Theories of Cognitive Development
advertisement

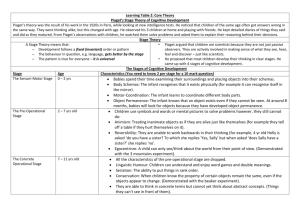
Learning Outcome: Evaluate theories of cognitive development (for example, Piaget and Vygotsky). Introducing Piaget Read the information on Piaget and answer the following questions (on a word document or in your green books): 1. Outline Piaget’s main assumptions about cognitive development. 2. Outline the role of schema’s in Piaget’s theory of cognitive development. 3. Describe the process of adaptation in relation to schemas. 4. Why is Piaget know as being “constructivist” in his approach? Summary of Piaget’s theory • http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/piagetstheory-of-cognitive-development.html#lesson Adaptation The process by which the child changes its mental models of the world to match more closely how the world actually is. Cognitive development As the child gets older its schemas become... More complex More numerous More abstract More interconnected Cognitive development The child’s understanding develops because... Its brain is developing (maturation) It is exploring the world around it (experience) Types of Adaptation 5. Using two examples, outline the process of Assimilation. 6. Using two examples, outline the process of Accommodation. Assimilation and Accommodation • http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/assimilation-andaccommodation.html#lesson Summary • Remember that Piaget’s assumptions are about child development in general. • His specific theory of cognitive development involves the use of schemas and the constructivist nature of learning. • Children are born with innate schemas to suck, reach and grip for example. • These schemas are are modified (constructed) as a result of experience in a process called adaptation. • Adaption involves Assimilation and Accommodation. • Assimilation-consolidation of existing knowledge • Accommodation-creation of new knowledge and the rejection or adaptation of existing schemas. Assimilate Equilibrium Adaptation of schemas Accommodate Disequilibrium Piaget proposed four stages each child moves through in sequential order during cognitive development. • The sensorimotor stage • The pre-operational stage • The concrete operational stage • The formal operational stage Task • In three’s outline two of Piaget’s stages and evaluate research that provides evidence for these theories. Present this to the rest of the class. Operations • As well as knowledge of things we will encounter in the world, we also need to understand the rules by which the world operates. • Piaget called these rules operations. • Piaget suggested that the reason that children think in different ways at different stages of their development is because the operations of which we are capable change with age. • Piaget believed that while schemas develop with experience, operations develop as the child’s brain matures (biologically controlled). • Very young children do not have operations at all, and are said to be pre-operational. • The first operations that appear are concrete. This means that children understand the rules governing something as long as they can see it. • Later, rules governing abstract concepts are understood.