CHAPTER 8- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CELL 1. All
advertisement

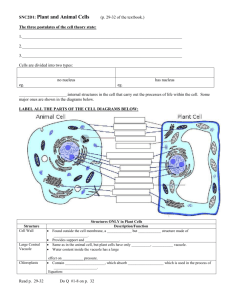
CHAPTER 8- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CELL 1. All plants and animals are made up of honeycomb like structure which are building blocks of life. 2. Cells are the structural and functional units of life. STRUCTURE OF A CELL 1. Cell is bounded by cell membrane 2. Inside the cell, jelly like mass is known as cytoplasm. 3. Each cell contains darkly stained nucleus which is the brain of the cell and it contains nucleoplasm. LEVELS OF ORGANISATION 1. 2. 3. 4. The smallest particles on earth are the atoms. Atoms make up various molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc. These molecules combine together to form a cell. Some similar cells combine together to form tissues and performs a particular function. 5. Tissues combine to form an organ. 6. Organs with closely related functions combine to form organ system. 7. Many such organ systems form an organism. PARTS OF A CELL 1. Cell wall Structure: (i) it is a non-living , protective covering outside the plant cell only. (ii) it is rigid and permeable and allows liquids / gases to pass through it. (iii) it is made up of complex carbohydrate like cellulose. Occurance: In plant cells only. Functions: (i) Provides rigidity and strength to the cell. (ii) Provides protection and determines the shape of the cell. (iii) Permits the free passage of all substances through it. 2. Cell membrane Structure: (i) it is delicate , elastic and living. (ii) it is made up of lipids and proteins. Occurance: both plant and animal cells. Function: (i) regulates the entry and exit of some molecules in and out of the cell (semi-permeable). (ii) it gives mechanical support and acts as protective layer. CELL ORGANELLES Name Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure A system of tubes joining the nucleus to the inner side of the cell. Plastids These are of 3 types Plant cell only. 1. Chloroplast – contains Green leaves & green colour pigment stems chlorophyll. 2. Leucoplast – Contains colourless plastids. 3. Chromoplast – contains coloured (red, yellow) plastids. Mitochondria 1. Double walled living structure. 2. Inner membrane is thrown into folds. Ribiosomes Living single walled granular bodies. Golgi 1. Living bodies complex membrane bounded. 2. Consist of tubules and vesicles. Lysosomes Centrosomes Vacuole Occurrence Plant cell and animal cell Function Forms link between the cell and nuclear membrane. When ribosomes are attached to ER, it helps in protein synthesis. Helps in transport of substance within the cell. Site for photosynthesis. Manufacturers food and known as kitchen of the cells. Roots & underground modified stems. Fruits & flowers Stores food in the form of starch. Imparts colour to fruits & flowers Plant & animal cells. Site of respiration for energy currency of the cell. Known as power house of the cell. Helps in protein synthesis. Both plant & animal cell. In animal known as golgi apparatus and in plants known as dictyosomes. Animal cell only 1. Vesicles, triangular structure 2. Also known as suicidal bags as they contain digestive enzymes and can destroy itself. Star like structure Animal cell only containing two centrioles. Non living fluid filled Plant cell – about space containing cell sap. 50 to 90% of the cell space is occupied by vacuole. Secretion, storage and synthesis of enzymes and proteins. Help in destruction of foreign material. Helps in cell division Stores cell sap and preserve food. Animal cell – small and few in numbers.