenon Movement is created when two or more lights blink on and off in quick succession Review Monocular Cues Find Monocular cues the artists drawing on p. 242 Constancy - perceiving objects as unchanging Color Constancy – even when Shape illumination changes we perceive objects as having a consistent color. Ex. Red Car Shape Constancy – even when our retinal images change, we perceive objects as maintaining Size a certain shape. Ex rect. door Size Constancy – even when our distance changes we perceive items as remaining the same size Ex Football field Hanging Munchkin Wizard of Oz VCR tape of Munchkin Hanging in Wizard of Oz. Hanging Munchkin Suicide The wizard of oz munchkin suicide- (HD) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=08jXp2DB hiw Perceptual Set Perceptual Set – a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another. Ex. The Loch Ness monster Ex. UFOs Ex. Watching Indy v Butler football game. Activity: Look at picture Perceptual Set Look at the picture of a trained seal act. Do you see: 1. Man 2. women 3. small fish 4. cane 5. woman 6. ball 7. handkerchief 8. large mammal Ex Last day of kindergarten Perceptual Set - YouTube Context Effects bullets on 253 Magician’s Cabinet Anyone have a day (A or B) where they like 3 and dislike 1? If you were to switch the one to the other day What would happen? your perception would make a difference Context Effects Some Americans consider themselves to be poor within the context of their neighbors. Perceptual Adaptation The ability to adjust to an artificially displaced or even inverted vision. Re: paragraphs 2, 3 and 4 (250) Picture on (250) module # 10 ESP Q What is it? Q. What do you know about it? Re: 264 to 265 Do 2 cartoons 264, 265 and 269 Re: 267 2nd paragraph Close books. Parapsychology Lab is in Duke. Look at cards