Lecture 2
advertisement

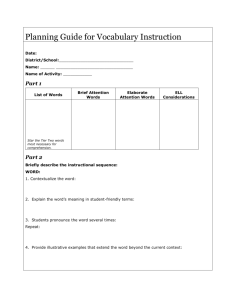
EN 4313 (Lecture 2) Contextualizing teaching & language tasks Personalizing teaching & language tasks Using different sensory input Making interactive-decisions Engaging different classroom interaction patterns Engaging different classroom discourse formats Contextualizing your teaching Context = a situation in which there’s a call for meaningful or purposeful communication the communication calls for the use of a specific language item (collocation) The context should signal to Ss the situation with which the particular language item can be associated. To contextualize your teaching means to create a meaningful communicative context for what students are going to learn Contextualize both your teaching and major language tasks so that your students can learn the communicative use of the language item(s)/skills Examples of context and details involved An event / a story: a robbery, a birthday party, a personal crisis / problem, etc. A place: at MacDonald’s, at the Peak, etc. People involved: a policeman, a friend, a counselor, etc. The communication needed / particular language item needed: describing an event, giving instructions, looking up information for a project, etc. The communication mode: email, telephone, face-to-face discussion,etc. Task 1 Is Task A in the handout contextualized? If so, is it well-contextualized? Comment. What can we do to contextualize the task? Is Task B in the handout contextualized? If so, is it well-contextualized? Comment. What can we do to contextualize the task? Personalizing your teaching Personalizing = signaling to Ss that what you’re going to present or what you want them to do is related to them generated from them to be owned by them Ways of personalizing your teaching (presentation) When presenting/teaching the use of a language item or a skill, draw on the experiences, views of your students solicit examples or linguistic data (language) from your students acknowledge the contribution of the above Personalizing a learning task Assigning a topic / context that concerns your Ss or that interests them Allowing Ss to personalize their own products by encouraging them to express their views, thoughts about a topic in a piece of writing create a personal title for their own products decorate their own products publish their work (creating a sense of recognition) Why personalizing our teaching? Personalizing can create a sense of ownership of things produced during the learning process make your classroom a personal and ‘human’ place motivate learning lubricate the process of learning Knowledge required of you: Interests of youngsters Your Ss’ interests The practice of your CTs Any other types of knowledge? If possible, contextualize and personalize when planning for a teaching unit and in particular for the start / warm-up stage of A major reading task A major writing task A major speaking task A major vocabulary learning unit A major grammar item learning unit Making use of different sensory input to spice up your lessons Use Music (e.g., MTVs) Video clips Internet resources, etc. Pictures Objects Etc. to stimulate thinking and to generate ideas Making interactive decisions Interactive decisions = ad hoc decisions made during your teaching regarding the pace; the amount of input to give the strategies of teaching for the next step of your teaching in order to maximize the effectiveness of your teaching Observations to make for interactive decisions pace of learning / ability to learn mood discipline level of interest in the activities /your teaching the previous & the next lessons Some likely scenarios in your PT which may affect the progress ofyour lesson: Sleepy Ss (2:00 in a hot afternoon) Slow learners Confused learners A rowdy group Ss have returned from a P.E. lesson Ss have finished a test in a previous lesson Ss will be writing a test in the next lesson Ss have been punished in a previous lesson Students have suggested some good examples. Ss in a festive mood. Solutions? Slowing down Repeating a teaching procedure Rephrasing your explanation Introducing a brief game / a fun activity Allowing several minutes for settling down Allowing a short break Allowing Ss to talk about the previous / upcoming lesson Staying away from sensitive topics Adopting Ss’ examples Interactive decisions on your use of equipment, materials, etc. When equipment breaks down or when you suddenly find a mistake in your materials, quit using the equipment quit using the materials if the mistake is serious point out the problems of the materials check the equipment / materials first before the class starts think of some fallback strategies Flexibility counts! Exercise flexibility in the execution of your plan. Don’t panic when things don’t run according to your plan. Do what you think is appropriate to the flow of your lesson (logical enough?). Do what you think is conducive to the achieving of the lesson objectives. Don’t stick to your lesson plan just because your CT or Tutor has a copy of if and is observing your lesson. Classroom interaction patterns T Ss (lecturing) S—S—S (group) S-S (pair) S What are the strengths and limitations of these various interaction patterns? Classroom Talk (Discourse formats) T-initiated talk: Monologue IRF IR(group discussion – group responding)F IRF (F from peers – F from T) I(Genuine questions)R-Inc (incorporation of ideas for teaching) What are the various formats good for? What are the strengths and weaknesses of the variations of IRF? Classroom Talk (continued) Student-initiated talk: IR (teacher) IR (peer) F (teacher) I I (teacher) R(peer) F(teacher) What are some strengths and weaknesses of the above formats? Initiation involves questioning/elicitation skills (practised in Tut 2/3). Response takes time, may need motivation or encouragement, may mean overcoming the classroom cultural barrier. Feedback requires your interactive decisions. Implications? Implications for MT / on-site PT? You will be assessed on how well you can do the following: Contextualization Personalization Use of different sensory input Use of different interaction patterns Use of different discourse formats