Marine Biomes: Ocean
advertisement

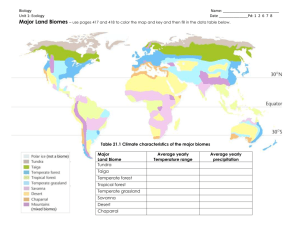
Earth’s Terrestrial Biomes Temperate Deciduous Forest Average Yearly Rainfall 75 to 125 cm Average Temp. (Summer: 28ºC Winter: 6ºC) mammals, birds, & reptiles thrive on leaves, seeds, nuts, & insects Taiga Forest •Average Yearly Rainfall 35 to 75 cm •Average Temp. (Summer: 14ºC Winter: −10ºC) Squirrels, insects Birds: finches, chickadees, & jays Herbivores: porcupines, elk, & moose ground covered by a layer of needles very little light reaches the ground few plants can grow beneath trees due to lack of light Tropical Rain Forest •Average Yearly Rainfall up to 400 cm •Average Temp. (Daytime: 34ºC Nighttime: 20ºC) greater variety of organisms than any other biome most nutrients are found in the plants soil is very thin & poor in nutrients trees grow roots above ground for extra support Temperate Grassland •Average Yearly Rainfall 25 to 75 cm •Average Temp. (Summer: 30ºC Winter: 0ºC) few trees fires, drought, & grazing prevent growth of trees & shrubs support small seed-eating animals: prairie dogs & mice large mammals graze on grasses Savanna (Grassland) •Average Yearly Rainfall 150 cm •Average Temp. (Dry season: 34ºC Wet season: 16ºC) Africa, India, & South America dry season: grasses dry out & turn yellow deep roots survive for many months without water African savanna large herbivores: elephants, giraffes, zebras, & wildebeests Hot Desert •Average Yearly Rainfall less than 25 cm •Average Temp (Summer: 38ºC Winter: 7ºC) plants grow far apart so they won’t compete for water plants have shallow, widespread roots that grow just under the surface to take up water during a storm cactuses have fleshy stems & leaves to store water leaves have a waxy coating to prevent water loss many animals are active at night when temperatures are cooler, some borough in the ground, & are dormant during the dry season (estivation). tortoises eat flowers or leaves and store the water under their shells Tundra •Average Yearly Rainfall 30 to 50 cm •Average Temp (Summer: 12ºC Winter: −26ºC) soil beneath the surface stays frozen: permafrost surface soil only thaws in summer soil is too shallow for deep-rooted plants so only shallowrooted plants: grasses & small shrubs mosses & lichens grow beneath the plants insects lay eggs in the mud, birds feed on the insects other animals include: musk oxen, wolves, & caribou Arctic Tundra Alpine Tundra Alpine tundra has permafrost found at the top of tall mountains trees cannot grow on mountain plenty of sunlight & precipitation Marine Biomes: Ocean Abiotic factors: water temperature, water depth, & the amount of sunlight that passes through the water As the depth of the water increases the temperature decreases. Ocean cont…Abiotic factors: water temperature, water depth, & the amount of sunlight that passes through the water Intertidal zone: adaptations to survive air exposure & keep from being washed away by the waves water is warm & receives lots of sunlight Plants and animals: corals, sea turtles, fishes, & dolphins Neritic zone: deep water of open ocean Plankton found near the surface Animals: fishes, whales, & sharks Some animals live in very deep water & get food from material that sinks down from the surface Benthic zone: no sunlight, very cold Animals: fishes, worms, & crabs which get food by eating material that sinks from above Chemosynthesis: organisms get energy from chemicals that escape from thermal vents Marine Biomes cont. Intertidal Areas found near the shore. Include: mudflats, sandy beaches, & rocky shores organisms must be able to live both underwater & out of water mudflats include: worms and crabs, shorebirds feed on these animals sandy beaches: worms, clams, crabs, & plankton rocky shores organisms have adaptations to keep from being swept away by crashing waves: use root-like structures called holdfasts to attach to rocks, others attach themselves by releasing a special glue-like substance. Marine Biomes cont. Coral Reefs found in warm, shallow areas of the neritic zone made up of small animals called corals that live in large groups when corals die, they leave hard skeletons & new corals grow on their remains skeletons build up and form a reef which is home to many marine animals & plants organisms include: algae, brightly colored fishes, sponges, sea stars, & sea urchins. Marine Biomes cont… Estuaries where fresh water from streams & rivers spill into the ocean the fresh water from rivers & salt water from the ocean are always mixing so amount of salt in the water changes Plants and animals must be able to survive in changing salt content fresh water is rich in nutrients which support large numbers of plankton Plankton provide food for many animals. Marine Biomes cont… The Sargasso Sea the Sargasso Sea in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean contains floating algae called sargassums animals that live in the Sargasso Sea are the same color as the sargassums, helping them hide from predators . Desert Ice: Antarctica Mean Temps: Winter: (-40 to -70°C) Summer:(-15 to -35°C) icy waters surrounding Antarctica are rich in nutrients that support large numbers of plankton fishes, birds, and mammals rely on the plankton for food. Animals include: penguins, seals, whales, & birds Streams & Rivers Important abiotic factor: how quickly water moves Plants line the edges of streams and rivers Fish live in the open waters Clams & snails live in the mud at the bottom of a stream or river Organisms in fast-moving water have adaptations to keep from being washed away: algae and moss are attached to rocks, tadpoles use suction disks to hold rocks, insects live under rocks. Ponds and lakes Life near Shore littoral zone: closest to the edge of a lake or pond Sunlight reaches the bottom and makes it possible for algae and plants to grow Plants include: cattails and rushes The plants are home to small animals: snails and insects Clams and worms bury in the mud Frogs, salamanders, turtles, fish, and snakes live in this zone. Life Away from Shore open-water zone: extends from the littoral zone across the top of the water goes as deep as sunlight can reach home to bass, lake trout, & other fishes, photosynthetic plankton deep-water zone: beneath the open-water zone, no sunlight Catfish, carp, worms, crustaceans, fungi, & bacteria live here & often feed on dead organisms that sink from above. Wetland Ecosystems area of land underwater or whose soil contains a great deal of moisture supports many different plants and animals play an important role in flood control : during heavy rains or spring snow melt, wetlands soak up large amounts of water water in wetlands moves deeper into the ground to help replenish underground water supplies Wetland Ecosystems cont… Marshes treeless wetland ecosystem found in shallow areas along the shores of lakes, ponds, rivers, & streams plants vary depending on the depth of the water & the location of the marsh grasses, reeds, bulrushes, & wild rice are common muskrats, turtles, frogs, and birds live in marshes Wetland Ecosystems cont… Swamps ecosystem of trees and vines found in low-lying areas & beside slow-moving rivers most swamps are flooded part of the year willows, bald cypresses, and oaks are common trees vines grow up tree trunks plants, like orchids, may hang from tree branches water lilies grow in standing water fish, snakes, & birds live in swamps