241Course Syllabus2013
advertisement

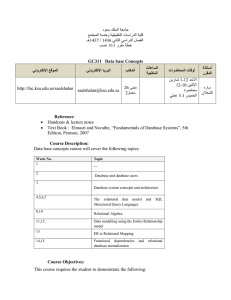
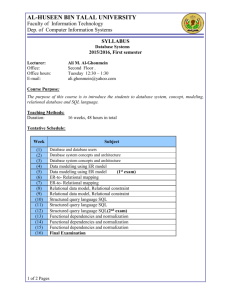
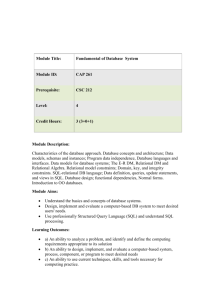
CPCS 241 Database Systems (I) 1st semester 2013 Instructor Information Name of the instructor: Shahd Al-Ahdal Office location: room 233 E-mail: shahd.alahdal@hotmail.com Website: saalahdal.kau.edu.sa Group Link: http://groups.yahoo.com/group/cpcs_241_f2013 Office hours: Day Saturday Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Time 9-11 12.30-2 12.30-2 9-11 12.30-2 12.30-2 9-1 Course Information: Course Name: Database Systems (I) Course Number: CPCS 241 Text book: Elmasri and NAvathe, “Database Systems”, 6th edition, Pearson. ISBN 10: 0-13-214498-0 ISBN 13: 978-0-13-214498-8 Reference: Connolly and Begg, “Database Systems: A practical Approach to Design, implementation, and management”, 5th edition, Pearson. ISBN-10: 0-321-52306-7 ISBN 13: 978-0-321-52306-8 Course Description: Data, Information, File System, Database and Database Users, Database System Concepts and Architecture, Data Modeling using the Entity Relationship (ER) Model, The Relational Data Model and Relational Database Constraints, Functional Dependencies and Normalization for Relational Databases, The Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus, Relational Database Design by ER and EER to Relational Mapping, Disk Storage, Basic File Structure and Hashing. Course Prerequisite: CPCS 204 Course Objectives: It is expected that upon successful completion of the course, the students should be able to: 1. Define Database, characteristics and functions of Database Management System and types of Database Users 2. Distinguish between a Traditional File System and a Database System 3. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of Database System with traditional File system 4. Describe Data Models, Schemas, Instances, Three Schema Architecture and DBMS Component Modules 5. Define the Relational Data Model, its constraints, and the Relational Database Schema. 6. Demonstrate the use of SQL for Database creation and maintenance 7. Design Queries in relational Algebra and relational Calculus. 8. Use SQL queries for data aggregations, calculations, views, sub-queries, embedded queries, manipulation and report generation. 9. State the informal design guidelines for Relational database. 10. Interpret advantages of standardized database system. 11. Illustrate the definition of Functional Dependency, Inference rules, Equivalent of Sets to FDs, and Minimal Sets of FDs. 12. Review the Three Normal Forms based on Partial and transitive dependencies. 13. Apply normalization techniques to DB. 14. Describe the Entity-Relationship (ER) modeling tool using Unified Modeling Language (UML). 15. Convert a conceptual Data Model into relational logical schema. 16. Model real world database system using ERD from the requirements specifications. 17. Identify the data integrity and security requirements of DB. 18. Design and implement a full real size database system Homework submission policy Homework should be submitted as physical copies. Please submit your assignments on the due date. Any assignments submitted after the due date, 50% will be deducted. Homework will NOT be accepted any more than three days after the deadline under any circumstances. No homework will be accepted if the solutions have been released for any reason. Finally, please remember to save a copy of your homework, in the unlikely event that something happens to it. Course Schedule Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Description Data, Information, File system, data Base, and data Users Database System concepts and Architecture The Relational Data Model and Relational database Constraints Schema Definitions, Constraints, Queries, and Views (DDL and DML) The Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus Data Modeling using ERD. Relational Database design by ERD and Relational Mapping. Functional Dependencies and Normalization for Relational DB Duration in Weeks 1 2 2 2 3 1 1 2 Course Evaluation Course Assessment Tools Final Exam First Exam Second Exam Third Exam Assignments LAB Project Total Percent 30 10 10 15 5 30 100