Lecture 1
advertisement

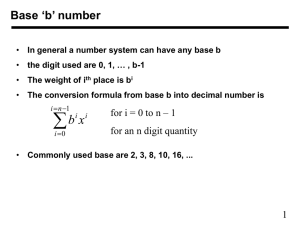
Lecture 1 Class Overview and Appendix A -- Number Systems 1-1 Other courses in computer sequence ELEN 350 ELEN 449 ELEN 450 ELEN 454 ELEN 468 ELEN 472 ELEN 473 ELEN 474 ELEN 475 Computer Architecture and Design Microprocessor Systems Design Computer Interfacing and Communications Digital Integrated Circuit Design Advanced Logic Design Microelectronic Circuit Fabrication (electronics) Microelectronic Device Design (electronics) VLSI Circuit Design (electronics) Introduction to VLSI Systems Design Careers related to Computers VLSI Fabrication Programmers System engineers Micro-programmers (micro-processor controllers) Others 1-2 Appendix A Number Systems 1-3 Positional Number Notation • Positional Number Notation – Decimal , Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal – A digit’s place in the sequence determines its weight • Decimal Numbers - Base 10 -- Digits 0-9 – Example – 15410 = = 1-4 Positional Number Notation • Binary- Base 2 - Digits 0 and 1. Binary Digits (bits) • Example • 100110102 = 1-5 Positional Number Notation • Octal- Base 8 - Digits 0 - 7. • Example • 2328 = 1-6 Positional Number Notation • Hexadecimal- Base 16 - Digits 0 - 9, A-F • A16 = 1010 B16 = 1110 C16 = 1210 • D16 = 1310 E16 = 1410 F16 = 1510 • Example • 9A16 = 1-7 Conversion Between Binary, Octal, and Hexadecimal Systems • Conversion from Binary to Octal or Hexadecimal. – Octal – Group into 3 bit groupings, starting at right. – Ex. 100110102 – Hexadecimal – Group into 4-bit groupings, starting at right. – Ex. 100110102 1-8 Conversion from Octal to Hexadecimal and Hexadecimal to Octal (1) Convert to binary (2) Convert from binary to hexadecimal or octal. • Ex. 2328 Convert to hexadecimal • (1) • (2) • Ex. • (1) • (2) 9A16 Convert to octal 1-9 Conversion from Decimal to Binary (1) Perform successive division -successively divide the base 10 number by the base to which it is to be converted (2) Collect the remainder to form the number in the target base (3) 1st division yields the least significant bit as its remainder (4) Continue until the quotient is 0. 1-10 Conversion from Decimal to Binary (1) Ex. Convert 15410 to binary 1-11 Conversion from Decimal to Octal (2) Ex. Convert 15410 to octal 1-12 Conversion from Decimal to Hexadecimal (3) Ex. Convert 15410 to hexadecimal 1-13 Binary Arithmetic Operations • Base 10 (review) -- addition 9510 +_1610 11110 • Base 10 (review) -- subtraction 9510 -_1610 7910 1-14 Binary Arithmetic Operations • • • • • • Addition in Base 2 -- Laws 0+0=0 0+1=1 1+0=1 1 + 1 = 0 with a carry of 1 Ex. 1 0 12 1 0 1 1 1 1 12 11 10000 1-15 Binary Arithmetic Operations • • • • • • Subtraction in Base 2 -- Laws 0-0=0 0 - 1 = 1 with borrow of 1 1-0=1 1-1=0 Ex. 1 0 0 0 02 1 0 1 1 1 1 12 1 10000 1-16 Homework Assignment HW #1 -- Appendix A 1-17