6th Math LF Sept 15
advertisement

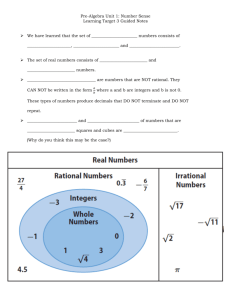
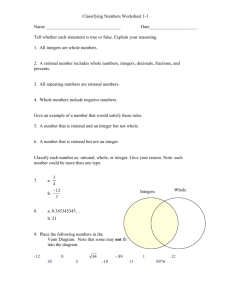
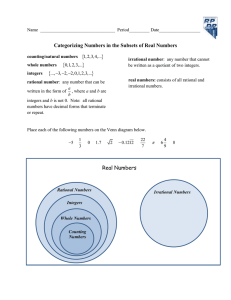
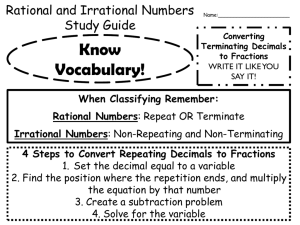
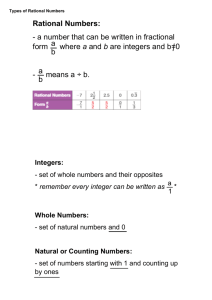
FRAME THE LESSON Student Expectations Bundled in Lesson Noun=Underline Verb=Italicize Readiness TEKS: 6.2(D)- Order a set of rational numbers arising from mathematical and real-world contexts 6.4(G)- Generate equivalent forms of fractions, decimals, and percent using real-world problems, including problems that involve money Supporting TEKS: 6.2(A)- Classify whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers using a visual representation such as a Venn diagram to describe relationships 6.2(C)- Locate, compare, and order integers and rational numbers using a number line Process TEKS: 6.1A, 6.1B, 6.1C, 6.1D, 6.1E, 6.1F, 6.1G TEACHER: CLASS: 6th Math LESSON DATE: September 15 Unit 2: Ordering Fractions, Decimals, and Integers M T W TH F 1st 6 Week Period Engage: Spiral Review #15 In Go Math: Teacher Edition use “Questioning Strategies” and “Avoiding Common Errors” to create a class discussion and encourage academic vocabulary as well as higher level questioning. The strategies are on page 9 for Lesson 1.1 in your TE (Teacher Edition). Engage: Explore: Explain: Elaborate: Explore/Evaluate: Utilize 1.1 Independent Practice to create a game. o Create a flash card set from the questions and have students work on whiteboards with expo markers to race as they flip over the problems. I generally give the first person done, four points, the second person done three points, the third person done two points, and the remaining players one point when they finish. They may show their work in their workbooks if it is easier. o You could also have students take turns racing for their team on the big whiteboard. If you do this, I would also have students seated solve it to win points for their team for a “Sit Down Challenge.” Week 4 Resources/ Materials: Flash Cards Whiteboards Expo Markers Evaluate: ELPS: c.1.D, c.2.D, c.3.D Critical Writing Prompt: Stop & Check for Understanding—High Level Questions Objective/Key Understanding: The student will apply mathematical process standards to develop an understanding of proportional relationships in problem solving. The student will apply mathematical process standards to solve problems involving proportional relationships. The students will work in collaborative groups to build math skills. Closing Product/ Question/ Informal Assessment: Visual representations can be used to represent relationships between sets and subsets of numbers. How are counting (natural) numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers related? What types of visual representations can be used to represent the relationships between sets and subsets of numbers? Numbers can be ordered based on their numerical value (positive and negative rational numbers). How is place value used to order a set of numbers? How are quantifying descriptors used to determine the order of a set of numbers? (e.g., How do the quantifying descriptors such as ascending order, least to greatest, fastest to slowest, shortest to longest, etc. determine the order of a set of numbers?) Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems: How can an equivalent decimal be generated given a fraction or percent? How can an equivalent percent be generated given a decimal or fraction? What relationships exist between equivalent fractions, decimals, and percent? Rigor & Relevance (Real World Connection) Numbers are used in everyday life. How can an equivalent fraction be generated when given a decimal or percent? What are numbers and how are numbers used in everyday life? How and why do different situations or labels affect the relative size (magnitude) of the number? Beginning on February 10, 2011, the average temperature in Nowata, Oklahoma was -31°F. For seven consecutive days, the average temperature was recorded in the table below. Vocabulary: Counting (natural) numbers Place value Rational numbers Integers Positive rational numbers, Whole numbers Order numbers a) Create a visual representation, such as a Venn diagram, to organize and display the relationships between the sets and subsets of numbers: