objective
advertisement

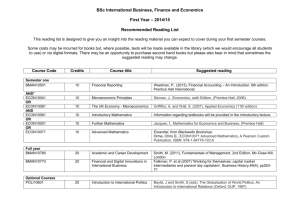
SCHOOL OF BUSINESS, ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT BBA 120- BUSINESS MATHEMATICS Course Outline OBJECTIVE The course aims to provide an introduction to mathematical concepts and lay down a foundation for applications of basic tools and techniques for various areas of business such as economics, accountancy and the life and social sciences. It begins with non calculations topics as Basic mathematics, equations, functions, matrix algebra, mathematics of finance etc. Then it progress through both single-variable and multi-variable calculus. An abundance and variety of applications appear throughout the course. Students continually see how the mathematics they are learning can be applied to practical business problems. These applications over such diverse areas as business, economics, sociology, finance etc. CONTENT 1.0 2.0 SET OPERATIONS EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES Operations expressions, factorizing, fractions, linear equations, quadratic equations. Linear inequalities, non-linear equations, absolute value, applications of equations and inequations. 3.0 FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS Definition of a function, special functions, combination of function, plotting functions in rectangular co-ordinates, inverse functions, transformations. 4.0 TYPES OF FUNCTIONS 4.1 The Straight line and Applications Demand, Supply, Cost, Revenue, Translations, Elasticity Of Demand, Supply And Income Budgeters And Cost Constraints. 4.2 Simultaneous Equations Solving simultaneous linear and non-linear equations, equilibrium and break-even, consumer and producer surplus. . 4.3 Non-Linear functions and Applications Quadratic, cubic and other polynomial function, exponential function, logarithmic functions, hyperbolic functions. 5.0 MATHEMATIC OF FINANCE Simple Interest And Simple Discount, Compound Interest And Compound Discount, Sequences, 6.0 MATRIX ALGEBRA Definition, matrices as stores of data, organizing and handling business data, matrix addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, matrix multiplication, method of reduction, inverse, determinant, Cramer’s rule, inverse using the adjoint, 7.0 CALCULUS 7.1. Limits and Continuity Limits, continuity of a function of one variable, economic applications of continuous function, intermediate value theorem. 7.2. Differentiation The derivative, rules for differentiation, the derivative as a rate of change, differentiability and continuity, product and quotient rules, the chain rule and power rule, derivative of logarithmic functions, derivatives of exponential functions, implicit differentiation, logarithmic differentiation, higher-order derivatives. 7.3. Differentiation and Applications Slope of a curve, marginal function, average functions, optimization for functions of one variables, elasticity and the derivative etc. 7.4. .Integration and Application The indefinite integral, integration with initial, conditions, techniques of integration, the definite integral, the fundamental theories of integral calculus, areas, area between two curves, the consumer’s surplus (CS) and producer’s surplus, integration by parts, GRADING The course grade will be determined approximately as follows:40% from tests and assignments (continuous assessment) 60% from the final comprehensive Examination. RECOMMENDED TEXTBOOKS. 1. Introductory Mathematical Analysis for Business, Economics, and the Life and Social Sciences, Ernest F Haeussler, Jr, Richard S Paul. 2. Mathematics for Economics and Finance Methods and Modeling, Martin Anthony and Norman Biggs. 3. Essential mathematics for Economics and Business, Teresa Bradey and Paul Patton. 4. Calculus for Business and Economics, Tailoka F P 5. Mathematical Analysis for Business, Economics, and the Life and Social Sciences, Jagdish C Arya and Robin W Lardner. 6. Essential Mathematics for Economics, 2nd Edition, J Black and J F Bradley.