E-Learning/An-Najah National University
advertisement
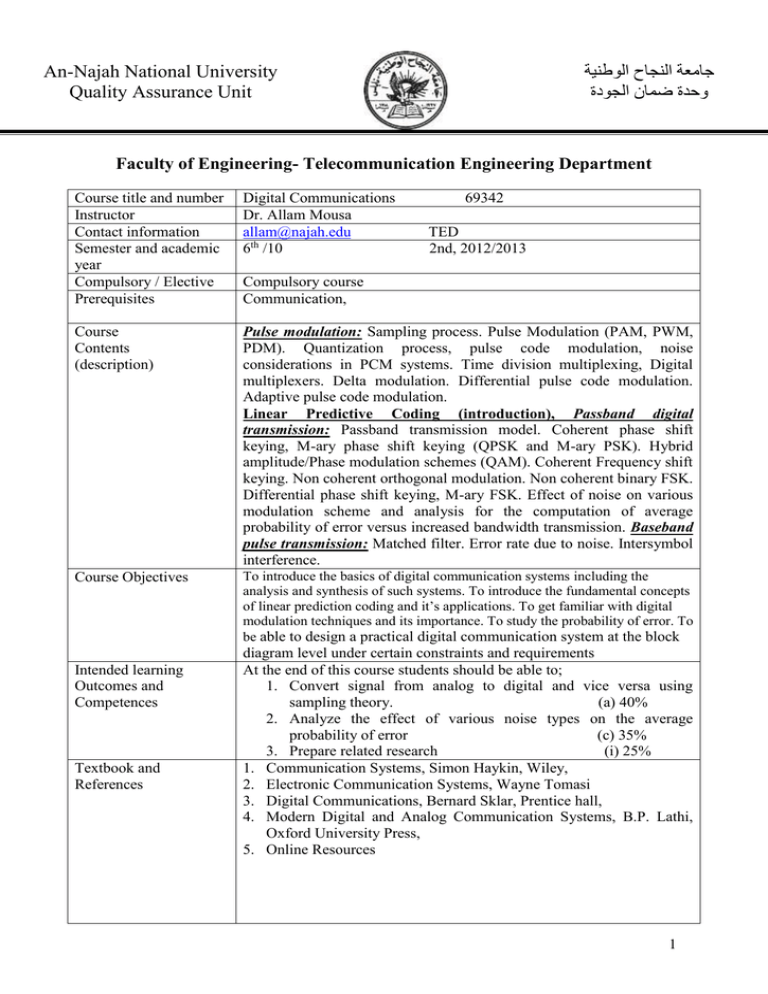
جامعة النجاح الوطنية وحدة ضمان الجودة An-Najah National University Quality Assurance Unit Faculty of Engineering- Telecommunication Engineering Department Course title and number Instructor Contact information Semester and academic year Compulsory / Elective Prerequisites Digital Communications Dr. Allam Mousa allam@najah.edu 6th /10 Course Contents (description) Pulse modulation: Sampling process. Pulse Modulation (PAM, PWM, PDM). Quantization process, pulse code modulation, noise considerations in PCM systems. Time division multiplexing, Digital multiplexers. Delta modulation. Differential pulse code modulation. Adaptive pulse code modulation. Linear Predictive Coding (introduction), Passband digital transmission: Passband transmission model. Coherent phase shift keying, M-ary phase shift keying (QPSK and M-ary PSK). Hybrid amplitude/Phase modulation schemes (QAM). Coherent Frequency shift keying. Non coherent orthogonal modulation. Non coherent binary FSK. Differential phase shift keying, M-ary FSK. Effect of noise on various modulation scheme and analysis for the computation of average probability of error versus increased bandwidth transmission. Baseband pulse transmission: Matched filter. Error rate due to noise. Intersymbol interference. Course Objectives To introduce the basics of digital communication systems including the analysis and synthesis of such systems. To introduce the fundamental concepts of linear prediction coding and it’s applications. To get familiar with digital modulation techniques and its importance. To study the probability of error. To be able to design a practical digital communication system at the block Intended learning Outcomes and Competences Textbook and References 69342 TED 2nd, 2012/2013 Compulsory course Communication, diagram level under certain constraints and requirements At the end of this course students should be able to; 1. Convert signal from analog to digital and vice versa using sampling theory. (a) 40% 2. Analyze the effect of various noise types on the average probability of error (c) 35% 3. Prepare related research (i) 25% 1. Communication Systems, Simon Haykin, Wiley, 2. Electronic Communication Systems, Wayne Tomasi 3. Digital Communications, Bernard Sklar, Prentice hall, 4. Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systems, B.P. Lathi, Oxford University Press, 5. Online Resources 1 Assignment Criteria Activity Midterm Exam Project/ exam Final Exam Week Subject 1 Sampling theorem. Ideal sampling and aliasing. 2 Pulse amplitude modulation. Pulse duration modulation, Pulse position modulation (generation and demodulation) Pulse code modulation. Delta modulation, slope overload and granular noise in delta modulation. Time division multiplexing. Differential pulse code modulation, sigma delta modulation. Electrical representation of binary data. 3 4 Percent (%) 25 25 50 5 Linear quantization, Linear Prediction (introduction) 6 Quantization noise 7 8 Midterm exam 1 Non linear quantization(mu-law ,A-law) 9 Digital modulation concept , Shannon’s theorem(capacity) 10 Binary amplitude shift keying ,frequency shift keying phase shift keying ,M – array coding 11 BPSK, QPSK modulators/demodulators 12 8-PSK,16-PSK,QAM modulator/demodulators. 13 14 15 16 Midterm Exam 2 Energy per bit, noise power density, Probability of error (BER) Baseband Pulse Transmission (ISI,…) Final Exam a. An ability to apply knowledge of advanced mathematics, science and engineering to telecommunication engineering problems. b. An ability to design and conduct telecommunication engineering based experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data. c. Ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs, within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability. d. Ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams. e. Ability to identify, formulate, and solve telecommunication engineering problems. f. Understanding of professional and ethical responsibility. g. Ability to communicate effectively. h. Broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context. i. Recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning. j. Knowledge of contemporary issues. k. Ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for telecommunication engineering practice. 2




