Intro to Christian Ethics
advertisement

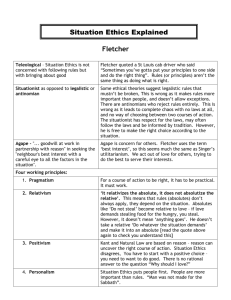
I will recap the different sources of authority within the Christian tradition I will know about Situation Ethics Response to C S Lewis. ‘These are the two points that I wanted to make. First, that human beings, all over the earth, have this curious idea that they ought to behave in a certain way, and cannot really get rid of it. Secondly, that they do not in fact behave in that way. They know the Law of Nature; they break it.’ C S Lewis pg 8 ‘We want to know whether the universe simply happens to be what it is for no reason or whether there is a power behind it that makes it what it is … The only way in which we could expect it to show itself would be inside ourselves as an influence or a command trying to get us to behave a certain way.’ pg 24 Response to Law Law questions the assumptions that morality is dependent upon God and religion, that there cannot be moral value without God, and that we will not be good unless religion is there to show us the way. Can a sense of purpose be derived from Law’s conclusions? Is humanity’s main goal to improve and to better themselves? Does this actually happen? I will justify my response to the view that Morality can exist without God. What do you think and why? Write a few sentences. Turn to page 120-121 of your AS text books. Remind yourself of the difference sources of authority that are used within the Christian tradition. Read through the article by David Torevell answer the following questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Why does Fletcher choose to give more emphasis to love rather than the law? Should we totally disregard rules? Why? What is Agape? Describe the ‘indecent proposal’ mentioned in the first scene What are the three working principles derived from Fletcher, which get mentioned. What was the outcome of the first scene? What do you notice from the second and third scenes? What conclusions do you make? What are the criticisms to Fletchers theory? Go on to moodle Religious Studies A Level – Yr 12 Ethics 101 and then under ‘Socratic ideas power points’ go to ‘3. click here for the periodic table.’ Once you have opened the power point, go to slide 3, ‘The Philosophers Periodic Table’ and in the ‘situationist’ column, at the bottom, you need to click on the face of the man with white hair, glasses and a black bow tie. That is Joseph Fletcher! Your homework is to go through the first 15 slides and add to your notes on Joseph Fletcher (stop when you get to Utilitarianism.) We will not be going through this in class so it is being set for homework instead! Make sure you note the following: AGAPE Four Principles of Situation Ethics Six Propositions If there is anything that is unclear, note down questions and bring to tomorrows. I will know the main ethical teachings within Christianity An introduction Ethics is to do with right behavior. From this clip, note down as many ‘behaviours’ as you can. E.g. Be a peacemaker. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4MeH8YyLlDE Using page 122-123 In threes you are going to look at how Christian ethics has developed from three main sources. Have something written down ready to share with the class. Others will make additional notes from what you say. We won’t spend long on this, hence why the work load is being split up amongst you! http://www.teachit.co.uk/custom_content/timer/timer.html The ethics of Jesus A Jewish foundation and the Bible The ethics of Paul Now 1 group will present to 2 other groups. The groups being taught will be required to take notes. When one group has finished the next will proceed. Audience Audience Presenter Love = Supreme Ethic So long as it glorifies and honours God Is Christianity inconsistent when it comes to reading the whole Bible (Old and New Testament.) Aren’t they picking and choosing what to believe? Answer: Some might Others try not to. Read article by Tim Keller What are the main Ethical principles of Christianity? Can you explain Fletchers Situation Ethics?