Consultant Learning - University of San Diego Home Pages
advertisement

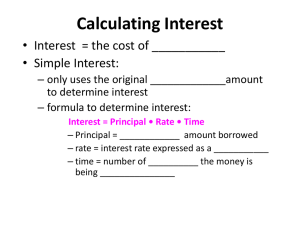
Consultant Learning: A Model for Student Directed Learning Scott W. Kunkel University of San Diego © 2003 Scott W. Kunkel Consultant Learning • Empowers students and places them in control of your own learning process. • Turns the classroom into a laboratory for the free enterprise system, using price as the allocation mechanism for grades earned. • Changes the grading dimension: – from quality of work performed – to quantity of excellent quality work performed. In the Traditional Course • All students do the same quantity of work. • Grading based on quality: – excellent quality = “A” – mediocre quality = “B” – poor quality = “C” • Poor quality work is accepted and the grade is reduced. In Consultant Learning • All accepted work is excellent quality. • Work that is not excellent quality is redone until it is excellent quality. • Grading is based on the quantity of excellent quality work the student performs. • Every student produces work of which he/she can be proud. In Consultant Learning • • • • Students must redo unprofessional work. Students compile their work in a portfolio. The portfolio can be used for job search. The students’ completed portfolios are submitted at the end of the semester. • The amount earned determines course grade: – Turns classroom into mini-economy. – Mimics real-world consulting environment. Theoretical Foundation • “Mastery Learning” by Bloom (‘71, ‘81). • Bloom said education should no longer be about “weeding out” students. • The normal curve is a valid predictor of random events, not purposeful events. • Learning is a purposeful event. Theoretical Foundation • “Mastery Learning” is a model that must be implemented across an entire curriculum. • Consultant Learning can be implemented in a single class without changing the assessment and grading standards of an entire institution. Theoretical Foundation • “Problem-Based Learning” sometimes called “Project-Based Learning” (Bridges, ‘92). • Builds educational objectives into projects. • Students complete the projects that require fulfillment of the learning objectives. • “Problem-based learning . . . fits exceptionally well in multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary learning and teaching styles” (Glasgow, ‘97). The Consultant Learning Process • You design projects based on your own interests. • For each project, you must submit a proposal explaining what you wish to do. • You assign a consulting fee to each project using the Suggested Projects booklet. • If the proposal and the fee are approved, you are authorized to do the project. The Proposal • Proposal includes 9 items: – 1. Type of project – 6. Perspective and Audience – 2. Topic – 7. Consulting Hours – 3. Rationale – 4. Research Method – 8. Consulting Fee – 9. Due Date – 5. Output/Report Method Possible Family Business Projects • • • • • • • • Family Business History ($3,000) Business Family Genogram ($2,000) Resume and Cover Letter Project ($1,000) Book Executive Summary Project ($1,000-$2,500) Case Summary ($400 - $1,000) Current Events Analysis ($200 - $800) “Presentational” Speech ($400 - $1,000) Interview the Owner or Junior Member of a Family Business ($2,000 - $3,000) • Family Business Forum Meeting ($2,000) • Student Designed Project (Up to $5,000) Possible Small Business Projects • The Business Disc computer simulation ($4,000) • A Major Team Small Business Analysis (Up to $10,000) – (a group of related projects) • Book Executive Summary Project ($1,000-$2,500) Resume and Cover Letter Project ($1,000) • Case Summary ($400-$1,000) • Current Events Analysis ($400-$800) • Presentational Speech ($400-$1,000) • Interview of a Small Business Owner ($2,000-$3,000) • Attendance at a Professional Meeting ($2,000) • Student Designed Project (Up to $5,000) Possible Entrepreneurship Projects • • • • • • • • • • • New Venture Feasibility Analysis ($2,000) New Venture PowerPoint Presentation (up to $10,000) Resume and Cover Letter Project ($1,000) Book Executive Summary Project ($1,000-$2,500) Case Analysis Project ($500-$1,000) Current Event Analysis Project ($500) Presentational Speech Project ($500) Interviewing an Entrepreneur ($2,000) Interviewing a Service Professional ($2,000) Entrepreneurial Key Contact File ($1,000-$2,000) Student Designed Project (Up to $5,000) Possible Strategic Mgmt. Projects • • • • • • • • • • • Team Computer Simulation ($6,000 + oral report fees) Major Company Strategic Analysis (up to $10,000) Business History ($3,000) Resume and Cover Letter Project ($1,000) Book Executive Summary Project ($1,000-$3,000) Case Analysis Project ($400-$1,000) Current Event Analysis Project ($200-$800) Presentational Speech Project ($400-$1000) Interviewing an Owner/Executive ($2,000-$3,000) Attendance at a Professional Meeting ($2,000) Student Designed Project (Up to $5,000) The Project • When the project is submitted, it is either approved or returned to be redone. • If project is returned, you must rewrite the project and resubmit it. • This process continues until the project is judged to be of “professional quality” and, therefore, acceptable. The Project • When the project is accepted, the agreed-upon fee is marked Paid (for example, “PAID $2,000”) and it is given back to you. • There are no partial fees - the project is either professional quality or it is not - it is either paid or returned to be rewritten and resubmitted. The Project • When a project is paid, it is returned to you (I keep no records). • You put paid projects in your portfolio. Pay for In-Class Work • You are also paid for attending class. – A fee schedule is in the Student Guide to CL. • “Call-on-Me” list pays you for being prepared to discuss the readings. – Sign “Call-on-Me” means you are prepared and I can call on you without you raising your hand. – “Call on Me” list pays you a fee for each class you sign it. The Portfolio • At the end of semester, you will put two accounting sheets on top of the portfolio showing what you have earned. • You submit the portfolio to me. • I “audit” the portfolio to make sure that the accounting sheet is accurate. • I assign the grade based on how much you have earned during the semester. Name: John Student Course: BUS 102W.01 In-Class Consulting Fees Earned Tuesday Week Attended Thursday Call on me 0 Attended 9/5 1 9/10 9/12 2 9/17 9/19 ///// ////////// 12 11/26 13 12/3 14 12/10 Col. Totals 12 ////////// Call on me ////////// 11/28 12/5 12/14 13 8 8 Totals Classes Attended # 25 $ 4,700 Total Call-On-Me Lists # 16 $ 3,200 Total In-Class Fees Earned $ 7,900 Name: John Student Course: GBA 537.01 Project Consulting Fees Earned Submitted Week Date Description of Project 3 9/24 Current Event 4 10/3 Book Report ///// ///// 9 11/7 10 ////////// Bus. History 11/14 Attend Prof. Meeting Cr/(Dr) $800 $800 $2,500 $3,300 ////////// ////////// $3,000 $17,500 $2,000 $19,500 Total Projects Consulting Fees Total brought forward from my “In-Class Consulting Fees Earned” sheet TOTAL CONSULTING FEES EARNED GRADE EARNED FOR THE COURSE Cumulative Balance $19,500 $7,900 $27,400 B+ Undergraduate Grading Scale • Undergraduate grades are assigned on the following scale: – – – – – $25,000 = A $23,000 = A $21,000 = B + $19,000 = B $17,000 = B - $15,000 = C + $13,000 = C $11,000 = C Less than $11,000 = F Graduate Grading Scale • Graduate grades are assigned on the following scale: – – – – – $30,000 = A $28,000 = A $26,000 = B + $24,000 = B $22,000 = B - $21,000 = C + $19,000 = C $17,000 = C Less than $17,000 = F Important Skills Students Learn • • • • Defining a question in researchable terms Identifying information sources Collecting information Organizing information into a readable, professional quality report • Writing a report that will be useful to others. Important Skills Students Learn • You learn these skills by doing them: – with guidance and coaching from me – including discussions in class Examples of Student Projects • Reviewed franchises then bought MBE. • Proposal to start an R & R band’s fan club, and they hired him. • Proposal to manage a country band, and they hired him. • “SnoAds,” ecologically sensitive advertising in the snow at ski resorts. • Proposal for family to expand family farm. • Surfing theme-park. Pros • Student centered - highly motivating to students. • Uses money/economics concepts to motivate behavior - it’s “real world.” • Students benefit from rewriting. • Course design is extremely flexible. • Motivates students to work for high grades. Student Reactions • Students generally love the Consultant Learning approach. It is motivating and interesting. • Two complaints from student are: – The Consultant Learning approach places too much responsibility on students. – It is too easy to procrastinate. Consultant Learning - Summary • Empowers students and places them in control of their own learning process. • Turns the classroom into a laboratory for the free enterprise system, using price as the allocation mechanism for grades earned. • Changes the grading dimension: – from quality of work performed – to quantity of excellent quality work performed. Consultant Learning: A Model for Student Directed Learning Scott W. Kunkel University of San Diego © 2003 Scott W. Kunkel