Developing Training Needs Analysis
advertisement

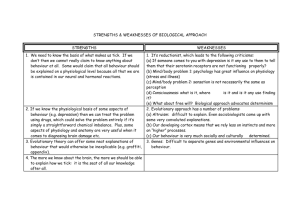
Introduction Successful organisations always have provided timely training to their staff. The definition of a training needs analysis is “an analysis of training, learning and development needs of staff, volunteers and trustees in an organisation” (Skill third sector, 2011). A training needs analysis can be a questionnaire which is completed by individuals within an organization. Questionnaires can be useful in obtaining a big picture of what a large number of employees think and feel, while they have had an opportunity to participate in the need analysis process. The key advantage of a questionnaire is that help considers the skills, knowledge and behaviours that your staffs need, and also how to develop them effectively. Another definition of a training needs analysis is “a process of series activities that can conducted to identify problem or other issues in the workplace, and to determine whether training is an appropriate response.” (Directory journal, 2011). A training analysis usually is the first important step taken to cause a change because it can specifically to define the gap between current competencies and the desired competencies that the company expects. Methodology The GAP The GAP analysis is the core basis for developing the training needs analysis. It is an essential tool that most businesses use and what it does is it compares the actual performance to the potential performance of the business. It is important that businesses make use of its utilities effectively and maximise the use of its resources. It is as easy as asking two simple questions: “Where are we now?” and “Where do we want to be?” Basically the first thing that needs to be done is to outline the objectives of your company. The space that divides the two questions mentioned earlier is the socalled gap, and it needs to be closed. To do this you will need strategies, plans and tactical approaches to implement in order to close the gap. Developing Training Needs Analysis Before training needs analysis it is very important to understand the problem. The simple and often neglected solution is to conduct a training needs analysis. Whether you are an experienced or inexperienced training professional or the person responsible for ‘people’ issues, making your training count is the way to influence the future success of your organization. In order to do this, you must be able to match all training directly to the needs of the organization and the people in it. TYPES OF TRAINING NEEDS Training can involve the changing of employees' knowledge, skills, attitudes and behaviour.: o Knowledge - facts, procedures, principles and basic skills. Training which involves improvement of knowledge is tending to move more towards the use of self-instruction methods. o Skills - aims to change the behaviour of the trainee, usually by seeing and hearing the new skills, practising them and receiving feedback on progress. o Attitudes - this is the hardest factor to alter, as it is affected by many variables outside the training process, such as the manager's behaviour, company policy, the peer group, etc. Examples of attempts to change attitudes could include making employees more customer and service-oriented, gaining acceptance of organisational change or improving loyalty and commitment towards the organisation. o Behaviour - replacing old work habits with new ones, by attempting to modify employee behaviour. Behaviour is activity which can be seen and measured. Note that training of this nature will require reinforcement once the employee returns to the job. Training needs can generally be classified as either individual or group needs. Individual needs may relate to orientation (induction) training, initial (basic) training, remedial training (to correct perceived faults - this situation is an alternative to recruiting new staff), refresher training (such as in company policy, safety, fire drill) or personal development. Group needs refer to the need for a number of employees to change their behaviour collectively. Examples include team-building exercises designed to increase group cohesion or introducing new technical information to a group. In addition, types of training needs can be reactive or proactive. 1. Reactive Training - identifies existing weaknesses and acts to remedy them. These weaknesses take the form of barriers which prevent the achievement of set objectives, and can be identified by various symptoms. Examples may include production problems, poor quality control, labour turnover, absenteeism, accidents, grievances, interpersonal conflicts, customer complaints, ineffective use of staff specialists, poor supervision and management practices, unknown or misunderstood objectives, and various others. (Note that the symptoms may require solutions other than training - this will require further investigation.). 2. Proactive Training - prepares of employees to handle future changes, both within and external to the organisation. This is a longer-term approach, oriented towards development. Changes which may affect organisation plans include product type and demand, work process, technology changes, legislation, financial factors, political issues and business expansion/contraction. TYPES OF TRAINING NEEDS ANALYSIS Determining training needs involves collecting data on both the current situation within the organisation and its actual requirements. There are several techniques available which can achieve this, including: o o o o o interviews of employees and managers/supervisors performance appraisal data observation and work study using consultants outside assessment centres analysis of other data from the workplace The most common type of tna (training needs analysis) is really a combination of reviewing both how well a job is performed in total, and how well the individual tasks are performed within the job. i.e. a combination of performance and task analysis. Recommendations Based on the data and information gathered, the students have come up with the following recommendations: 1. A variety of strategies be used to conduct a training needs analysis in the SIMWEN environment. Trainers should make use of different approaches such as interviews, survey questionnaires, interactive discussions, and observation. 2. Conduct a regular assessment of training needs for employees. 3. Re-evaluate the goals and processes that the company undertakes to ensure that employees (SIMWEN students) are meeting their full potential in regards to the work that they do. Identifying Training Needs Question Yes/No 1. Are we committed to providing training and developing the knowledge and skills of our employees? 2. Is there an induction process in place for new staff? 3. Are the managers competent in supporting the learning and development of their staff? 4. Is there a training strategy for development of staff? 5. Do we have a training budget? 6. Is there an appraisal system in place for employees? 7. Do we evaluate our training? 8. Do we have a system to support employees in identifying their learning needs? 9. Do we have up to date job descriptions for all employees? 10. Do we want to work towards good practise standards in managing and developing our people? S.W.O.T. Analysis Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats References 1. Skill third sector, 2011, What is training needs analysis, Retrieved: 12th May 2011, from: http://www.skillsthirdsector.org.uk/training_needs_analysis/what_is_training_needs_analys is/ 2. Directory journal, 2011, How to conduct a training needs analysis, Retrieved: 12th May 2011, from: http://www.dirjournal.com/guides/how-toconduct-a-training-needs-analysis/ 3. The Marketing Teacher, 2011, The GAP Analysis, Retrieved: 19 th May 2011, from: http://www.marketingteacher.com/lesson-store/lesson-gapanalysis.html 4. Leopard-learning,n.d., http://www.leopard-learning.com/tna.html, Retrieved from: 25th May 2011