physics 2 syllabus _2013-2014_-1 - Baltimore Polytechnic Institute
advertisement

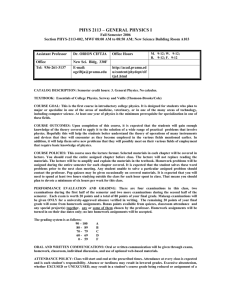
BALTIMORE POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE PHYSICS 2 COURSE SYLLABUS Overview of the Course Physics 2 is a whole-year course that is a continuation of your previous physics course. The emphasis of this course is on electricity, magnetism and modern physics. Your understanding of the concept of force, motion and vectors are necessary to facilitate the learning of this course. At the end of every semester, an examination will be administered to evaluate the students’ understanding and learning of the concepts covered in the semester. The following topics will be covered during the year: Static electricity Electric fields Current electricity Series and parallel circuit Magnetic fields Electromagnetic induction Electromagnetism Quantum theory The atom Relativity Quarter Grading System Assessments 60% Labs/Activities 20% Homework/Classwork 20% Semester Grading System 40% First/Third Quarter Grade + 40% Second/Fourth Quarter Grade + 20% Semester Exam Overall Course Grade (First Semester Grade + Second Semester Grade)/2 Materials Scientific calculator Notebook/Binder Textbook Physics: Principles and Problems Reminder: In order to become successful in this course the students must come to class prepared at all times. Academic honesty will be strictly enforced in this class. Copying of homework, drill, classwork, test and quiz is not allowed and will not be tolerated. A grade of zero, for the assignment, will be given both to the person who copied and the person who let others to copy his/her work. Habitual dishonesty will also be referred to the administrators. Week Number 1 2 Date 3 Aug. 26 – Aug. 30 Sept. 2 – 6 Sept 2 – Schools closed (Labor day holiday) Sept. 9 – 13 4 Sept. 16 – 20 5 Sept. 23 – 27 Sept 27 – Schools closed (Professional Devt) Sept 30 – Oct 4 6 9 10 Oct. 7 – 11 Oct. 14 – 18 Oct. 17 - 18 – Schools closed (Professional Devt) Oct. 21 – 25 Oct. 28 – Nov 1 11 Nov. 4 – 8 12 Nov. 11 – 15 Nov 15 – Schools closed (Professional Devt) Nov. 18 – 22 Nov 21-22 – Schools closed (Thanksgiving Holiday) Nov. 25 – 29 7 8 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Topics and Activities* Electric charge and Coulomb’s law Coulomb’s law involving three or more charges LAB: Investigating Static Electricity Electric field Capacitance and electric potential difference LAB: How can large amount of charge be stored Energy stored in capacitors Current, resistance and resistivity LAB: The capacitor Resistance and temperature Ohm’s law LAB: Ohm’s law Electric power and energy Using electric energy: calculating the amount of energy used and its cost LAB: Electric circuits Direct-current series circuits: voltage, current and resistance in series circuits Polarity of voltage drops, total power in a series circuit, voltage drop by proportional parts LAB: Series resistance Direct-current parallel circuits: voltage, current and resistance in parallel circuits Open and short circuits, division of current in two parallel branches, power in parallel circuits LAB: Parallel resistance Dec. 2 – 6 Series- parallel combination Dec. 9 – 13 Batteries Kirchhoff’s rules LAB: Cells in series and parallel Dec. 16 – 20 Kirchhoff’s Rules December 23 – January 1 – Winter Break Jan. 2 – 3 Delta-Wye transformation/ Open & Short circuits LAB: Voltmeter-ammeter method of measuring resistance LAB: Internal resistance of cells and batteries; potential drop Jan. 6 – 10 REVIEW WEEK FOR SEMESTER EXAM Jan. 13 – 17 SEMESTER EXAM WEEK SECOND SEMESTER 21 Jan. 20 – 24 Jan 20 – MLK Holiday 22 Jan. 27 – 31 Jan 31 – Schools closed (Professional Devt) Feb. 3 – 7 Feb. 10 – 14 23 24 25 26 27 Feb. 17 – 21 Feb 17 – Schools closed (Presidents’ Day Holiday) Feb. 24 – 28 Mar. 3 – 7 Magnets: permanent and temporary, forces caused by magnetic fields LAB: The nature of magnetism Creating electric current from changing magnetic field LAB: Principles of electromagnetism Changing magnetic fields induce EMF Transformers LAB: Magnetic field about a coil Interaction between electric and magnetic fields and matter LAB: Electromagnetic induction 1 Photoelectric effect The Compton effect LAB: Electromagnetic induction 2 28 Mar. 10 – 14 Particles behave like waves 29 Mar. 17 – 21 The Bohr model of the atom LAB: How can you measure the number of electron energy transitions? 30 Mar. 24 – 28 Radioactive decay and nuclear reactions 31 Mar. 31 – Apr. 4 The building blocks of matter: particle accelerators, Apr 4 – Schools closed detectors and the elementary particles (Professional devt) LAB: What can you learn from an emission spectrum? 32 Apr. 7 – 11 Holding the nucleus together: the strong nuclear force and binding energy April 14 – 21 – SPRING BREAK 33 Apr. 22 – 25 Using nuclear energy: artificial radioactivity, nuclear fusion and nuclear fusion LAB: Planck’s constant 34 Apr 28 – May 2 Solid state electronics 35 May 5 – 9 Theory of relativity 36 May 12 – 16 SENIOR EXAM REVIEW 37 May 19 – 23 SENIOR EXAM 38 May 26 – 30 Underclassmen review week May 26 – schools closed (Memorial day holiday) May 27 – Senior Farewell May 28 – Senior Status Day, Senior Prom May 29 – Senior Awards 39 Jun. 2 – 6 Underclassmen Semester Exams June 6 – last day for students 40 Jun 10 Last day for teachers Prepared by: Dennis B. Barles, Physics Teacher *dates and order of topics subject to change. All topics will be covered by the end of the semester