Digestion notes
advertisement

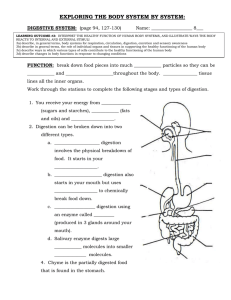
Suspension feeders -sift small food particles through water Clams oysters baleen whales Substrate-feeders -live in or on their food Caterpillars, worms Fluid-feeders may be parasites that live on the fluid of other organisms -aphids (on phloem sap of plants) -mosquitoes (on blood of mammals) May not be parasites -hummingbirds and insects on nectar Bulk-feeders -eat large quantity of food -most animals Digestion occurs in specialized compartments The simplest is the gastrovascular cavity No anus Wastes leave via the mouth Crop -moisten & store Gizzard -grind Intestine/ceca -absorb Oral cavity Bulk-feeders -eat large quantity of food -most animals Human Digestive System • True digestive structures vs. accessory structures • Mechanical digestion vs. chemical digestion Digestion begins in the oral cavity: chewing (mechanical digestion) and addition of saliva to food to form a bolus Salivary amylase digests starch and glycogen (chemical digestion) Antibacterial agents pharynx Involuntary contractions of smooth muscle surrounding the digestive tract propels food Occurs in esophagus and the intestines Stomach structure secrete pepsinogen. secrete HCl HCl converts pepsinogen into pepsin An adaptation which prevents stomach from digesting itself Mucus cells secrete mucus -lubricates and protects stomach Helicobacter pylori Bile emulsifies fat Physically breaks up fat globules Made in Liver Stored in gall bladder Including bicarbonate Pancreatic enzymes (released into the duodenum via a duct) • • • • Trypsin (protein digestion) Pancreatic amylase (glycogen/starch) Lipase (fats) Nucleases (nucleic acids) Intestinal enzymes (from wall of small intestine) • Disaccharidases (maltase, sucrase, lactase) • Dipeptidases Anatomy of the small intestine Villi Blood vessels -absorbs amino acids -absorbs monosaccharides -takes nutrient rich blood to liver LACTEAL -part of lymphatic system -contains fluid called lymph -collects components of fat digestion -will eventually empty into blood vessels Hepatic Portal system Large intestine (colon) Small intestine End of small intestine Rectum Anus Unabsorbed food material Cecum Appendix Cecum is blind pouch at the intersection of the small and large intestines In humans it is a vestigial organ called the ???? Fig. 21-13a Stomach Small intestine Cecum Colon (large intestine) Carnivore Herbivore