Nerve Impulse Lab Simulations
advertisement

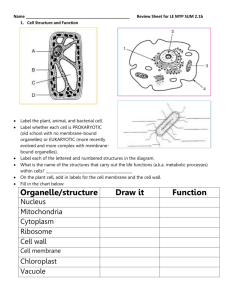
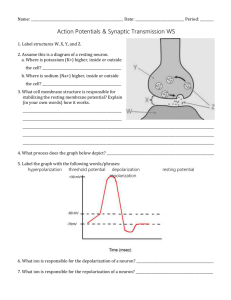
Name:___________________ Nerve Impulse Computer Simulation Directions: Go to http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/actionpotential_short.swf Watch the animation of action potentials in the nervous system for each of the categories listed below. Read the comments and answer the questions as you watch. You can pause the animation at the bottom of the right hand screen, if you need more time to answer the questions. Introduction: 1. Which type of neuron is sending the message to move the foot? _______________ (Hint: what is the signal causing?) 2. What are electrical message sent by neurons called? 3. What do Shwann cells do to help action potentials? 4. When can an action potential exist? _____________________ Draw what an action potential looks like across a membrane below. Indicate which area is + and which is Outside cell Inside cell 5. What happens during the propagation of an action potential? 6. What two ions are responsible for generating membrane action potentials in neurons? 7. When a neuron is resting (not signaling), how do ions move across the membrane? 8. How does the sodium potassium pump generate an action potential? What is pumped out of the cell, what is pumped into the cell? Where is there a greater + charge across the membrane? Resting Potential: 1. What are the charges inside and outside of the neuron membrane during resting potential? Draw this below. Outside cell Inside cell 2. The concentration of _______________ ions is higher outside the cell, creating a relative _______________ charge. Depolarization: 1. What is the first step of sending a nerve impulse? What happens? Draw an example below. Outside cell Inside cell 2. What channel closes to allow an increase in charge inside the neuron membrane. Explain how this makes the inside of the neuron more positive. 3. What is the charge of the neuron cell after depolarization? Repolarization: 1. What is repolarization? 2. How is this achieved? What happens to the ions? 3. What is the charge of the neuron after repolarization? Return to Resting Potential: 1. Which protein channel is responsible for restoring the original concentrations of sodium and potassium? Summary of Action Potential: Draw the membrane potential graph below. Identify and label the different action potential stages. Neuron Computer Simulation Directions: Go to http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations.htm Click on the “Synaptic Transmission” icon to start. Watch the animation and answer the following questions: Neuron Review: 1. Label and define structures of the neuron: 2. Define/explain the function of the following terms: a. Synapseb. Presynaptic neuronc. Postsynaptic neurond. Vesiclee. Neurotransmitterf. Synaptic cleftg. Receptor moleculesSynaptic Transmission: 1. Draw an arrow in the above neuron diagram to indicate the direction of nerve impulses through a neuron. 2. Describe the events that occur when an action potential reaches the axon terminal. 3. Skip the ‘Exercise’ and go to the next website. Effects of Drugs and Alcohol Computer Simulation Directions: Go to http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/synapse.swf Use the animation to determine the effects of drugs and disease on neural activity: o Alcohol- o Caffeine- o Nicotine- o Heroin- o Cocaine- o Depression- Brain Anatomy Computer Simulation Directions: Go to http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations.htm Click on the brain anatomy icon. Locate and label the appropriate structures on each of the diagrams Define the function/activities controlled by each brain structure: o Medulla oblongata o Pons o Midbrain o Hippocampus o Hypothalamus o Thalamus o Cerebrum o Occipital lobe o Parietal lobe o Temporal lobe o Frontal lobe o Primary somatosensory cortex o Primary motor cortex