Children should add
advertisement

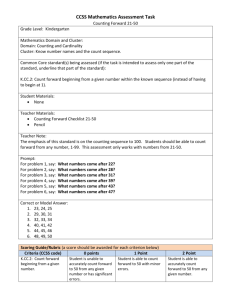
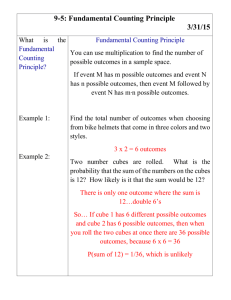
Mathematics in the Early Years and Infants – Addition. New Mastery Curriculum. • The principles underpinning the new mathematics curriculum reflect a ‘mastery approach’ to teaching mathematics. • ‘Mastery’ – A full command of a study of a subject, expert skill and knowledge. • A mastery curriculum expose all children to the content with the large majority progressing at the same pace. Skills Needed • Counting and ordering numbers 1 – 20. • Use appropriate vocabulary Expectations • To count numbers within 20 using pictures and objects. • Tell an addition story • Lots of practical counting using a range of objects. Gelmans and Gallistel’s 5 Principles of Counting – Step 1 • The one-one principal – To have a distinct counting word to each of the items to be counted. Gelmans and Gallistel’s 5 Principles of Counting – Step 2 • The stable-order principle – to be able to count confidently in a repeatable order. • 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …………….. Gelmans and Gallistel’s 5 Principles of Counting – Step 3 • The cardinal principle – the number name allocated to the final object in the collection represents the number of items in total. Gelmans and Gallistel’s 5 Principles of Counting – Step 4 • The abstraction principle – when a child has the ability to count non-physical things. • For example: counting sounds, counting imaginary objects. Gelmans and Gallistel’s 5 Principles of Counting – Step 5 • The order-irrelevance – the child is able to count in any order and understands that they count from right to left or left to right. • Year 1 – Skills needed, • Counting and ordering numbers 1 – 100 • Count in 2s and 5s and in 10s to 100 • Number bonds to 20 • Use appropriate vocabulary (add, total, altogether, plus, increase, more, addition). • Solve problems. Expectations. • Children should add: • U+U • TU + U (up to 20 including zero). • Suitable Methods: • Practical • Number line Year 1 Addition Year 2 – Skills needed. • Count in steps of 2, 3, 5 and 10 forwards and backwards from 0. • Recognise the place value of each digit in a 2 digit number. • Compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100. • Read and write numbers to at least 100. • Understand that addition is commutative ( can be done in any order) • Solve problems using addition. Year 2 – Expectations. • Children should add: • TU + U • TU + multiples of 10 • TU + TU • U+U+U • Suitable Methods: • Practical • Number Line • Expanded columnar Year 2 – Addition. Using a number square. Number line 0 counting on. Year 2 Addition. Empty Number Line. Number line – Bridging 10 then adding on. Expanded Columnar. References: • Gelman, R. & Gallistel, C (1978) ‘The Child’s Understanding of Number’ Cambridge, MA. Harvard University Press.