Political Systems
advertisement

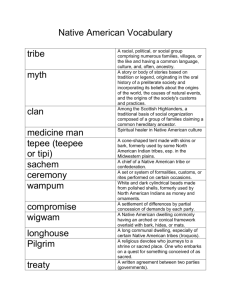
Political Systems Kinds Of Political Systems • Uncentralized systems – Bands – Tribes • Centralized systems – Chiefdoms – States Bands • Small group of politically independent, though related, households. • The least complicated form of political organization. • Found among nomadic societies. • Small, numbering at most a few hundred people. Bands • No need for formal political systems. • Decisions are made with the participation of adult members, with an emphasis on achieving consensus. • Those unable to get along with others of their group move to another group where kinship ties give them rights of entry. Tribes • Tribes consist of small, autonomous local communities, which form alliances for various purposes. • Economy based on crop cultivation or herding. • Population densities generally exceed 1 person per square mile. • Leadership among tribes is informal. Tribes The Big Man • Big Man from New Guinea wearing his official regalia. • Has informal authority, but “can’t tell people what to do” Question • Bands and tribes are both A. centralized. B. associated with industrialism. C. dependent on age groups for political organization. D. uncentralized and egalitarian. E. hierarchical in social organization. Answer: D • Bands and tribes are both uncentralized and egalitarian. Question • In the band, disputes are settled informally through ___________ A. B. C. D. E. gossip. ridicule. direct negotiation. mediation. all of these choices Answer: E • In the band, disputes are settled informally through gossip, ridicule, direct negotiation and mediation. Question • The form of social organization typical of hunter-gatherers is the _________, whereas horticulture and pastoralism are usually associated with the form of social organization called the _________. A. tribe/chiefdom B. tribe/state C. tribe/band D. band/chiefdom E. band/tribe Answer: E • The form of social organization typical of hunter-gatherers is the band, whereas horticulture and pastoralism are usually associated with the form of social organization called the tribe. Chiefdoms • The chief is at the head of a ranked hierarchy of people. • The office of the chief is usually for life and often hereditary. • The chief’s authority serves to unite his people in all affairs and at all times. • Highly unstable as lesser chiefs try to take power from higher ranking chiefs. Chiefdoms • A Kpelle town chief in Liberia, West Africa, listens to a dispute in his district. • Settling disputes is one of several ongoing traditional tasks that fall to State • The most formal of political organizations. • Political power is centralized in a government, which may use force to regulate the affairs of its citizens and its relations with other states. • Since their first appearance 5,000 years ago, states have shown a tendency toward instability and transience. A Nation without a State The Kurds, most of whom live in Iran, Iraq, and Turkey, are an example of a nation without a state. Nation (review): A people who share a collective identity based on a common culture, language, territorial base, and history Gender and Politics • Above Liberian President Ellen Johnson Sirleaf inspects members of the Liberian police after taking the presidential oath in January 2006. • The first female president on the African continent, Sirleaf is a Harvard-educated economist who took the world by surprise when she won the head office in her war-torn and poverty-stricken country.