Competency's Are King….Improving Staff and Organizational

COMPETENCIES ARE KING…
IMPROVING ORGANIZATIONAL
AND STAFF PERFORMANCE
FAR Luncheon
Presented by Dawn Godaire, PHR and Chris Busky, CAE
Heart Rhythm Society
Learning Objectives
• Develop a basic understanding of competencies and key terminology.
• Learn how HRS designed and implemented its competency model and enhanced its performance management, staff development, and recruiting initiatives.
Competency 101 -
Creating a High Performing Organization
Creating a High Performing Organization
• Job descriptions typically articulate the skills and knowledge necessary for success. They describe
“what” needs to be accomplished.
Skills &
Knowledge
• Core behavioral competencies encompasses the interpersonal skills, traits, and values needed for organizational and individual success and describe the
“how” work should be accomplished.
The Winning Formula
Behaviors
Attitudes
Achievements
Values
Traits
Job Knowledge/Skills +
Behavioral Competencies =
A High Performing Organization
Defining Competencies 101
Competencies are generally defined as a skill, knowledge, or behavior that is observable and allows an employee to successfully perform his or her job.
Director of Accounting
Defining Competencies 101
• Generic competencies (core attributes) – Behaviors that apply to each employee regardless of role or level. Considered the price of “admission” into the organization. Examples include:
• Professionalism
• Integrity
• Ethical
• Core competencies – Also apply to all employees. However, proficiency levels and expectations differ based on role/level. Examples include:
• Communication
•
• Innovation
Relationship building
Defining Competencies 101
• Technical competencies – Specialized skills or knowledge needed to be proficient in a particular job. Examples include:
• Budgeting
•
• Project Management
Analytical
• Leadership competenciesSkills and behaviors that apply to individuals in a leadership role. Examples include:
•
• Developing people
Inspiring others
• Strategic thinking
Defining Competencies 101
• A competency model is a framework listing organizational competencies. The competencies are usually clustered together in categories. Most models include a competency title, definition, proficiency levels, and behavioral indicators.
•
•
•
•
Proficiency LevelsProficiency levels and accurate behavioral indicators define successful performance at various levels within an organization. A basic model may include:
• P1 = Awareness (Beginner)
P2 = Application (Intermediate)
P3 = Integration (Advanced)
P4 = Strategic (Subject Matter Expert)
The competency model should align with and support the organization’s mission, values and strategic plan .
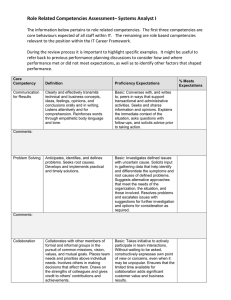
Sample Competency
Accountability
Willingness to accept full responsibility in meeting performance expectations. Displays honesty and truthfulness; confronts problems quickly; displays strong commitment to the success of HRS.
P1- Awareness
• Maintains ethical behavior, admits mistakes, and exhibits responsible behavior in the meeting of performance expectations.
• Follows through and meets commitments to others in a timely fashion.
P2- Application
• Actively seeks out solutions to achieve results.
• Holds self accountable for achieving results as an individual as well a team member.
P3 - Integration
• Chooses to take ownership of outcomes by seeking out solutions with appropriate stakeholders.
• Identifies and assists in addressing areas of weakness that may impact the department’s performance.
• Maintains a positive or constructive approach and actively develops solutions to achieve organizational results.
• Holds self and others accountable for appointed responsibilities.
P4- Strategic
• Holds ultimate responsibility for the overall performance in successfully meeting the organization’s strategic goals and mission.
• Takes ownership of outcomes by focusing on the actions necessary to move the strategic goals of the organization forward.
• Defines objectives and ensures successful outcomes in meeting the needs and requirements of stakeholders.
Competency
Sample Proficiency Map
Assistant,
Customer
Service
Coordinator,
Accounting
Manager,
Accounting
Director,
HR
Organizational
Knowledge
Accountability
Communication
Initiative
Innovative
Thinking
Organizing and
Planning
Relationship
Building
Continuous
Learning
P1
P1
P1
P1
P1
P1
P1
P1
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P3
P3
P2
P3
P3
P3
P3
P3
P4
P4
P4
P4
P3
P4
COO
P4
P4
P4
P4
P4
P4
P4
P4
IMPLEMENTING THE HRS
COMPETENCY MODEL
How a Competency Model Benefited HRS
HRS
Challenges
• Lacked a common language to describe successful organization and individual performance.
• Subjectivity in the performance management process.
• Not enough focus on assessing critical behaviors for success in the recruiting process.
• Staff frustrated with unclear performance expectations.
Competency
• Clarified performance expectations.
• Created a common language to describe high performance.
• Linked all HR functions to the organizational strategy.
• Increased ability to recruit, hire, and retain the right talent.
• Provided strategic insight on organizational development needs.
Benefits
Getting Started - The HRS Way
Create individual development plans
Identify and define competencies
Assess current employee proficiency
Create proficiency maps for each position
Establish proficiency levels and behavioral indicators
Integrating the Competency Model into
HR Initiatives
Performance
Management
Training and
Development
Career
Roadmaps
Succession
Planning
Comp
&
Rewards
Recruitment
&
Selection
Mission &
Strategy
Enhancing the Recruitment Process
Traditional Recruiting
Method
Competency-Based
Recruiting Method
• Focus solely on technical skills and job knowledge.
• Incomplete job descriptions.
• Inconsistency and subjectivity in the recruitment and evaluation process.
• Focus on the skills, knowledge, and behaviors critical for organizational success.
• Job descriptions that accurately capture all aspects of the job.
• Formal and consistent recruitment and evaluation process. Creation of behavioral event interview questions.
Enhancing the Performance Management
Process
• Performance is reviewed and measured in three areas:
• Goal achievement
• Technical job knowledge
• Proficiency with core competencies
• Competency Assessment Process
• Individual Development Plans
• Commitment to Development