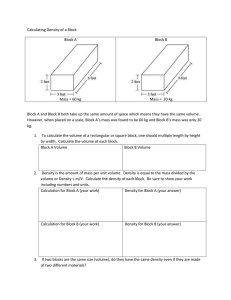
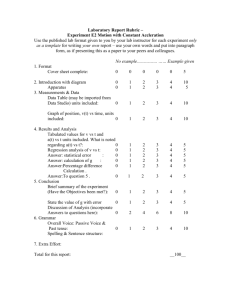
File
advertisement
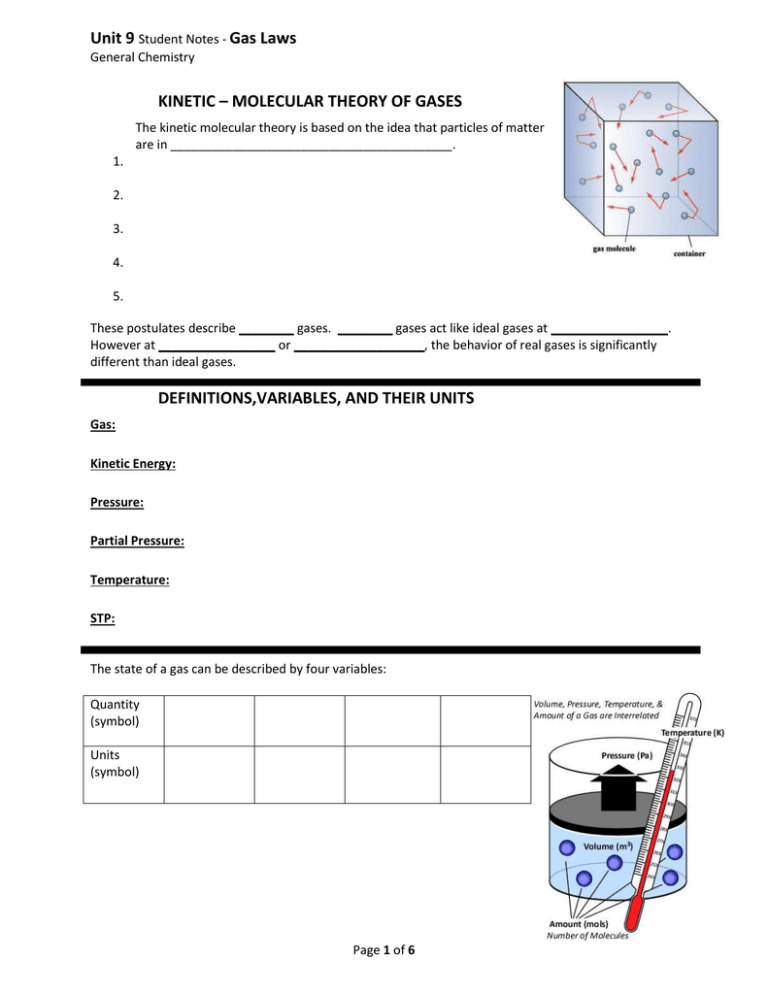
Unit 9 Student Notes - Gas Laws General Chemistry KINETIC – MOLECULAR THEORY OF GASES The kinetic molecular theory is based on the idea that particles of matter are in _________________________________________. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. These postulates describe ________ gases. ________ gases act like ideal gases at _________________. However at _________________ or ___________________, the behavior of real gases is significantly different than ideal gases. DEFINITIONS,VARIABLES, AND THEIR UNITS Gas: Kinetic Energy: Pressure: Partial Pressure: Temperature: STP: The state of a gas can be described by four variables: Quantity (symbol) Units (symbol) Page 1 of 6 Unit 9 Student Notes - Gas Laws General Chemistry Conversions: *The temperature MUST be in KELVIN UNITS for any calculation in this unit! Remember: __________________________________________ Example: *It doesn’t matter what unit Pressure and Volume are in, as long as you use the ________________ within a single calculation. Remember: __________________________________________ Examples: Combined Gas Law: Example Calculation: What would be the volume in liters of an 8.90 liter sample of gas at 100.oC and 113 kPa if conditions were changed to STP? DON’T FORGET: The term ____ stands for Standard Temperature and Pressure. Mathematically, this means ___________________ (or 760 mm Hg or 101.3 kPa) and _________ (or 273 K). Boyle’s Law: Real Life Application: Example Calculation: 1.00 L of a gas at standard temperature and pressure is compressed to 473 mL. What is the new pressure of the gas? Page 2 of 6 Unit 9 Student Notes - Gas Laws General Chemistry Charles’s Law: Real Life Application: Example Calculation: A man heats a balloon in the oven. If the balloon initially has a volume of 0.4 liters and a temperature of 20 C, what will the volume of the balloon be after he heats it to a temperature of 250 0C? 0 Gay-Lussac’s Law: Real Life Application: Example Calculation: If the pressure on a gas in a rigid container changes from 800. mmHg to 2.15 atm, and at the lower pressure, the temperature is found to be 40.0°C, what was the final temperature in Kelvin? Avogadro’s Law: Real Life Application: Example Calculation: A 36.2 mole sample of carbon dioxide occupies a volume of 5.20 liters. If 15.4 more liters are added, how many moles would you have if the pressure and temperature remains constant? Page 3 of 6 Unit 9 Student Notes - Gas Laws General Chemistry Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure: What if the units are not the same??? Ptotal = PA + PB + PC + …for however many gases you have! Example Calculation: There is a container which has oxygen, xenon and helium in it. Its total pressure is known to be 972 mmHg. If the pressure of the helium is 0.458 atm and the pressure of the oxygen is 74.1 kPa, what is the pressure of the Xenon in mmHg? Dalton’s Law Over Water: The gas collected includes the desired gas AND water vapor… so… Example Calculation: 50.0 ml of hydrogen collected over water and has a pressure of 850. mmHg at 27.0oC. What is the pressure of the dry gas at STP? Vapor Pressure (torr) Temperature (°C) Vapor Pressure (torr) Temperature (°C) Vapor Pressure (torr) Temperature (°C) Vapor Pressure (torr) 2.1 2.3 2.5 2.7 2.9 3.2 3.4 3.7 4.0 4.3 4.6 4.9 5.3 5.7 6.1 6.5 7.0 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 18.7 19.8 21.1 22.4 23.8 25.2 26.7 28.3 30.0 31.8 33.7 35.7 37.7 39.9 42.2 44.6 47.1 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 97.2 102.1 107.2 112.5 118.0 123.8 129.8 136.1 142.6 149.4 156.4 163.8 171.4 179.3 187.5 196.1 205.0 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 Page95 4 of 6 96 97 369.7 384.9 400.6 416.8 433.6 450.9 468.7 487.1 506.1 525.8 546.1 567.0 588.6 610.9 633.9 657.6 682.1 Ptotal = Pwater + Pgas Unit 9 Student Notes - Gas Laws General Chemistry (torr = mmHg) Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT P= V= n= R= T= LmmHg Latm LkPa R 0.0821 mol or 62.4 or 8.314 mol K mol K K Example Calculation: How many moles of oxygen must be put in a 0.500 L flask at 20.00C to have a pressure in the flask of 1.77 atm? Example Calculation: If 1.17 grams of helium are put into a 500.0 ml container at 100C, what would be the pressure of the container (in mmHg)? Page 5 of 6 Unit 9 Student Notes - Gas Laws General Chemistry Gas Laws Intro Combined Gas Law 12:10 8:09 Unit 9: Video 2 Unit 9: Video 1 (video 1, Gas Laws Intro on YouTube channel) Boyle’s Law (video 2, Combined Gas Law on YouTube channel) Charles’s Law 4:22 Unit 9: Video 3 (video 4, Charles’s Law on YouTube channel) (video 3, Boyle’s Law on YouTube channel) Gay Lussac’s Law 4:07 Unit 9: Video 4 Avogadro’s Law 6:16 4:33 Unit 9: Video 6 Unit 9: Video 5 (video 5, Gay Lussac’s Law on YouTube channel) (video 6, Avogadro’s Law on YouTube channel) Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure 8:19 Unit 9 : Video 7 (video 7, Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure on YouTube channel) Ideal Gas Law 11:38 Unit 9: Video 8 (video 8, Ideal Gas Law on YouTube channel) Page 6 of 6