Transportation engineering
advertisement
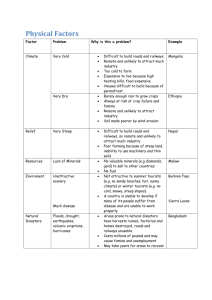
Ram Humbare Introduction:Transportation engineering deals with design ,development ,construction and maintenance of roadways , railways, airports, docks and harbours, tunnel , bridges etc. in other words, it deals with transport of man & materials , through different communication routes as land, water and air. Transport:The term transport is derived from the latin word ‘transportare’ . Trans means over &portare means carry i.e transportation means to carry from one place to another . Transport can be divided into three types as follow: Land transport Water transport Air transport Major types : Roads Railways Road network plays an important role in development of country & interior development of different areas of country. Function:-to connect all cities, towns and villages. National Highway(N.H) State Highway(S.H) District Road Village Road Express Road It connect capital cities of state. Width of road is 7 to 15 m. Carries fast and heavy traffic. Speed limit is @ 80kmph Important road link to transport men and materials effectively. It connect national to district places in state. Width of road is 7 to 10 m. Carry medium to fast traffic. Speed limit is @ 60 to 80kmph. It is two part:(a)Major district road.(b)other district road. Width of road is 5 to 8 m. Connects district places to taluka place. Speed limit is @ 60kmph. Carry moderate traffic It connect village to district road Width of road is <5 m. Very high traffic is expected. Speed is @ 40kmph. Heavy and very fast traffic is expected. No crossing are provided. Two wheelers & three wheelers are not allowed. Speed is @ 100kmph. Earthen roads. Water bound machadam roads. Bituminous or tar roads. Cement roads It is also called kuchha roads. Local earth is used in construction of these roads. These roads are provided in village areas. WBM roads are provided in village areas. WMB also act as the compact base for the bituminous road and concrete road. The large sized stones are laid in the bottom course. Broken stone of 25 mm to 75 mm are laid in three layers on prepared subgrade. It is flexible pavement. Bitumen act as binder, holds all material together. First WBM surface prepared and then stone chips of 16 to 20 mm with bitumen are laid. Thickness of this layer is 30 to 40mm. Smooth wearing course provided at the top. Durability is less as compared to concrete road. Corrugations are developed. It is Rigid pavement. It is more durable. Cement act as a binder. Corrugation are not developed. Less maintenance cost but repair difficult. It comprise of wearing surface on top, the base course below and sub-base at the bottom. There are two types of pavement. (a) Flexible pavement. (a) Rigid pavement. These pavements acquire the shapes of underlying base course layers on application of load. Strength and rigidity is less as compared to rigid pavements . e.g. 1) Bituminous pavements 2) WBM roads 3) stabilized soil bases. These pavements do not acquire the shape of underlying base course layers on application of load. These pavements have good strength durability. They also have more stiffness and thickness e.g.1)concrete roads. Railways play an important role in bulk transportation of men and material all over country. Indian railway possesses largest rail network in Asia. Delhi metro rail is one of the advance developments in Indian railways. Definition: “A clear distance between inner faces of rail.” Two rails run parallel to each other and maintain gauge distance between them. Gauge Distance between inner face of rail 1) Narrow gauge 0.765 m 2) Meter gauge 1.000 m 3) Broad gauge 1.676 m Central railways South central railways western railways South-eastern railways Eastern railways North-western railways North-eastern railways North-east frontier zone Southern railways Roadways Railways 1) Suitable for any distance. 1) Suitable for long distance only. 2) Maintenance cost is less. 2) Maintenance cost is more. 3) Suitable for steeper gradients. 3) Steeper gradients are avoided. 4) Problems of traffic jam, toll collection. 4) No such problems. 5) Frequency of accidents is more 5) Frequency of accidents is less. 6)Load carrying capacity is less. 6) Load carrying capacity is more. 7)Door to door service is available. 7)Such service is not available. 8) Speed achieved is 100-150 km/hr. 8)Speed achieved is 60-100 km/hr. Definition:“bridges can be defined as an over ground construction to cross over obstacles safely without disturbing the natural way below it.” It connect town and cities. In case of war destruction of bridges affect mobility of army and essential good. Bridges engineering has special important in military engineering. Culverts - up to 06 m Minor bridges - 6 to 30 m Major bridges - over 30 m Definition :tunnel can be defined as , “ an artificial under ground passage to by pass obstacles safely without disturbing the overburden i.e. land above it , to carry freights, passengers sewage, water etc. Tunnel are more economical than open cuts beyond the certain depth. In case of war, tunnels give the better protection. Tunnels prove cheaper than the bridges and open cuts to carry gas, electrical lines. Etc Cost of road project is deceased because of shortening of distance. Freedom for snow and iceberg hazard in cold countries. Initial cost of construction is high. Very heavy machinery, skilled labour is required for tunneling . Time required for construction is more. a) off-spur tunnels b) saddle or base tunnels c) slope tunnels d) spiral tunnels a) conveyance tunnels b) Traffics tunnels a) Tunnels In hard rock . b) Tunnels in soft material. c) Tunnels underneath river bed. Type of water transport:- a) Inland water transport a) Ocean water transport It is in the term of: a) River b)canal River transportation is popular is in rivers like in Gangas. Ocean transport is used for the trade and commerce. Ocean transportation has no limitation and possesses high flexibility. For national defence navy is established. It provides the powerful defence in emergency of national security. It is cheapest transportation. It is help to development of industry and international trade. Load carrying capacity is more. Cheap motive power is required for its works. It is slow and consume more time. Chances of attacks on naval ships by pirates. Chances of accident due to climate disasters such as storms, cyclones etc. Specific water level should be maintained in canal transportation. Definition:“A haven or road stead of navigable waters well protected naturally or artificially from action winds ,waves and is located along sea shore or river estuary or lake or canal connected to sea. Horbour is a place where ships, boats, and barges can seek shelter from stormy weather, or else are stored for future use. a) Natural harbour. b) semi-natural harbour. c) Artificial harbour . a) military harbour. b) harbours of Refuse. c) fishery harbours. d) commercial harbours. e) marine harbours. a) Canal harbourss. b) River or estuary harbour. c) lake harbour. d) sea or ocean harbour. Definition:“ an area of water for building or repairing or loading and unloading ships or ferries.” For unloading and loading of cargo ship required of days. It is used to avoid the inconvenience . 1)Wet docks:- docks used for berthing of vessel for loading and unloading of cargo and passenger are called ‘wet docks’. 2)Dry docks:- docks used for repair of the vessels are called as ‘dry docks’. Air transport is the fastest mode of transport, with speed more than 300kmph. It is also three times speed of the sound It does not required any tracks as in case of roads and railways. It is fast and speedy. It is highly used in case of disasters i. e floods, cyclones etc. Useful in national defence. It can be also used for aerial photography. Flight rules have to be followed strictly for smooth working of air transport. It is more costly. Frequency of accident is less but damage is tremendous. It can be affected by weather.