Understanding English Communications
advertisement

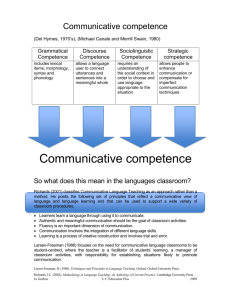
The world seldom notices who the teachers are, but civilization depended on what they do and what they say! English Language Institute/China Student Handbook Educator’s English ELIC Supplement Understanding English Communications Proverb Learning is an individual activity, but it is not a solitary one. Introduction Questions What is the goal of an English language teaching? What is communicative Teaching? What are some principles of good language teaching? Many times we get stuck in old ways or taught ways Page M8 Teaching English Communication Methods Communicative Competence is the goal of English language teaching Communicative Competence defined as: The ability to communicate successfully: It is achieved when “my thoughts becomes your thoughts” Page M9 Three Components of Communicative English 1. Linguistic Competence Relating to language or linguistics 2. Sociolinguistic Competence The study of language in relation to social factors 3. Strategic Competence Aim to achieve a specific purpose Page M9 Components of Communication Competence 1. Linguistic Competence, which includes use and understanding of… Page M9 Grammar Vocabulary Functions Pronunciation English Communication 2. Sociolinguistic Competence, which includes the understanding of …… A. Appropriate and inappropriate topics B. Polite and impolite topics C. Directness and indirectness Page M9 English Communication 3. Strategic competence, which includes the use of techniques to fill in linguistic gaps and weaknesses Page M9 Teachers Open Discussion of Teaching Learning Styles What What What What What What is the best way to teach? works for me? does the students respond to? are our weakness in teaching? are our strengths? works for you? If you're never willing to try and afraid of making mistakes you will never succeed or be proficient in English ! We learn from our mistakes!!!! Why Cooperative Learning Works 10% 20% 50% 70% OF WHAT OF WHAT OF WHAT OF WHAT OTHERS 80% OF WHAT 90% OF WHAT ELSE WE READ WE HEAR WE BOTH HEAR AND SEE IS DISCUSSED WITH WE EXPERIENCE PERSONALLY WE TEACH TO SOMEONE Learning-centered Teaching Styles and Strategies The Principle of learned-centered teaching Learning styles How to apply an understanding of learned styles to teaching Strategies How to teach strategies Page M13 Questions to answer 1. WHEN YOU ARE LEARNING ABOUT A NEW TEACHING METHOD, WHAT MOST HELPS YOU UNDERSTAND IT? 1. 2. 3. Reading an article about it. Listening to an expert give a lecture about it. Pretend to be a student while an expert demonstrates it. Circle your Answers we will use them later Page M14 Slide 1-3 Questions to Answer 2. When you are learning how to play a sport or a game you have never played before, what most helps you to understand how to play? 1. Watching other people play it. 2. Asking a friend to explain I to you. 3. Playing it. Slide 2-3 Circle your Answers Questions to Answer 3. When you are learning a new word, what helps you remember it? 1. Writing it down. 2. Hearing it used. 3. Trying to use it in conservation Slide 3-3 Circle your Answers Learner-centered Teaching Styles and Strategies When you are in a situation where you cannot learn in the way that you like to learn, what do you do? For example, if you like to learn a sports by playing it, what do you do when you cannot play the sport as you learn? How do you compensate? How do we compensate in our class rooms? Page M15 Terms to know Learning Style: The way a person learns best which can be visual, auditory, kinesthetic, or a combination of these. Learning Strategy: A technique or way to compensate for a learning weakness or gap Page M15 1-3 slides Terms to Know Visual: (learner) One who likes to learn by reading, seeing or watching with his own eyes. Auditory: (learner) One who likes to learn by listening, by having things explained 2-3 Slides Terms to know Kinesthetic: kin/es/thetic (learner) One who likes to learn by doing and touching or practice 3-3 Slides Learner–centered Teaching Styles and Strategies What is the principle of learnercentered Teaching? • They get students involved in speaking and focuses on the student’s needs-how they learn what they need to know. Page M16 Learner-center Making teaching learner-centered 1. Learning Styles: way in which students learn best. 2. Learning Strategies: techniques which students can use to help them when they have a problem learning or understanding. Page M16 1-2 Learner-centered 3. The difference between a learning style and a learning strategy: A. A style is the way a student usually learns best. B. Strategy is the technique (s) that a student uses to get around a difficulty in learning. 2-2 Learner-centered Learning styles and strategies should affect teaching. 1. Teachers can change teaching styles to match student’s learning styles. 2. Teachers can change students teaching strategies which help students figure out other ways of learning. Page M17 Learning Styles Auditory “Hearing” – Listening to lectures or an explanation about how to do something. Visual “Seeing” - Reading an explanation or watching someone do something. Kinesthetic “Touching” – Doing, practicing, using hands and body to experience. Page M17 Learning Strategies Strategies for comprehending written or spoken language: 1. The framework strategy is the technique of focusing on main ideas and how the main ideas are organized. This is done before trying to understand the details. Page M17 1-4 Learning Strategies 2. The guessing-meaning strategy is figuring out what a word means by looking at clues in the word itself, or by looking at the context in which the word is used. 2-4 Learning Strategies 3. The background-Knowledge strategy is used when knowledge or experiences of the past are compared with the new information. Relating new information to past experiences makes the new information easier to understand. 3-4 Learning Strategies 4. The predicting strategy is used to guess the subject of the current passage or topic by reading the title of the previous passage or topic. 4-4 Learning Strategies Steps for teaching strategies to students. 1. Select a strategy that is useful 2. Relate it to the material being studied. 3. Explain the strategy to the students. 4. Guide students in using the strategy. 5. Evaluate how it worked or didn’t work and why. 6. Practice using the strategy with new material. 7. Apply the strategy to new situations. M17 You cannot teach learning styles But you can teach learning strategies Contextualized (Construction of text) 1. The Meaningful Learning Principle 2. Contextualized learning 3. How to contextualize learning Page M23 Terms to Know Contextualized Learning: Learning that is centered around a context by topic that is familiar. Filing Cabinet: A cabinet or box for keeping papers organized by topic through the use of files. Popcorn style: Refers to the hap-hazard, random, unconnected way of teaching. Activate: To cause a response or make possible a reaction. Page M24 Contextualized Learning A. Contextualized learning mean that language exercises are centered around a context or around one topic. Page M25 1-4 Contextualized Learning B. The importance ! 1. It makes learning easier. 2. It makes language practice more natural. 3. It gives learners a reason to practice. 4. It makes learning more interesting. 2-4 Contextualized Learning Guidelines for contextualized learning: 1. Select appropriate context A. Students know something about the subject. B. Students are interested in the subject. C. Students can relate it with the language learned. 3-4 Contextualized Learning Use the contexts Connect everything in the exercise or in the whole lesson, if possible, to the topic. Activate the students’ background knowledge first! 4-4 Interactive Learning We will learn The Communication Principle Interactive learning How to encourage interactive learning in the classroom Page M31 Questions Communication Principle: One must not only learn about language, but he must also practice using the language. In large classrooms, you can use pair, small group, or whole class activities. Which type of activity do you think most helps your students to learn? Why? What are some of the different kinds of questions that you ask in the classes you teach? Try to give some specific examples. Page M32 Terms to Know Real World communication: using language in ways that native speakers would use it in actual situations. Interaction: action in which there is a continual exchange of information. Interactive Learning: learning that requires listening and understanding as well as speaking and making oneself understood as in real world situation. Factual: what is real, actual or undisputed. Page M32 Interactive Learning A. Interactive learning brings real world communications into the classroom. B. Apply interactive learning to any situation. 1. It can be used in any class and in any lesson: Grammar, vocabulary, listening, reading, writing, and speaking 2. By grouping students in pairs or groups of four, each person has more time and opportunities to interact with classmates. Page M33 Interactive Learning Use Type 1 and Type 2 questions to encourage interactive learning. Type 1: Ask for fractional information - require only one short answer Type 2: Ask for opinions – requires longer answer Note: Ask Type 1 questions for understanding, and Type 2 for real – world interaction Page M33 See Examples Next Slide Examples Type 1 – What is the name of the Chinese teacher that lives with the Martin’s? Type 2 Do you think you would like this teacher? Why or Why not? Page M35 Interactive Exercise Now think about the questions from a teacher’s perspective. What is the difference between the questions in the first column, Type 1, and those in the second column, Type 2? Page M35 Interactive Learning Get everyone involved 1. Every student must think of an answer. 2. Every student must write down his/her answer. 3. Students pair up, share their answers, and determine which is the better answer. 4. Two sets of pairs then share their answers and determine which is the best and/or most correct. This answer is then shared with the entire class. M38 Principled language Teaching • • • • You will learn The Communication Principle Task-based learning Communicative task How to create a communicative task. THINK WRITE PAIR SHARE Involve everyone there! The Communication Principle: Use it or Loose it. M38 Task-based Learning We will learn about The Communication Principle Task-based learning Communicative tasks How to create communicative task M41 Task-based Terms to Know Negotiation: The process of getting past an obstacle or of reaching an agreement. Negotiation of meaning: Learners with different opinions and/or information discuss together until a common understanding or solution is reached. M42 1-2 Gap: A hole, an empty space. Information gap: Incomplete knowledge. Opinion gap: A conclusion which is open to dispute because it is based on incomplete information. 2-2 Introduction The communication Principle is that every student must practice using language through Interactive Learning and Taskbased Learning. Interactive Learning is giving students time and opportunities to use-real-world communications in the classroom, especially by using Type 2 questions M43 Interactive Learning Task Based Requires task. interaction and communicative 1. Interaction is the negotiating of meaning with other people in order to fill in the knowledge and language skills which are lacking. 2. Communicative task are task or activities that require communication between students in order to complete something. (We will see an example shortly) M43 Characteristics Meaningful Context Pairs or Groups A Real Purpose Must Interact and Negotiate Choices in their responses Examples M43 M44-M45 Example Interactive Exercise Arrange yourselves in order according to the Months date of your birth. “Speak English Only” M46 I hear and I forget I see and I remember I do and I understand M47 Open Forum Please share some class strengths and weaknesses where you teach. To over come our weaknesses we must first find them, acknowledge them, and them pursue change. Proverb Education is a Team effort. Multiply your results by working together! If you dare to teach, then you must dare to learn! Principled language Teaching Microteaching We will learn Making your teaching reflective Preparing your Microteaching Evaluating other Microteachings M49 Terms To Know Reflective: Deep, thoughtful, philosophical, insightful. Reflective teaching: Teachers should reflect on what , when and why of their teaching activities. Microteaching: An activity based on Chinese middle school textbook used in middle school classes. It should follow the principles of good language teaching discussed in the methodology presentation and be based on a speaking or listening activity. M50 Introduction What is the Principle of Reflective Teaching? Teachers should reflect on the what, when, and why of their teaching activities through observing themselves and other teachers. Always think, “Why do I do it this way? Why does she do it that way?” M51 Proverb The Mediocre teacher tells. The Good teacher explains. The Superior teacher demonstrates. The Great teacher inspires. COMPLETE