The NIST Smart Grid Interoperability Framework and the Role of CIM
advertisement

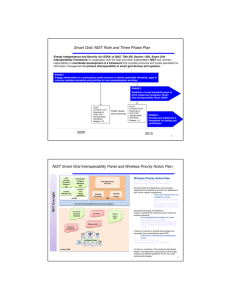
The NIST Smart Grid Interoperability Framework and the Role of CIM Jerry FitzPatrick National Institute of Standards and Technology CIM Users Group Meeting November 11, 2009 fitzpa@nist.gov Outline • Introduction - 2007 EISA • NIST Three Phase Plan • NIST Interoperability Framework and Roadmap, Release 1.0 • NIST Priority Action Plans (PAPs) for standards coordination and relation to CIM 2 The NIST Role Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) of 2007 Title XIII, Section 1305. Smart Grid Interoperability Framework In cooperation with the DoE, NEMA, IEEE, GWAC, and other stakeholders, NIST has “primary responsibility to coordinate development of a framework that includes protocols and model standards for information management to achieve interoperability of smart grid devices and systems…” NIST Interoperability Framework – History • 2007 EISA gives NIST responsibility for a Smart Grid Framework • 2008 NIST forms Domain Expert Working Groups – T&D, Home-to-Grid, Building-to-Grid, Industry-to-Grid, PEV-to-Grid, Business and Policy, Cyber Security • 2009 ARRA accelerates need for standards – EPRI selected as contractor • 2009 NIST holds large-scale workshops to identify standards – Several hundred stakeholders from a variety of groups – April 28-29: Produced draft list of 16 standards: “low hanging fruit” – May 19-20: Analyzed use cases, requirements and standards – August 3-4: Developed Priority Action Plans with SDO representatives • 2009 August EPRI produces Roadmap Report from workshops • 2009 September – NIST Smart Grid Framework draft 1.0 released – EnerNex selected as contractor for next phases 4 NIST Three Phase Plan PHASE 1 Identify an initial set of existing consensus standards and develop a roadmap to fill gaps PHASE 2 Establish Interoperability Panel to provide public-private forum with governance for ongoing efforts NIST Interoperability Framework 1.0 Released Sept 2009 5 March 2009 September PHASE 3 Testing and Certification Framework 2010 5 NIST Smart Grid Framework – 1.0 Draft 6 • Smart Grid Vision – Concepts, benefits – Importance to National Energy Policy – Key attributes • Conceptual Reference Model – To be used for discussing uses, relationships, use cases – Consists of domains, actors, applications, networks, paths • Standards Identified for Implementation – Original 16 from first workshop – Additional 15 in this document – Included 46 more “for consideration” – Asks for review of standards selection criteria • Priority Action Plans – Gaps in existing standards, missing standards, harmonization – Agreed on in workshops with SDO representatives Conceptual Reference Diagram First 16 Framework Standards 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 AMI-SEC System Security Requirements ANSI C12.19 End Device (Meter) Tables BACnet Building Automation & Control Net DNP3 – Distributed Network Protocol IEC 60870-6 – Inter-Control Center IEC 61850 – Comms Nets in Substations IEC 61968/61970 – Common Info Model IEC 62351 – Data Comms Security IEEE C37.118 - Synchrophasors IEEE 1547 – Distributed Resources IEEE 1686 – IED Cyber Security NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection NIST SP 800-53/82 Fed Info Sys Security Open Automated Demand Response Open Home Area Network Requirements ZigBee/HomePlug Smart Energy Profile 8 Draft Standards Acceptance Criteria • Enables Smart Grid characteristics as defined by EISA, DOE Smart Grid System Report • Is applicable to one of the priority areas identified by FERC and NIST • Enables the transition of the legacy power grid to the Smart Grid. • Is an open, stable and mature industry-level standard developed in consensus processes from a standards development organization • Is supported by an SDO or Users Group to ensure that it is regularly revised and improved to meet changing requirements and that there is strategy for continued relevance. • Is openly available under fair, reasonable, & nondiscriminatory terms. • Is developed and adopted internationally, wherever practical 9 NIST Three Phase Plan PHASE 1 Identify an initial set of existing consensus standards and develop a roadmap to fill gaps PHASE 2 Establish Interoperability Panel to provide public-private forum with governance for ongoing efforts Smart Grid Interoperability Panel Forming November 19 March 10 2009 September PHASE 3 Testing and Certification Framework 2010 10 SGIP Vision • • • • Public-private partnership to support NIST EISA responsibility Open, transparent body Representation from all SG stakeholder groups Membership open to any materially interested stakeholder organizations • Not dominated by any one group • SGIP does not directly develop or write standards – Stakeholders participate in the ongoing coordination, acceleration and harmonization of standards development. – Reviews use cases, identifies requirements, coordinates conformance testing, and proposes action plans for achieving these goals. 11 SGIP Vision (2) • SGIP Governing Board – Review and prioritizes the work of the SGIP – Coordinates necessary resources (in dialog with SDOs, user groups, and others) to carry out finalized action plans in efficient and effective manner. • Standing Committees – SG Architecture Committee (SGAC) – SG Testing and Certification (SGTC) – Additional Committees will be created as needed • Working Groups – Cyber Security Coordination Task Group – DEWGs • Structure will be refined as appropriate 12 NIST Oversight Smart Grid Identified Standards Stakeholder Category Members (22) SGIP Standing Committee Members (2) Priority Action Plans In Progress One Organization, One Vote Use Cases At large Members (3) Ex Officio (non-voting) Members SGIPGB Requirements Standing Committees Standards Descriptions Working Groups SGIP Smart Grid Interoperability Panel and Governing Board Conceptual Model Products (IKB) 13 Sun Mon Oct 11 Tues 12 Wed 13 Thu 14 Fri 15 Sat 16 17 23 24 30 31 6 7 Draft Charter Posted 18 19 25 26 Nov 1 2 20 21 22 Comment Period 27 28 29 3 4 5 Nominations & Comments Close 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 19 20 21 27 28 Final Draft & Ballot Posted 15 16 17 18 Election Results Ratify Charter GB Online Elections 22 23 29 30 24 25 26 14 What are Priority Action Plans (PAPs)? • NIST workshops identified priority standards issues – many standards require revision or enhancement – and new standards need to be developed to fill gaps • A total of 70 priority standards issues were identified in the EPRI report • NIST determined which require most urgent resolution and selected top 14 to initiate PAPs • The August SDO Workshop was used to develop the action plan for each priority issue. • Current status for each PAP is posted on the NIST website – broad SDO and stakeholder support and participation – aggressive milestones in 2009 or early 2010 established • The Smart Grip Interoperability Panel will guide oversee progress on PAPs and development of new PAPs. Priority Action Plans Smart meter upgradeability standard Target Date completed Common specification for price and product definition early 2010 Common scheduling mechanism for energy transactions year-end 2009 Common information model for distribution grid management year-end 2010 Standard demand response signals January 2010 Standard for energy use information January 2010 IEC 61850 Objects / DNP3 Mapping 2010 Priority Action Plans Smart meter upgradeability standard Target Date completed Common specification for price and product definition early 2010 Common scheduling mechanism for energy transactions year-end 2009 Common information model for distribution grid management year-end 2010 Standard demand response signals January 2010 Standard for energy use information January 2010 IEC 61850 Objects / DNP3 Mapping 2010 Priority Action Plans (continued) Target Date Time synchronization mid-2010 Transmission and distribution power systems models mapping year-end 2010 Guidelines for use of IP protocol suite in the Smart Grid mid-year 2010 Guidelines for use of wireless communications in the Smart Grid mid-year 2010 Electric storage interconnection guidelines mid-2010 Interoperability standards to support plug-in electric vehicles December 2010 Standard meter data profiles year-end 2010 Harmonize Power Line Carrier Standards TBD NIST Three Phase Plan PHASE 1 Identify an initial set of existing consensus standards and develop a roadmap to fill gaps PHASE 2 Establish Interoperability Panel to provide public-private forum with governance for ongoing efforts Testing Framework in place in 2010 March 19 2009 September PHASE 3 Testing and Certification Framework 2010 19 References NIST Smart Grid Site EPRI Roadmap Report Framework 1.0 Draft NIST Collaboration Site (w/PAPs links) Grid-Interop Conference 20 http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/ http://www.nist.gov/smartgrid/Report %20to%20NISTlAugust10%20(2).pdf http://www.nist.gov/public_affairs/rele ases/smartgrid_interoperability.pdf http://collaborate.nist.gov/twikisggrid/bin/view/SmartGrid/WebHome http://www.grid-interop.com/2009/