Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
advertisement

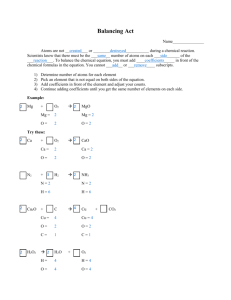
Please DO NOW Update your table of contents: 106. 5th 6 Weeks Test Review 107. Objectives 2 and 4 Review 108. Punnett Square Practice 109. Objectives 3 and 5 Review 110. 5th 6 Weeks Test April 24, 2011 Today’s Schedule Agenda: 1. Comp Book Update April 24, 2011 Homework: Complete TAKS booklet 2. Obj 3 and 5 Station Recap 3. Whiteboard Review 4. TAKS Review Booklet Announcement: TAKS test is Essential Questions What do I need to know for the TAKS test? Thursday! Come to tutoring for help finishing TAKS booklet. TAKS Review Booklet - PreAP April 24, 2011 To complete TAKS Review Booklet: • For each objective include AT LEAST 10 facts. • Facts may include sentences, formulas, labeled pictures, diagrams, or definitions. • The Review Booklet will be a major grade and is due on Thursday. Come to tutoring to use the study guide to find additional facts! TAKS Review Booklet - GL April 24, 2011 To complete TAKS Review Booklet: • For each objective include AT LEAST 5 facts. • Facts may include sentences, formulas, labeled pictures, diagrams, or definitions. • The Review Booklet will be a major grade and is due on Thursday. Come to tutoring to use the study guide to find additional facts! Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Equations Counting Atoms and Balancing Equations 1. Counting Subatomic Particles: Use the periodic table • The atomic number is the same as the number of protons. • The number of protons is the same as the number of electrons. • The mass number is the protons added to the neutrons. Atomic Number = Protons = Electrons (APE) Mass Number = Protons + Neutrons Neutrons = Mass Number - Protons 1. Counting Subatomic Particles: Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in: Lithium Atomic Number = Protons = Electrons (APE) Mass Number = Protons + Neutrons Neutrons = Mass Number - Protons 1. Counting Subatomic Particles: Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in: Lithium Atomic Number = 3 Protons = 3 Neutrons = 4 Electrons = 3 Mass Number = 7 1. Counting Subatomic Particles: Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in: Gold Atomic Number = Protons = Electrons (APE) Mass Number = Protons + Neutrons Neutrons = Mass Number - Protons 1. Counting Subatomic Particles: Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in: Argon 1. Counting Subatomic Particles: Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in: Lead 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients • Subscripts describe the number of that type of atom. They appear after the element symbol, are small, and written hanging below the symbol. • Coefficients describe the number of molecules present. Coefficients apply to all elements in the molecule. They are written before the formula for the molecule and are large. 4H2O Coefficient: There are 4 molecules of water. Subscript: There are 2 atoms of Hydrogen in each water molecule. 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients • Subscripts describe the number of that type of atom. They appear after the element symbol, are small, and written hanging below the symbol. • Coefficients describe the number of molecules present. Coefficients apply to all elements in the molecule. They are written before the formula for the molecule and are large. • H2O = 2 hydrogen and 1 Oxygen 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients • Subscripts describe the number of that type of atom. They appear after the element symbol, are small, and written hanging below the symbol. • Coefficients describe the number of molecules present. Coefficients apply to all elements in the molecule. They are written before the formula for the molecule and are large. • 3H2O = 6 Hydrogen and 3 Oxygen 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients Count and Draw the atoms in the molecule. NH4 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients Count and Draw the atoms in the molecule. NH4 N = Nitrogen = 1 H = Hydrogen = 4 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients Count and Draw the atoms in the molecule. 2NH4 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients Count and Draw the atoms in the molecule. NH4 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients Count the atoms present: C6H12O6 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients C6H12O6 Carbon – C – 6 Hydrogen – H – 12 Oxygen – O – 6 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients 3C6H12O6 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients 3C6H12O6 Carbon – C – 6 x 3 = 18 Hydrogen – H – 12 x 3 = 36 Oxygen – O – 6 x 3 = 18 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients 2NaC2H3O2 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients 2NaC2H3O2 Sodium - Na – 1 x 2 = 2 Carbon – C – 2 x 2 = 4 Hydrogen – H – 3 x 2 = 6 Oxygen – O – 2 x 2 = 4 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients KNO3 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients 4KNO3 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. • Count the total number of each type of atom on the reactant (ingredient) side. • Count the total number of each type of atom in the product (what you make) side • If the number of each type of atom matches, the equation is balanced. If the numbers do not match the equation is not balanced. • Equations must be balanced to show that the same atoms that go into a reaction are the atoms that come out, THEY ARE JUST REARRANGED to make new substances. 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 2Cu + O2 2CuO Reactants Element Copper Oxygen Products 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 2Cu + O2 2CuO Reactants Element Products 2 Copper 2 2 Oxygen 2 The Equation is Balanced!!! 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 2H2O 3H2 + O2 Reactants Element Hydrogen Oxygen Products 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 2H2O 3H2 + O2 Reactants Element Products 4 Hydrogen 6 2 Oxygen 2 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 3Fe + 4H2O 4H2 + Fe3O4 Reactants Element Iron Hydrogen Oxygen Products 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 3Fe + 4H2O 4H2 + Fe3O4 Reactants Element Products 3 Iron 3 8 Hydrogen 8 4 Oxygen 4 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 2Fe2O3 + 3H2 2Fe + 3H2O Reactants Element Iron Oxygen Hydrogen Products 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 Reactants Element Calcium Carbon Oxygen Products 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. 2NaCl 2Na + Cl2 Reactants Element Products 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. C5H12 + 6O2 5CO2 + 6H2O 2. Counting Atoms in Chemical Formulas: Examine the subscripts and coefficients C6H12O6