Measuring Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) in ICU
advertisement

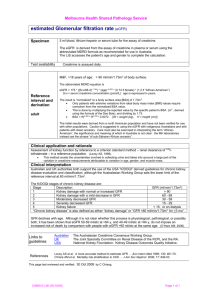
Measuring Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) in ICU Daljit K Hothi Great Ormond Street Hospital, London What is GFR? ▪ GFR is the volume of fluid filtered from the glomerular capillaries into the Bowman’s capsule per unit time ….the cumulative performance of all functioning nephrons ….the most reliable marker of functioning renal mass ▪ GFR influenced by age, sex, BSA ▪ GFR also varies by a number of other variables ▪ time of day, protein intake, pregnancy, extracellular fluid status, blood pressure extremes, use of anti-hypertensives Why is Assessment of GFR Important? Diagnosis ▪ Detection of Acute kidney Injury ▪ Change in level of GFR: improvement and deterioration ▪ Challenging ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ in extremes of body size In neonates severe malnutrition (cirrhosis) high or low creatinine intake grossly abnormal muscles mass Definition and Staging of Acute Kidney Disease AKI Classification ▪ AKI staged by cause and severity of abnormal kidney measures. Example: Pediatric modified RIFLE AKI classification system (pRIFLE) URINE OUTPUT? ▪ No benefit using 1-h vs 6-h urine output in diagnosing AKI ▪ 32% increase in the incidence of AKI with urine output criterion [Macedo et al. 2011] Why is Assessment of GFR Important? Prognosis ▪ Critically ill children with pRIFLE I or pRIFLE F (>50% decrease in est Crt clearance) at increased risk of persistent AKI of >48 hours and exhibit higher mortality rates ▪ Percentage fluid overload at the time of RRT initiation in children with AKI is independently associated with mortality Why is Assessment of GFR Important? Guiding Therapy ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Dosing and monitoring for medication Determining safety of diagnostic tests/procedures Referral to nephrologists Placement of dialysis access GFR ▪ GFR cannot be measured directly. ▪ Most common method is based on the concept of clearance ▪ The renal clearance of substance x (Cx) is calculated as: CX = UXV/PX V is the urine flow rate (ml/min) UX is urine concentration of substance x PX is the plasma concentration of substance x ▪ If the substance is freely permeable across the glomerular capillary and is not synthesized, transported, or metabolized by the kidney, CX is equal to GFR Children –Specific Considerations ▪ Significant developmental changes influence measurement of GFR ▪ All nephrons are terminally differentiated at birth, only the juxtamedullary glomeruli are used at birth. ▪ Continuous recruitment of additional glomeruli until 18–24 months of age ▪ Growth spurts [1st year of life & puberty] and rapid increase of muscle mass have significant impact on measuring GFR ▪ GFR by renal clearance: practically challenging in children not toilet trained or incomplete bladder emptying Measured GFR ▪ Clearance measured with plasma or urinary methods record renal clearance of endogenous or exogenous substances ▪ Ideal substance: freely filtered at the glomeruli, neither secreted reabsorbed by the renal tubules ▪ Renal clearance of inulin is the gold standard in children and adults ▪ Inulin is not protein bound, freely filtered by the glomerulus and not secreted, metabolized, or reabsorbed by the renal tubules ▪ However need for continuous infusion, multiple blood and urine samples makes it difficult, time consuming ▪ Alternatives exogenous markers: 51Cr EDTA, 99mTc-DTPA radioisotopes, iohexol ▪ In children owing to expense, time, requirement for multiple blood samples mGFR only reserved for situations where accuracy essential Estimated GFR ▪ Estimates GFR without need for urine collection ▪ Uses endogenous markers ▪ The National Kidney Foundation guidelines recommend the use of serum marker-based prediction equations for eGFR as opposed to serum markers alone eGFR Creatinine • Derived from creatine and phosphocreatine in muscle • Freely filtered, not reabsorbed or metabolised but significant proximal tubular secretion which increases with lower GFR – Proximal tubular creatinine secretion equates to 10–20% of the excreted load – Can reach up to 50% when GFR is reduced, resulting in overestimation of GFR • Age and muscle mass dependency of serum creatinine creates difficulties measuring GFR challenges in children with co-morbidities: – spina bifida – neuromuscular disease – anorexia nervosa – liver cirrhosis eGFR Creatinine in PICU CHALLENGES…. • Positive fluid balance and volume of distribution dilutes sCr concentrations and delays diagnosis • Rapidly fluctuating renal hemodynamics • Plasma creatinine is not in a steady state • Inhibition of secretion by the renal tubule – For example trimethoprim • Interference with extrarenal elimination by gut bacteria – Broad spectrum antibiotics • Errors common with standardized assays due to interference from substances such as ketones Creatinine Based Prediction Equations ▪ In children Schwartz formula most commonly used clinically ▪ eGFR = k x L/Scr L is height in cms Scr is serum creatinine in mg/dl k is an empirical constant ▪ Cockroft-Gault equation gives an appropriate estimate of creatinine clearance in children >12 yrs of age ▪ Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula used in adults. More accurate than Cockroft-Gault equation but grossly inaccurate in children and underestimates GFR …..resulting in false positive diagnosis of CKD ▪ The CKD-Epidemiology Collaboration equation performs better than MDRD especially at GFR above 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 eGFR Cystatin C • A non-glycosylated protein produced by all nucleated cells • Cystatin C freely filtered, reabsorbed and completely metabolized in tubular cells • However cystatin C is catabolized and almost completely reabsorbed by renal proximal tubular cells, it cannot be used to measure GFR, only offers estimation of GFR • More stable rate of production & less influenced by race and ethnicity than eGFRcr • Serum cystatin C levels are also influenced by non GFR determinants – uncontrolled thyroid disease, corticosteroid use, age, sex, adipose tissue • Meta-analysis of 46 studies, in adults & children: the reciprocal value of CysC closely related to GFR with higher area under the curve (0.93 vs 0.84) Dharnidharka VR 2002 Levey et al. Jama 2015 eGFR in Children CKiD Study ▪ eGFR using demographic variables and endogenous biochemical markers of renal function including creatinine, cystatin C, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) eGFR = 39.1 x [height (m2)/Scr(mg/dl)]0.516 x [1.8/cystatin C (mg/L)]0.294 x [30/BUN (mg/dl)]0.169 x [1.099male] x [height (m)/1.4]0.188 ▪ This equation shows the highest accuracy and correlation and the narrowest 95% limits of agreement with measured GFR ▪ More precise eGFR with combined cystatin C and creatinine demographic-based formulas Schwartz et al C JASN 2009 In AKI….. • eGFRcr can be improved by incorporating data on creatinine generation and fluid balance • In adults the Jelliffe's equation accounts for fluctuations in serum creatinine over time in AKI • Modified Jelliffe's equation also takes into account the variations in fluid balance In AKI….. • Cystatin C has 1/3 the volume of distribution of creatinine & reaches a new steady state 3 x faster than creatinine • An increase in plasma cystatin C precedes plasma creatinine • Subtle decrements in GFR are more readily detected by changes in serum cystatin C than by serum creatinine partly due to the shorter half-life of cystatin C. • The affect of acute illnesses on cystatin C production rate in unknown • Although a standardized reference material is now available, considerable variation remains among cystatin C assays • More costly than serum creatinine measurements Alternative Markers • Several biomarkers proposed • Still experimental Aminoglycoside Clearance • Aminoglycosides clearance can provide an estimation of renal function • In ICU gentamycin and tobramycin clearance was compared with standard MDRD and CG formulae along with serum cystatin C • Gentamycin clearance performed the best, being within 10% of the value on 44% of occasions and within 20% on 78% of occasions. • Gentamycin clearance better estimate of creatinine clearance than the 24-h urine estimate [TE Jones et al. 2009] MicroRNAs • In humans 700 -1000 miRNAs estimated • Implicated in several physiological events as well pathologic processes • Most studies have measured miRNA in tissue, therefore cumbersome to measure in clinical practice Magnetic resonance imaging • Measure GFR through dynamic imaging of uptake of contrast agent using a two-compartment model • Gadolinium based exogenous filtration markers • Quick….direct measurement of GFR 4 min following injection of gadolinium • Risk of systemic nephrogenic fibrosis in renal impairment Ratiometric Approach • Use two-photon microscopy to monitor the ratio in renal capillaries of a filterable and a nonfilterable fluorescent marker following simultaneous intravenous injection of both [Yu et al.] • This technique is promising for use in critically ill patients with varying GFR, but validation required Renal Angina… Alternative Approach: Goldstein et al • Proactive approach versus reaction • Predict AKI prior to its development • Allowing for earlier intervention Step 1: Identify Children at risk of AKI Epidemiology of AKI in children has changed from primary kidney disease to diseases in which the kidneys are affected as a result of another systemic disease or its treatment Step 2: Renal Angina Syndrome • In AKI no characteristic syndrome that prompts concern and investigation • Alerts….. – small changes in serum creatinine/estimated creatinine clearance – increasing degrees of fluid overload Conclusion • Several biomarkers to screen and diagnose kidney disease • Each has its limitations….all at best only provide an ESTIMATION • Most commonly use eGFRcrt • Cystatin C promising alternative but widespread use not yet recommended due to incomplete understanding of non-GFR factors affecting serum concentration, higher costs and incomplete standardization of assays • Practically eGFR show the direction and magnitude of kidney function changes and rarely inhibit clinical decision making • New biomarkers …but none validated to make clinical decisions • If accuracy required…need to measure clearance