tutorial8
advertisement

תקשורת
באינטרנט
Tutorial 8
socket
Contents
Socket programming
What is a socket ?
Sockets architecture
Types of Sockets
The Socket system calls
Data Transfer
Service functions for sockets
programming
Examples for Client - Server
communication
STREAM Communication (TCP)
DATAGRAM Communication (UDP)
Port reservation
Example
2
What is a Socket ?
First appeared in 4.1 BSD UNIX
1982.
Sockets:
is an abstraction used as communication
endpoints.
is implemented as file descriptor with
some state information stored in the
socket library.
3
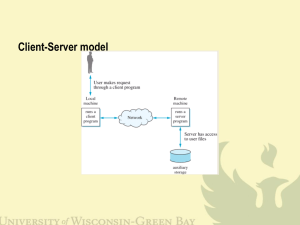
The Client Server model
request
port 2353
telnet
port 24
reply
client 2
ip = 132.68.44.79
port 20
ftp
port 3328
se rve r
ip = 132.68.8.1
client 1
ip = 132.68.44.73
4
Example:
UDP Echo
The simplest form of client-server interaction
uses unreliable datagram delivery to convey
messages from client to server and back.
Request sent to
a well-known port
client
server
Response sent to
the client’s port
• The program becomes a
UDP echo client when it allocates
an unused UDP protocol port
• Sends a UDP message to the
UDP echo server
• Waits for the replay
• Reserves the source and destination
addresses (IP addresses and ports)
• Waits for a datagram to arrive to
the echo port
• Returns the datagram to its original
sender
5
Example: UDP Echo (Cont.)
The example illustrates two important points
that are generally true about client-server
interaction:
The difference between the lifetime of
servers and clients.
The use of reserved and non-reserved port
identifiers.
6
Sockets architecture
Application
User
Socket API
Kernel
TCP/UDP layer
IP (network) layer
MAC layer
7
Type of Sockets
Socket has an associated type
that determine the semantic of
the communication :
SOCK_STREAM:
connection
oriented byte stream - TCP
SOCK_DGRAM: unreliable,
connectionless communication UDP
and more
8
Protocol family for
sockets functions
The family specifies the address
family: group of protocols with
the same address format
Example of address family
constants:
AF_INET
- IPv4 protocols
AF_INET6 - IPv6 protocols
AF_LOCAL (AF_UNIX) - Unix
domain protocols
9
Data Structures
struct sockaddr_in
{
short int sin_family; /* we use AF_INET */
unsigned short int sin_port; /* port number */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /* comp. address */
unsigned char sin_zero[8]; /* filled with 0s */
};
struct in_addr
{
u_long s_addr; /* unsigned long */
};
10
The Socket system calls
The Socket system calls:
int socket (int family, int type, int protocol)
allocate a socket
return: a socket descriptor or -1
family: communication domain
type: type of socket- SOCK_STREAM, SOCK_DGRAM,
SOCK_RAW
protocol: particular protocol to use - 0
int
bind (int sd, struct sockaddr *addr, size_t addrlen)
Bind a name to a socket
return: 0 on success or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
addr: pointer to the socket address
addrlen: socket address length
int connect (int sd, const struct sockaddr *addr,
size_t addrlen)
Try to connect to a socket (done by the client)
return: 0 on success or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
addr: pointer to the socket address
addrlen: socket address length
11
The Socket system
calls (cont)
int
listen (int sd, int backlog)
a queue for incoming connections is activated using
listen()
return: 0 on success or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
backlog : Maximum queue length of processes waiting for
connection
int accept (int sd, struct sockaddr *addr, size_t
*addrlen)
Wait for a connection request (done by the server)
return: new socket descriptor with the properties of sd
or -1 in case of failure
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
addr: pointer to the address of the connecting entity
addrlen: socket address length
int close (int sd)
Close the socket or the connection with the remote host.
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
12
Data Transfer - send
int
send (int sd, char *buf, int buf_len)
transmit a message to another socket. send() can be
used only when the socket is in a connected state.
return: the number of bytes that has been delivered or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
buf: the transmitted message
buf_len: the data length of buf
int
sendto (int sd, char *buf, int buf_len,
const struct sockaddr *to_addr, size_t to_len)
used to transmit data to remote host
return: the number of bytes that has been delivered or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
buf: a pointer to the data location
buf_len: the data length
to_addr: the socket address of the destination
to_len: the “to_addr” structure length
13
Data Transfer - receive
int
recv (int sd, char *buf, int buf_len)
Obtain data from the socket. Used only when the socket is
in a connected state.
return: the number of bytes at the obtain input or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
buf: the address of buffer holding the received data
buf_len: the buffer length
int recvfrom (int sd, char *buf, int bub_len, struct
sockaddr *from_addr, int from_len)
Obtain data from the socket.
return: the number of bytes at the obtain input or -1
sd: socket descriptor (from the socket() system call)
buf: the address of buffer holding the received data
buf_len: the buffer length
from_addr: the socket address of the transmitter
from_len: the “from_addr” structure length
14
Service functions for
sockets programming
Byte ordering
Deal with IP address
short htons(short) - convert 16-bit value from host to
network
long htonl(long) - convert 32-bit value from host to
network
short ntohs(short) - convert 16-bit value from network to
host
long ntohl(long) - convert 32-bit value from network to
host
ina.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("132.68.1.8")
returns the address in Network Byte Order already.
DNS
int gethostname(char* name, int namelen)
return local host name
struct hostent *gethostbyname(char* name)
use to get computer address by the name.
struct hostent *gethostbyaddr(char *addrp, int len, int
type)
15
Stream Sockets
TCP Client
TCP Server
sd = socket(…)
sd = socket(…)
bind(sd,port)
bind(sd,port)
listen(sd)
new_sd = accept(sd)
connect(sd,dest)
send(sd,…)
recv(new_sd,…)
recv(sd,…)
send(new_sd,…)
close(sd)
close(new_sd,...)
16
Datagram Sockets
UDP Client
sd = socket(…)
UDP Server
sd = socket(…)
bind(sd,port)
recvfrom(sd,…)
sendto(sd,…)
recvfrom(sd,…)
close(sd)
sendto(sd,…)
17
Port reservation
Ports 0 through 1023 are reserved.
Other ports are used by system for
assignment to clients.
18
Example (UDP Client)
// This program sends UDP packets to the given address
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define SERVER_ADDR "127.0.0.1"
#define SERVER_PORT 5555
void error(char *str)
{
printf("\n%s", str);
exit(0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char message[100], message2[10];
int sockfd, res;
struct sockaddr_in client_addr, server_addr;
int i, mesNum;
printf("\nClient is running...");
if (argc < 2)
error("\nYou should supply parameter: the number of
messages to send");
19
Example (UDP Client)
// Opening socket
if ((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0)) < 0)
error("Could not open socket");
// Sending a message to the server
bzero((char*) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(SERVER_ADDR);
server_addr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
mesNum = atoi(argv[1]);
if (mesNum == 0)
error("\nIllegal parameter");
for (i=0; i<mesNum; i++) {
strcpy(message, "Test message: ");
sprintf(message2, "%d", i+mesNum);
strcat(message, message2);
res = sendto(sockfd, message, strlen(message)+1, 0,
(struct sockaddr*)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
printf("\nClient sent %d bytes", res);
}
}
20
Example (UDP Server)
// This program receives UDP packets
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define SERVER_PORT 5555
#define MAX_MESSAGE_SIZE 100
void error(char *str)
{
printf("\n%s", str);
exit(0);
}
int main()
{
char message[MAX_MESSAGE_SIZE];
int sockfd, res;
struct sockaddr_in client_addr, server_addr;
int addr_len;
printf("\nServer is running..."); fflush(stdout);
21
Example (UDP Server)
// Opening socket
if ((sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0)) < 0)
error("Could not open socket");
// Bind local ip and process addresses
bzero((char*) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
server_addr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
if (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&server_addr,
sizeof(server_addr)) < 0)
error("Could not bind to the socket");
while (1) {
// Receiving a message from the client
addr_len = sizeof(client_addr);
res = recvfrom(sockfd, message, MAX_MESSAGE_SIZE,
0, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &addr_len);
printf("\nServer received %d bytes", res);
printf("\n%s", message); fflush(stdout);
}
}
22