The Body in Motion
advertisement

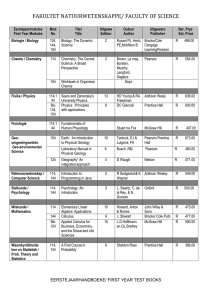
Biology, Seventh Edition Solomon • Berg • Martin Chapter 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Environmental challenges of living on land required evolution of adaptations • Anatomical • Physiological • Reproductive Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Examples of adaptations • Cuticle to prevent water loss • Stomata for photosynthesis • Alternation of generations –Gametophyte –Sporophyte Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Basic plant life cycle Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Generalized reproductive structures of algae and plants Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Alternation of generations, cont. • Gametophyte produces gametes by mitosis • Gametes fuse to form zygote • Zygote develops into embryo Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Alternation of generations, cont. • Mature sporophyte develops from embryo, producing sporogenous cells • Sporogenous cells undergo meiosis to form spores Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Examples of adaptations, cont. • Gametangia protect gametes –Antheridia –Archegonia • Xylem conducts water and sugar nutrients • Phloem conducts dissolved sugar Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Plant gametangia Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Plants are probably descended from charophytes • Both have similar biochemical characteristics –Same photosynthetic pigments –Same cell wall components –Same carbohydrate storage material –Similarities in fundamental processes Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Plant evolution Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Features distinguishing bryophytes from green algae and other plants • Bryophytes have cuticle, stomata, etc. • Bryophytes are non-vascular and do not have xylem or phloem • Bryophytes have a dominant gametophyte generation Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • The three phyla of bryophytes • Phylum Bryophyta (gametophytes grow from protonema) • Phylum Hepaticophyta (some have gametophytes that are thalli) • Phylum Anthocerotophyta (thalloid gametophytes) Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • The life cycle of mosses • Green moss gametophyte bears archegonia and/or antheridia • During fertilization, sperm cell fuses with egg cell in archegonium • Zygote develops into embryo • Embryo develops into moss sporophyte Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition Life cycle of mosses CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • The life cycle of mosses, cont. • Moss sporophyte is attached to gametophyte • Meiosis occurs in capsule of sporophyte to produce spores • When spore germinates, it germinates into a protonema that forms buds Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Life cycle of Marchantia polymorpha Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Features distinguishing ferns and other seedless vascular plants from algae and bryophytes • Ferns and fern allies have adaptations including –Vascular tissues –A dominant sporophyte generation Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Evolution of microphylls and megaphylls Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • The four phyla of seedless vascular plants • • • • Phylum Polypodiophyta Phylum Psilotophyta Phlylum Equisetophyta Phylum Lycophyta Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • The life cycle of ferns • Fern sporophytes have megaphylls • Their fronds bear sporangia in clusters (sori) • Meiosis in sporangia produces haploid spores • Prothalli develop from these and bear both archegonia and antheridia Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Life cycle of ferns Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Generalized life cycles of homosporous and heterosporous plants • Homospory –Bryophytes, whisk ferns, horsetails, most club mosses, and most ferns –Spores give rise to gametophyte plants producing both egg and sperm cells Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants • Generalized life cycles of homosporous and heterosporous plants, cont. • Heterospory –Some clubmosses, some ferns, and all seed plants –Microspores give rise to male gametophytes –Megaspores give rise to female gametophytes Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Basic life cycle of heterosporous plants Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning Biology, Seventh Edition CHAPTER 26 The Plant Kingdom: Seedless Plants Life cycle of Selaginella Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning