17.1 w.s.
advertisement

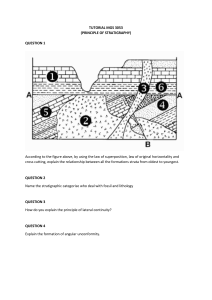
Name ________________________________________ Date ______________ Class section _______ Chapter 17: The Rock Record Earth Science 12 pts Section 17.1: Determining Relative Age (p. 323-326) Multiple choice: Choose the one best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. _____ 1. The concept that the present is the key to the past is part of the ___. a. type of unconformity c. law of crosscutting relationships b. law of superposition d. principle of uniformitarianism _____ 2. Sedimentary rocks are generally laid down in nearly horizontal layers called ___. a. strata b. striations c. foliates d. sheets _____ 3. Which of the following would most likely be used to determine the relative age of undisturbed sedimentary strata? a. principle of uniformitarianism c. a bedding plane b. law of superposition d. law of crosscutting relationships _____ 4. A gap in the sequence of rock layers is called a(n) ___. a. bedding plane b. varve c. unconformity d. uniformity 5. Determine the age of each of the layers in the diagram to the right. On the lines provided, write the letters, in order, from oldest to youngest. ___C__ _____ _____ _____ __A__ oldest youngest 6. Identify the layer labeled “D” in the diagram. ______________________________________ Short answer: Answer each question below using complete sentence(s). (2 pts each) 1. _____________________________ indicates that one layer is older or younger than another layer, but not the exact age of the rock. 2. How can the law of superposition be used to determine the relative age of sedimentary rock? Write in complete sentences! ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________