32781
advertisement

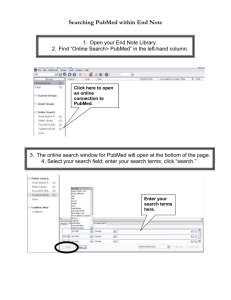
Browsing through Biology & Medicine Paul R Earl Sistemas e Informática Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León San Nicolás, NL, 66451, Mexico pearl@dsi.uanl.mx What do HTTP and WWW mean ? WEB BROWSERS were developed around 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee. WorldWideWeb (WWW) was the first. To browse is to look up or search for. Web browsers communicate with Web servers primarily using HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol) to fetch webpages. HTTP allows Web browsers to give information to Web servers as well as fetch Web pages from servers. HTTP/1.1 is commonly used. Pages are located by means of a URL (uniform resource locator). The file format for a Web page is usually HTML (hypertext markup language) and is identified in the HTTP protocol using a MIME content type. MIMEs are multipurpose internet extensions as used in email (electronic mail). Popular Browsers WorldWideWeb, February 26, 1991 Mosaic, April 22, 1993 Netscape Navigator, 1994 Netscape Communicator, October 13, 1994 Internet Explorer, August 1995 Opera, 1996 Safari, January 7, 2003 (Apple = Mac) Mozilla Firefox, November 9, 2004 The Browser Inventor An Oxford graduate, Tim Berners-Lee holds the 3Com Founders chair and is a Senior Research Scientist at the Laboratory for Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence (CSAIL) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He is codirector of the new Web Science Research Initiative (WSRI) and is a professor in the Computer Science Department at the University of Southampton, UK. He directs the World Wide Web Consortium, founded in 1994 In 1989 he invented the World Wide Web, an internet-based hypermedia initiative for global information sharing while at CERN, the European Particle Physics Laboratory. In 2004 he was knighted by Queen Elizabeth. He wrote Weaving the Web with Mark Fischetti, (Harper, San Francisco,1997). Browse Subjects Agricultural & Biological Sciences Arts & Humanities Biochemistry, Genetics & Molecular Biology Business, Management & Accounting Chemical Engineering Chemistry Computer Science Decision Sciences Earth & Planetary Sciences Economics, Econometrics & Finance Energy Engineering Publication Types of PubMed The publication type limit will restrict your search based on the type of material the article represents, such as: Clinical Trial Editorial Letter Meta-Analysis Practice Guideline Randomized Controlled Trial Review The complete list of publication types is available under the Limits Type of Article, More Publication Types of PubMed. What is ToxNet ? Biomedical Orientation Pubmed Leads to Pubmed Central, MeSH and Entrez of the US health system along with browsers like Stanford’s great HighWire dominate biomedical searching. This is distant from the demands of world commerce on the Internet, e. g., taxonomy is academic. HighWire will bring home free full texts. Sciuris, BIOSIS Previews, Biological Abstracts, CAB Abstracts, Index of Organism Names, Open Helix, ZooBank and the Zoological Record, while necessary for biomedical and other subjects have little or no impact in business. PubMed, available via the NCBI Entrez retrieval system, was developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the US National Library of Medicine (NLM), located at the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). Entrez is the text-based search and retrieval system used at NCBI for services including PubMed, Nucleotide and Protein Sequences, Protein Structures, Complete Genomes, Taxonomy, OMIM and others. LinkOut provides access to full-text articles at journal Web. See the fine article by Edwin Sequeira (2000) which is found at: http://www.cendi.gov/presentations/ref_link_sequera.ppt# 303,18,PubMed Central MEDLINE is the NLM's premier bibliographic database that contains references to journal articles in the life sciences with a concentration on biomedicine. A distinctive feature of MEDLINE is that the records are indexed with NLM's Medical Subject Headings (MeSH). MeSH terms, publication types, GenBank accession numbers and other indexing data are available and displayed with the tag [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE]. See also the MEDLINE/PubMed Resources Guide. Chemical, Toxicological and Environmental Health Data ChemIDplus Chemical Identification/Dictionary HSDB CCRIS CPDB GENETOX IRIS ITER LactMed TRI TOXMAP Haz-Map Hazardous Substances Data Bank Chemical Carcinogenesis Information Carcinogenic Potency Database Genetic Toxicology Data Integrated Risk Information International Toxicity Estimates for Risk Drugs and Lactation Database Toxics Release Inventory Environmental Health e-Maps Occupational Exposure/Toxicology Household Products Health & Safety Information on Household Products Your Dictionary Seven Languages English French German Italian Japanese Spanish Russian Yahoo! Fish Babel does translations, and many other translation programs are available. Using the Boolean Operators AND, OR and NOT Many many people browse without the so logical algebra of George Boole (1814-1864), and that’s OK. Next: What does binary mean? It means a state of 2 like on-off, man:woman, False:True. Most browsers are binary. Addition x+y, multiplication xy and negation -x, have their counterparts in the algebra created by George Boole (18151864) by 1854 as the Boolean operations OR, AND and NOT respectively, also called disjunction x∨y, conjunction x∧y, and negation ¬x. Conjunction x∧y behaves on 0 and 1 as multiplication does for ordinary algebra. If either x or y is 0 then so is x∧y, but if both are 1 then so is x∧y. Disjunction x∨y works almost like addition with 0∨0 = 0 and (1∨0 = 0∨1 = 1). However, there is a difference: 1∨1 is 1 not 2. This difference is written x∨y to be (x+y-xy, not simply x+y). Complement is defined arithmetically as ¬x = 1−x. The values of x∧y, x∨y, and ¬x are expressed in this truth table... x 0 1 0 1 y 0 0 1 1 x∧yx∨y 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 X ¬x 0 1 1 0 The 3 Venn diagrams below represent respectively conjunction x∧y, disjunction x∨y, and complement ¬x. Venn diagrams use circles to visually represent Boolean search results. We have A, B, both and B-A. You should know that your search results depend on Boolean analysis. Addition x+y, multiplication xy and negation -x, have their counterparts in the algebra created by George Boole (1815-1864) by 1854 as the Boolean operations OR, AND and NOT which are disjunction x∨y, conjunction x∧y, and negation ¬x. Conjunction x∧y behaves on 0 and 1 exactly as multiplication does for ordinary algebra: if either x or y is 0 then so is x∧y, but if both are 1 then so is x∧y. Disjunction x∨y works almost like addition with 0∨0 = 0 and 1∨0 = 0∨1 = 1. However there is a difference: 1∨1 is not 2 but 1. This difference is written x∨y to be x+y-xy, not simply x+y. Complement can be defined arithmetically as ¬x = 1−x. Doublequotes are used to combine space-separated words into a single search term. Use upper case for the operators ! Check on this. A space is used to specify logical AND, as it is the default operator for joining search terms. "Search term 1" "Search term 2" The OR keyword is used for logical OR: "Search term 1" OR "Search term 2" The minus sign is used for logical NOT (AND NOT): "Search term 1" -"Search term 2" Let us review what the Boolean terms mean. For any system, there must be initial assumptions or postulates that the system follows. Final Remarks The main communication problem is jargon. Shoptalk with names for newly invented products may only be understood by a certain group of people. One objective of this lecture is to cut through jargon. This lecture could be much enhanced if you feed back terms and other suggestions in the field of information retrieval.