DeWittScience__Bees
advertisement

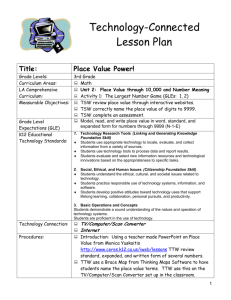
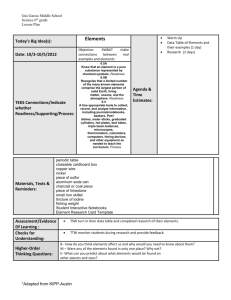
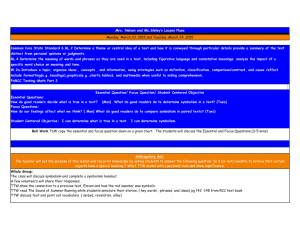
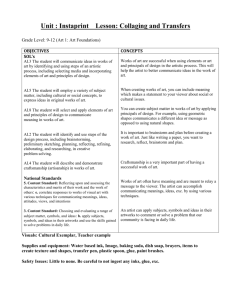
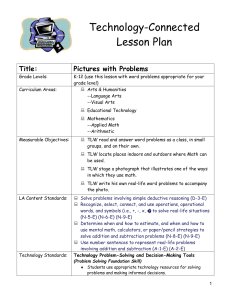
University of Montevallo Science Lesson Plan Format Name: Catherine DeWitt Subject/Grade level: Science/3rd Date lesson taught: Group size: 23 School: Valley Intermediate Goals: •TSW understand the basic anatomy of a bee through brainstorming and exploration. •TSW understand and discuss how bees help fertilize certain plants, such as the Brassica. NSES: Life Science ALCOS: Standard 7.) Describe the life cycle of plants, including seed, seed germination, growth, and reproduction. •Describing the role of plants in a food chain •Identifying plant and animal cells •Describing how plants occupy space and use light, nutrients, water, and air •Classifying plants according to their features Examples: evergreen or deciduous; flowering or nonflowering •Identifying helpful and harmful effects of plants Examples: -helpful: provide food, control erosion -harmful: cause allergic reactions, produce poisons •Identifying how bees pollinate flowers •Identifying photosynthesis as the method used by plants to produce food Prerequisite Skills/Concepts: •Students should accept all ideas nonjudgmentally. •Students should state their ideas in a positive way. •Students should consider others’ input when developing their own ideas. Objectives (action verb – Bloom’s) Assessment TSW draw and label the parts of a bee. Labeled diagrams (see attached) TSW write the steps in the pollination process. KWL chart (see attached) “You Better Bee-lieve It!” sheet (see attached) Procedures Engage (5-10 minutes) TTW say, “It finally feels and looks like spring! Raise your hand if you have noticed anything changing outside.” TSW respond. Possible responses: warmer weather, flowers in bloom, allergies*, bugs* TTW say, “I agree! I have lots of flowers around my house starting to bloom, and for some reason, I have noticed that bees are everywhere too! Raise your hand if you have seen more bees outside.” TSW respond and TTW ask TS where they noticed the bees. (TTW emphasize that the bees are often found near flowers or other bright plants.) TTW say, “I have also noticed that my allergies are getting bad. I, like lots of other people, am allergic to pollen. Raise your hand if you are allergic or if you have heard someone talk about pollen.” TSW respond. TTW explain, “Pollen is the yellow powder-like “stuff” that floats in the air and gets on cars and is washed up on the side of the road when it rains. It’s no coincidence that bees and pollen come out during the same time in spring. We’ll talk more about that in a little bit.” Materials & Resources “It’s Spring” Powerpoint slide “Pollen” Powerpoint slide Explore TTW say, “Bees are such an important part of the spring season, so we are going to find out what we already know about bees.” TTW say, “Turn and talk with your partner and come up with three things you know about bees. You may write your answers on your desk with your Expo.” TSW have three minutes to turn and talk. TTW say, “I am going to go around the room and ask partner 2 what you both know. If your answers are already on the chart, just say “pass”.” TTW write the students’ responses on the KWL chart beneath the ‘K’ column. TTW say, “You guys already know a lot about bees! Now, raise your hand and tell me what you want to learn about bees.” “Turn and Talk” Powerpoint slide Expo markers (each student has one in their desk at all times.) KWL chart KWL chart TSW respond. TTW write the students’ responses on the KWL chart beneath the ‘W’ column. 25 sheets of white copy paper Crayons and pencils (the students have their own in their desks) TTW say, “Those are great questions! Now, I need my two weekly helpers to pass out a piece of white paper to each student.” “Draw It!” Powerpoint slide As the helpers are distributing papers, TTW turn to the “Draw It!” slide. Extra crayons and pencils TTW say, “Please quietly and quickly get out your crayons and a pencil from your desk. Once you are seated and quiet, I will know you’re ready to do the activity.” TSW have 1-2 minutes to get settled. TTW refer to the slide and say, “I need you to take 2 minutes and draw your best bee. None of us are expert artists, but try and include realistic details and do as well as you can.” TSW have ~2 minutes to draw what they think a real bee looks like. TTW walk around the room to observe student progress. TTW say, “These look awesome! I love how creative your bees are. Do three volunteers want to share their drawings on the ELMO?” TSW volunteer. *If there are no volunteers, TTW share a prepared drawing. TTW say, “As awesome as these are, I think it might be a good idea to see a realistic picture of a bee. (TTW display the picture on the ELMO.) Explain TTW refer to the “Bee Anatomy” slide and say, “Since bees are so small, it’s hard for us to see how they really look. Even though their small size makes them seem simple, they have several body “Draw It!” Powerpoint slide ELMO *Prepared bee drawing (see attached) Realistic bee picture (see attached) ELMO “Bee Anatomy” Powerpoint slide parts that help them survive and do their jobs, just like humans do.” TTW explain and define the following parts: -Bees and all other insects have three major parts: the head, the thorax, and the abdomen. Head- front Thorax- middle Abdomen- end (body systems inside, like a human abdomen) -Two antennae are top of the bee’s head. These help the bee communicate with other bees. -While a bee’s huge eyes cannot see as human eyes do, they can sense light and dark. The eyes are located on the head. how bees eat: Link on “Bee Anatomy” slide “Draw it Again!” Powerpoint slide -Instead of teeth, bees have long mandibles (jaws) which help them eat pollen and drink nectar. -The bee’s wings allow it to fly up to 15 mph from plant-to-plant and are attached at the thorax. -All bees (and other insects) have six legs which help them move and feel. The legs are also attached at the thorax. -The pollen sac is very important. It attaches on one of the bee’s back legs and falls when the be lands. -The stinger is located at the end of the abdomen. Female worker bees have stingers, but not all bees do. Stingers help protect bees from small enemies, but the stinger will come off and kill the bee if it stings a large predator. TTW turn to the “Draw it Again!” slide and ask the helpers to pass out white construction paper. (1/student) TTW say, “Now that we know the individual parts of the bee, let’s take five minutes to draw an accurate picture of a bee. Do your best, please!” TTW walk around the room and observe TS drawing. After about five minutes, TTW say, “These look like they could be in our textbook! Now that they are accurate, let’s label them with the body parts we learned about earlier.” TTW say, “I need everyone to please clear their desks of everything except your second drawing and a pencil. Once your eyes are up front, we can label the drawings together.” On the ELMO, TTW label the following parts on the “Bee Diagram” sheet: head, abdomen, thorax, antennae, eyes, mandible, legs, pollen basket, wings, and stinger. TSW label their drawings. TTW say, “Your diagrams are awesome! Please put those to the side, and let’s think back to when we said that bees are often found near flowers—especially during this season. Raise your hand if 25 sheets of white construction paper Crayons Pencils “Bee Diagram” sheet (see attached) you have a guess as to why that might be.” TSW respond. Best answer: Bees help the flowers bloom. Bees help us grow plants. TTW refer to the ‘Pollination Sensation’ slide and say, “Exactly! When a bee lands on a flower or plant to drink nectar (a sweet liquid), a pollen sac from the plant can get stuck on the bee’s back legs. When the bee lands on another plant, the pollen sac from the first plant falls off and fertilizes the second plant. This helps them bloom. That’s why there is so much pollen outside during this time of year. This video will show how bees get pollen on their feet.” “Pollination Sensation” Powerpoint slide Pollination: link on “Pollination Sensation” slide 25 copies of the “You Better Beelieve It!” sheet (see attached) TTW turn back to the “Pollination Sensation” slide and ask TS if they have any specific questions before the last activity. Evaluate TTW say, “Now, I need you to clear everything off of your desk except for your second bee diagram, and a pencil.” TTW distribute the “You Better Bee-lieve It!” worksheet. As TS complete the task above. TTW say, “Complete the front page of your worksheet independently. Once everyone is finished, we will do the bottom part together. You may use your diagram, but not your neighbor. There should be absolutely no talking. If you have a question, please raise your hand and Ms. Bailey or I will come to your desk. When you finish the front, turn your paper over and touch-up your second drawings. I’m going to come around and put an index card on your desk. Please do not touch it until I give you more directions.” TSW have 5-7 minutes to complete the front page of their worksheet. TTW give each student one blank index card as they are working. TTW say, “Raise your hand if you need one more minute.” TSW respond. Once TS finish, TTW use the ELMO to help the students with the back page. TTW say, “The directions tell us to list the steps of the pollination process. Raise your hand if you can tell me what happens first.” TTW use the students’ input to list the steps in the pollination process. Possible response: 1. Bee drinks nectar 2. Bee gets pollen on feet 3. Bee flies to 2nd plant 4. Bee drops pollen 5. Plant is fertilized *Extend TTW say, “Bees are pretty interesting for such little insects, aren’t they? Since you guys have been so fantastic during the lesson, I’m going to read you some crazy 25 blank index cards ELMO Copy of “You Better Bee-lieve It!” sheet “Fun Facts about Honey Bees” sheet (see attached) facts about honey bees that will shock and amaze your friends.” After reading from the “Fun Facts…” sheet, TTW ask TS to raise their hands if any of the facts were surprising to them. TTW show a YouTube video about the life cycle of a honey bee. Life Cycle of a Honey Bee: link on last slide Closure TTW refer to the KWL chart and say, “Raise your hand if you can tell me one thing you learned about bees.” TSW respond and TTW write responses under the “L” column. TTW say, “I am so impressed with how much you all know about bees! If you still have a question or want to learn something else about bees or pollination, write it on the index card on your desk. I will take them home to find some answers for you by the next time we meet. You do not have to write your name on it.” TTW say, “Please quietly turn in your worksheet and your index card (if you wrote a question) in the science folder and return to your desks.” Accommodations (e.g. alternate explanation of material, struggling readers, ESL, special needs, enrichment for gifted students) Gifted: Students who need more enrichment will be provided with a short creative writing assignment titled, “A World Without Bees”. (see attached) Modifications (IEP) N/A *Extensions (additional activity to reinforce lesson objective(s)) See above in 5E procedures. References Alabama Department of Education (2007). Alabama learning exchange 3rd grade courses of study for science. Retrieved March 11, 2013, from the ALEX website: http://alex.state.al.us/standardAll.php?grade=3&subject=S1&summary=2 National Science Education Standards (1996). Chapter 6: Science content standards. Retrieved March 17, 2013, from the NAP website: http://www.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=4962&page=103 http://www.fcps.edu/islandcreekes/ecology/honey_bee.htm http://www.utahcountybeekeepers.org/fun_facts.html KWL: Bees What I Already Know What I Want to Know What I Learned Name:_______________________________________ You Better Bee-lieve It! (front page) Directions: Circle ‘true’ if the sentence is correct or ‘false’ if it is wrong. 1. Bees have eight legs. True False 2. The bee’s wings are attached at the thorax. True False 3. Bees make pollen. True 4. Bees help fertilize plants. False True 5. Bees are not important to people. False True False Directions: Use the word bank to label the bee. Thorax Head Eyes Abdomen Wings Antennae Legs Pollen sac Mandable Stinger (draw it) You Better Bee-lieve It! (back page) ***We are going to do this side together!*** Pollination Steps: Name:__________________ Enrichment Write a creative, detailed paragraph describing what life would be like if bees did not exist. Be sure to include at least three facts to support your points. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________.