Name: Date: Block:
advertisement

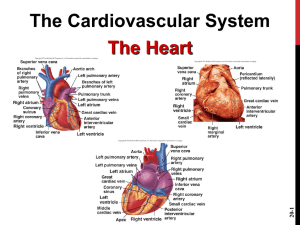
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System Pages 360-362 1. The cardiovascular system includes not only the heart, but also: 2. The major function of the cardiovascular system is _________________________. 3. The force to move the blood around the body is provided by the beating _________________ and by ______________ __________________. 4. “The cardiovascular system can be compared to a muscular _________________ equipped with one-way _____________________ and a system of large and small __________________ tubes within which the blood travels”. The Anatomy of the Heart pages 362-368 5. The heart weighs less than __________________________________ and is ________________ shaped. 6. Describe specifically where the heart is located: 7. The pericardium is: _______________________________________________________ 8. The purpose of the serous fluid in the heart is: _________________________________ 9. Name and give the functions of the three layers of the heart: a. __________________________________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________________________ c. __________________________________________________________________ 10. The atria are primarily the __________________________ chambers. Blood enters these chambers from _____________________________. 11. The ventricles are the _______________________ chambers, or actual _____________ of the heart. 12. The right ventricle forms most of the heart’s _____________________ surface; the left ventricle forms its ______________________. 13. The ______________________ divides the heart longitudinally. 14. Explain in detail why the heart is considered to be a “double-pump” system. 1 Name: Date: Block: 15. What is pulmonary circulation? 16. What is systemic circulation? 17. Why are the walls of the left ventricle much thicker than in the right ventricle? Valves pps. 366-368 18. Valves allow blood flow in ____________________________________. 19. Atrioventricular Valves (AV Valves): a. Bicuspid ( _____________________) valve has ______________ flaps. b. Tricuspid (right ____________) valve has _______________ flaps. c. Chordae tendineae – when the ventricles _____________________, they press on the blood in their chambers. This forces the _________________________ flaps upward, _____________________ the valves. They prevent ____________________ into the atria when the ___________________________ are contracting. 20. Semilunar Valves (SL Valves): guard the bases of the two large _____________________ leaving the ventricles. a. Pulmonary SL Valve b. Aortic SL Valve c. Both are made up of ____________________ leaflets that fit tightly together when the valves are closed. 21. Each set of valves operates at a different time. AV valves are open during ________________________________________ and closed when the _____________________ are contracting. The SL valves are closed during _____________________________________ and are forced open when the ______________________ contract. 22. The heart is not supplied with nutrients with the blood that it pumps. Instead, _______________________ arteries and _____________________ veins supply the myocardium with nutrients and oxygen. Physiology of the Heart pps. 368-374 23. In a single day, the heart pumps the body’s ____________ quarts of blood over ______________ times. 2 Name: Date: Block: 24. Control of the heart beat involves the intrinsic conduction system, or __________________ _________________. This sets the heart’s basic ___________________. 25. This causes heart depolarization in only one direction: from _____________________ to _________________________. 26. Creates a heart contraction equal to about __________________ beats per minute. 27. The sinoatrial node (SA node) is located in the ______________________ and has the job of: 28. The atrioventricular node (AV node) is located at the junction of the ________________ and the ______________________ and has the job of: 29. The Purkinje fibers function to: 30. Heart “problems” include those listed below. Give a brief definition of each: a. Ischemia b. Fibrillation c. Tachycardia d. Bradycardia e. Murmurs (p. 371) 31. Define a. Systole: b. Diastole: 32. The average length of a ______________________ ___________________ is about __________ second. 33. There are three events to the cardiac cycle. Briefly describe below: a. Mid-to-late Diastole b. Ventricular Systole c. Early Diastole 3 Name: Date: Block: 34. Heart sounds: The first sound is the __________ and is caused by the closing of the ______________________. The second sound is the ______________ and occurs when the _____________________________________ close at the end of _______________________. 35. The amount of blood pumped out by EACH side of the heart in 1 minute is called ________________________ __________________________. It is the product of the _________________________________ and the _______________________________. 36. A healthy heart pumps about ______________% of the blood present in its _________________________. 37. When blood volume drops suddenly or the heart has been weakened, the _______________ _____________________ declines, and cardiac output is maintained by a ___________________ ______________________. 38. Under physical or emotional stress, the nerves of the ANS more strongly stimulates the ______ and ______ nodes, and results in a _____________________ heart beat. 39. How do these drugs affect the heart: a. Digitalis b. Epinephrine c. Thyroxine 40. How does temperature affect heart rate? Blood vessels pps. 374-386 41. The vascular system is a ________________ transport system. 42. Blood travels from the aorta arteries ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ __________________. 43. Three layers of a blood vessel: a. Tunica intima/interna b. Tunica media c. Tunica externa 44. The walls of arteries are much _____________________ as compared to veins. This is because the arteries are closer to the pumping action of the _______________ and must be able to ____________________ and ________________ as the blood flows. 45. In contrast, veins are ______________ from the heart and the pressure in them is ________. Larger veins even have ____________________ that prevent backflow of blood. Also, the _________________ activity of skeletal muscles aids in the flow of blood in the veins. 4 Name: Date: Block: 46. Capillary beds are important because: Physiology of Circulation pps. 387-397 47. Vital signs include the taking of: 48. Normally, the pulse rate equals the ______________________________________. 49. Define blood pressure: 50. Blood pressure is directly related to _______________________________ and __________________________________________. BP = CO x PR. 51. What factors can alter a person’s blood pressure? 52. Explain how the kidneys regulate blood pressure: 53. What is hypotension? 54. What is hypertension? Answer the “Review Questions” # 1-19 on Pages 399-400. 1. ___________ 11. ______________ 2. ___________ 12. ______________ 3. ___________ 13. ______________ 4. ___________ 14. ______________ 5. ___________ 15. ______________ 6. ___________ 16. ______________ 7. ___________ 17. ______________ 8. ___________ 18. ______________ 9. ___________ 19. ______________ 10. ___________ 5