Grade 12 Paper 2 (Chemistry) MEMO September 2014 B aa B aa A
advertisement
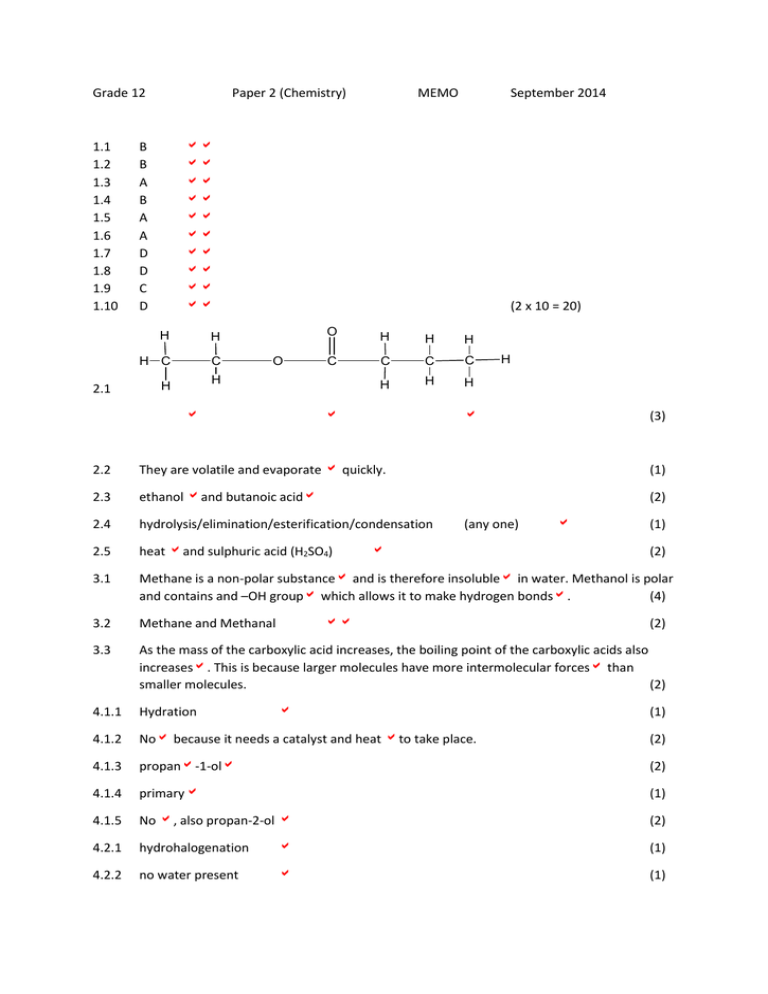
Grade 12 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 2.1 Paper 2 (Chemistry) MEMO September 2014 B B A B A A D D C D H H H C C (2 x 10 = 20) O O H H H C C C C H H H H H H (3) 2.2 They are volatile and evaporate quickly. (1) 2.3 ethanol and butanoic acid (2) 2.4 hydrolysis/elimination/esterification/condensation 2.5 heat and sulphuric acid (H2SO4) 3.1 Methane is a non-polar substance and is therefore insoluble in water. Methanol is polar and contains and –OH group which allows it to make hydrogen bonds. (4) 3.2 Methane and Methanal 3.3 As the mass of the carboxylic acid increases, the boiling point of the carboxylic acids also increases. This is because larger molecules have more intermolecular forces than smaller molecules. (2) 4.1.1 Hydration 4.1.2 No because it needs a catalyst and heat to take place. (2) 4.1.3 propan-1-ol (2) 4.1.4 primary (1) 4.1.5 No , also propan-2-ol (2) 4.2.1 hydrohalogenation (1) 4.2.2 no water present (1) (any one) (1) (2) (2) (1) H 4.2.3 H H H C C C H H H Br (2) 4.3 propene (2) 5.1.1 B = butanal (2) 5.1.2 F = 2,2-dibromo-3,3-dimethylpentane (6) 5.1.3 J = pent-1-yne (2) 5.2 C&E (1) 5.3 G & H or C & E (1) 5.4.1 Condensation polymerization H C C C H O C H O C 5.4.2 (1) H C H C H C O C C C C O H C H O H C H (2) 6.1.1 sufficient energy & correct orientation 6.1.2 A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing a permanent change. (2) 6.2 A: If the amount of the catalyst increases, then the rate of the reaction will also increase. OR B: If the catalyst is present, then the rate will increase. (2) (2) 6.3.1 volume of O2 produced (1) 6.3.2 A: amount of catalyst added OR B: presence of catalyst (1) 6.3.3 amount of H2O2 added OR conc of reactants (1) 6.4 (can be either endo or exo thermic as question doesn’t specify) Energy of Reactants Potenttial Energy Activation Energy Energy of the Products Activation Energy with Catalyst Reaction Progress (6) 6.5 7.1.1 As the slope of the graph increases, one can see that the hypothesis was correct. As more catalyst is added, the rate at which O2 is produced increases. (3) 𝐾𝑐 = [𝐴𝐵2 ]2 [𝐴2 ][𝐵2 ]2 (numerator) (denominator) (3) 7.1.2 i) when equilibrium in a closed system is disturbed , the system will re-instate a new equilibrium by favouring the reaction that will opposethe disturbance. (3) ii) This is because the forward reaction is exothermic. By removing heat, one will favour the forward reaction, thus increasing the concentration of the products (2AB2). (3) 7.2 N2 1.5 -0.5 1 c=n/v =1/0.5 2 mol.dm-3 Start Change Equilibrium Concentration 2NH3 0 +1 1 =1/0.5 1 mol.dm-3 =2 mol.dm-3 [𝐴𝐵2 ]2 [𝐴2 ][𝐵2 ]2 𝐾𝑐 = = 3H2 2 -1.5 0.5 =0.5/0.5 22 (2)(13 ) (numerator, denominator) =2 at 470°C (8) 7.3.1 remains the same 7.3.2 Only temperature changes Kc. the gases will stay in the same proportions with a change in volume. (2) 8.1 It is a strong acid because it ionizes completely in water to form a high concentration of H3O+ ions. (2) 8.2.1 Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + 2H2O 8.2.2 n=m/M = 8.3 0.25 = 58 (1) (2) 0.0043 mol Mg(OH)2 OR 4.3x10-3mol (3) pH= -log[H3O+] 1.5= -log[H3O+] [H3O+] = 0.032 mol.dm-3 8.4 𝑐𝑎 𝑣𝑎 𝑐𝑏 𝑣𝑣 𝑛𝑎 = 0.032∗1 109∗𝑥 𝑛𝑏 2 =1 (0.03 mol.dm-3 ) (3) x = 1.47x10-4dm3 of Gaviscon OR 0.03∗1 109∗𝑥 2 = 1 = 1.38 x 10-4dm3 Or c=n/v 0.032=n/1 n = 0.032 mol HCl HCl:Mg(OH)2 1:2 0.032:0.016 c=n/v 109 = 0.016/v v=1.47 x 10-4 dm3 (5) 9.1.1 copper (2) 9.1.2 K+ ions will move towards the silver solution (right or cathode) to make it more neutral. NO3- ions will move towards the copper solution (left or anode) making it more neutral. (2) 9.1.3 flow of electrons 9.1.4 EΘcell = EΘcathode - EΘanode (1) =0.80 – 0.34 =0.46 V 9.1.5 (4) Cu(s)/Cu2+(aq) (1mol.dm-3)//Ag+(aq)(1mol.dm-3)/Ag(s) at 298K (25⁰C) (3) 9.1.6 INCREASE (1) 9.1.7 Primary 9.2.1 2Cl- → Cl2(g) + 2e- (2) 9.2.2 NaOH or sodium hydroxide (1) 9.2.3 formation of soaps; making paper; purification of bauxite; making rayon, textiles, dyestuffs, or pharmaceuticals (any one) (1) 9.2.4 the membrane is cationic – meaning that cations (like Na+) can go through but not Cl-. (1) 10.1 Nitrogen (1) 10.2 fractional distillation (1) (1) 10.3 4NH3 + 5O2 (in presence of Pt & 1000°C) → 4NO + 6H2O (3) 10.4.1 ammonium sulphate (1) 10.4.2 growth of leaves (1) 10.5 Ostwald process (1) 10.6 NO2 OR nitrogen dioxide (1) 10.7 The extra fertilizer has run-off her land causing eutrophication in the dam water. By using less fertilizer or a system of crop rotation, she can avoid this in the future. (3) END of PAPER