Ch 9
advertisement

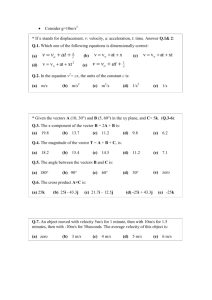
Unit 3: Motion, Forces, & Energy Chapter 9: Motion & Energy Big Idea: You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, & acceleration 4 Sections 1. 2. 3. 4. Describing Motion Speed & Velocity Acceleration Energy Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 2 Sec 1: Describing Motion KEY CONCEPTS • An object is in motion if it changes position relative to a reference point • Distance is the total length of the actual path between 2 points. Displacement is the length & direction of a straight line between starting & ending points Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 3 Sec 1: Key Terms • • • • • Motion Reference point Distance Displacement Vector Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 4 Sec 2: Speed & Velocity KEY CONCEPTS • To calculate the speed of the object, divide the distance the object travels by the time it takes to travel that distance • Speed = Distance Time • Changes in velocity may be due to changes in speed, changes in direction, or both Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 5 Sec 2: Speed & Velocity (cont’d) • The slope of a distance vs. time graph represents speed -- the rate that distance changes in relation to time • Slope = Rise Run Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 6 Sec 2: Key Terms • • • • • Speed Average speed Instantaneous speed Velocity Slope Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 7 Sec 3: Acceleration KEY CONCEPTS • In science, acceleration refers to: 1) increasing speed 2) decreasing speed or 3) changing direction • To determine the acceleration of an object, you must calculate its change in velocity per unit of time Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 8 Sec 3: Acceleration (cont’d) • Acceleration = Final velocity – Initial Velocity Time • You can use both a speed vs. time graph & a distance vs. time graph to analyze the motion of an accelerating object Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 9 Sec 3: Key Terms • Acceleration Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 10 Sec 4: Energy KEY CONCEPTS • The kinetic energy of an object depends on both its mass & its speed • Kinetic Energy = 1 x Mass x Speed2 2 • An object’s gravitational potential energy depends on its weight & on its height relative to a reference point Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 11 Sec 4: Energy (cont’d) • Gravitational potential energy = Weight x Height • Mechanical energy = Potential energy + Kinetic energy Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 12 Sec 4: Energy (cont’d) • Any object that rises or falls experiences a change in its kinetic & gravitational potential energy • According to the law of conservation of energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 13 Sec 4: Key Terms • • • • • Work • Elastic potential energy Energy • Mechanical energy Kinetic energy • Law of conservation Potential energy of energy Gravitational potential energy Mrs. Lee - Ch 9 14