Kinetic energy
advertisement
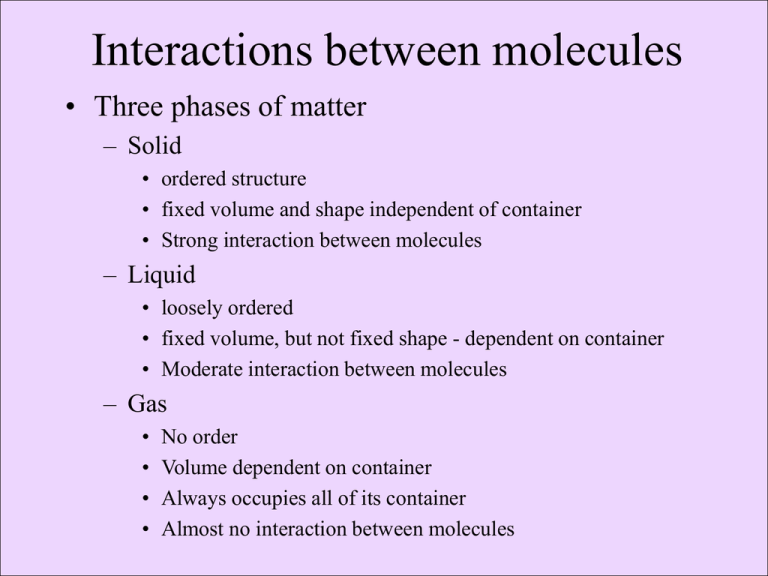
Interactions between molecules • Three phases of matter – Solid • ordered structure • fixed volume and shape independent of container • Strong interaction between molecules – Liquid • loosely ordered • fixed volume, but not fixed shape - dependent on container • Moderate interaction between molecules – Gas • • • • No order Volume dependent on container Always occupies all of its container Almost no interaction between molecules Role of Kinetic Energy and types of matter • Kinetic energy is the amount of energy needed to bring a body to rest or impart motion on a resting body • On the molecular level kinetic energy is dependent only on temperature • Heating a compound will raise its kinetic energy (the temperature will rise) Phase Transitions - change from one physical state to another • When enough energy is added to a solid, the molecules are no longer rigid and the solid melts (turns from solid to liquid) – The reverse (liquid to solid) is called freezing. • When enough energy is added to a liquid, the molecules are no longer moderately attracted to each other vapourises (turns from liquid to gas) – The reverse (gas to liquid) is called condensation. • When enough energy is added to a solid, the molecules sometimes sublime (go directly to the gas phase) – Dry Ice, Iodine (lab) • Question: Why do do molecules have different melting and boiling points? – Water (H2O) boils at 100°C and is a liquid at room temperature – Methane (CH4), with almost the exact molecular weight, boils at -164°C and is a gas at room temp. • Answer: Interactions between water molecules are stronger than methane’s. Attractive Forces Between Molecules (Van der Waal’s) • Dipole-Dipole Interactions – Attraction between polar molecules • Hydrogen Bond (strongest) special type of dipole-dipole – Found in molecules with HF, HO or HN bonds • difference between electronegativities of these molecules is large • Induced Dipole dipole (weakest) - Attraction from temporary dipole moments • temporary uneven distribution of electrons • Increase with size of molecule Like Dissolves Like • Why don’t oil and water mix? – A) Oil’s molecular mass is much greater than water’s. – B) Oil has only induced dipole forces and water has Hbonding. • Water will dissolve polar compounds (H-bonding or dipoledipole) but not non-polar. • Oil will dissolve non-polar compound (induced dipole forces) but not polar. • When attractive forces between different molecules are similar, they will dissolve • When attractive forces between different molecules are not similar, they will not dissolve Soap • The polar part of soap is hydrophilic (water loving) and interacts with water • The non-polar part is hydrophobic (water hating) and interacts with oil & grease




