Photosynthesis
advertisement

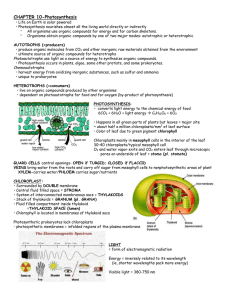
Ch. 10 PHOTOSYNTHESIS History Jan Van Helmont Joseph Priestley Plants only produce oxygen if in the light Melvin Calvin Mint plant keeps candle lit inside jar, plants produce oxygen Also discovered/named oxygen Jan Ingenhousz Mass of plant, container and soil, document mass of water – new growth was greater Steps of dark reactions using radioactive tracers CARBON DIOXIDE COMING INTO PLANT – CREATING CARBOHYDRATES ….. BIOMASS Energy Flow Energy flow is one directional Elements/ nutrients/ matter cycles From sun (solar energy) to chemical then mechanical energy….. Eventually heat C cycle, N cycle, Water cycle, etc. Food webs Autotrophs = self feeding; photoautotrophic and chemoautotrophic Heterotrophs = other feeding; herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, detritivores, decomposers, parasites, etc. Leaf Structure Chlorophyll is a chemical/ pigment Chloroplasts are structures that contain chlorophyll Other plastids Many layers (Membranes) chromoplast leukoplast amyloplasts Specialized cells/ tissues From chloroplast to leaf Light Reactions Require light to occur Require water Light energy is used to split a water molecule Thylakoid is site of reaction Provides H for NADPH, e- and Generates oxygen that is released Light Reaction Details Photons (units of light), at l just below 500 reach chloroplast and strike chlorophyll on thylakoid membrane e- on chlorophyll are excited e- are passed to primary acceptor Heat is given off Water is split Oxygen helps oxidize reaction, O loses H and e- returns to chlorophyll NADPH and ATP are generated Noncyclic electron flow Cyclic electron flow Dark Reactions Occurs in stroma of chloroplast Does not require dark ( or light ) Needs NADPH and ATP from light reactions Uses CO2 Generates glycerol 3 phosphate (1/2 of a glucose…. aka PGAl ) Details of Calvin cycle Phase 1: CO2 is incorporated, called ‘carbon fixation’ Phase 2: phosphorylation, ATP spent, efrom NADPH reduce the C chain so it stores more potential energy 6 molecules with 3 C are made – 5 are recycled and one is released as a future glucose Phase 3: cycles Summary Rubisco is the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of Calvin cycle – since in all chloroplasts of all cells of all leaves, it’s the most abundant protein on Earth. sunlight 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 chlorophyll Compare and contrast PHOTOSYNTHESIS Chloroplast stroma and inner membrane ETC and cycle ETC first CO2 in, O2 out Fixes C into chains Stores energy RESPIRATION Mitochondria matrix and inner membrane ETC and cycle ETC last C cpd in, CO2 out Breaks C bonds Releases energy Alternatives C3 plants ( rice and wheat; grasses) Close stomata, hot dry weather, less sugar – do photorespiration Photorespiration – process adds O2 by rubisco and this product then splits releasing CO2 C4 plants Sugar cane and corn Make 4 C cpd first then Calvin – making PEP that can fix CO2 easily, even when hot. CAM Succulent plants like cactus and pineapples Crassulacean Acid Metabolism make and store organic acids to be broken down to CO2 and used over night when cooler