Optics Notes - Worth County Schools
advertisement

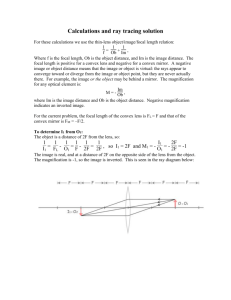
Optics The Study of Light Areas of Optics Geometric Optics Light as a ray. Physical Optics Light as a wave. Quantum Optics Light as a particle. Optical images • Nature • • • Orientation • • • real (converging rays) virtual (diverging rays) upright inverted Size • • • true enlarged reduced Law of Reflection • Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection. r i Plane Mirror + object 5 cm - Image -5 cm Spherical mirrors + (where reflected rays go) (dark side) concave shiny Focal length, f, is positive + (where reflected rays go) (dark side) convex shiny Focal length, f, is negative Parts of a Spherical Concave Mirror + - Vertex Center Focus Principle axis Spherical Concave Mirror (object outside center) c p C f F Real, Inverted, Reduced Image Spherical Concave Mirror (object at center) C F Real, Inverted, True Image Spherical Concave Mirror (object between center and focus) C F Real, Inverted, EnlargedI mage Spherical Concave Mirror (object at focus) C F No image Spherical Concave Mirror (object inside focus) C F Virtual, Upright, Enlarged Image Parts of a Spherical Convex Mirror + Principle axis Focus Center Spherical Convex Mirror F Virtual, Upright, Reduced Image C Mirror equation #1 • 1/si + 1/so = 1/f si: image distance • so: object distance • f: focal length • Mirror equation # 2 • M = -si/so = hi/ho si: image distance • so: object distance • hi: image height • ho: object height • M: magnification • Concave vs convex mirrors Concave Image is real when object is outside focus Image is virtual when object is inside focus Focal length f is positive Convex Image is always virtual Focal length f is negative Real vs Virtual images Real Formed by converging light rays si is positive when calculated with mirror equation Virtual Formed by diverging light rays si is negative when calculated with mirror equation Upright vs Inverted images Upright Always virtual if formed by one mirror or lens hi is positive when calculated with mirror/lens equation Inverted Always real if formed by one mirror or lens hi is negative when calculated with mirror/lens equation Definition: Refraction Change in speed of light as it moves from one medium to another. Can cause bending of the light at the interface between media. Index of Refraction n= speed of light in vacuum speed of light in medium n = c/v Snell’s Law angle of incidence 1 n1sin 1 = n2sin 2 n1 2 angle of refraction n2 n1 < n2 light bends toward normal 1 n1 2 n2 n1 > n2 1 light bends away from normal n1 2 n2 Dispersion The separation of white light into colors due to different refractive indices for different wavelengths. Dispersion Due to different indices of refraction for different wavelengths of light. Critical Angle of Incidence c Light would refract 90o so it reflects instead, undergoing total internal reflection. n1 r n2 n1 > n2 Calculating Critical Angle n1sin(1) = n2sin(2) o n1sin(90 ) = n2sin(2) n1 = n2sin(c) Total Internal Reflection i r Occurs only when angle of incidence > critical angle n1 n2 Announcements 3/23/2016 Turn in homework (lens problems) on overhead. Lab report will be due next week (on looseleaf or graph paper). Consider a lens with f = 20 cm. You place a 5 cm tall object 30 cm in front of the lens. a)Draw the ray diagram and construct the image. b)Calculate the image distance and height using the lens/mirror equations. c) Name the image. Converging lens #1 2F Real, Inverted, Reduced Image F + C F 2F Converging lens #2 2F Real, Inverted, True Image F + C F 2F Converging lens #3 2F Real, Inverted, Enlarged Image F + C F Converging lens #4 F Virtual, Upright, Enlarged Image + C F For converging lenses • • • • • f is positive so is positive si is positive for real images and negative for virtual images M is negative for real images and positive for virtual images hi is negative for real images and positive for virtual images Diverging lens F Virtual, Upright, Reduced Image + C F For diverging lenses f is negative • so is positive • si is negative • M is positive and < 1 • hi is positive and < ho •