American Imperialism
advertisement

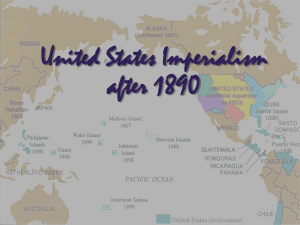
Use Chapters 5 and 7 of textbook to define these words Chapter 5 Chapter 7 Imperialism Militarism Yellow Journalism Nationalism Sphere of Influence Propaganda Open Door Policy Guerrilla Espionage Reparations American Imperialism Today’s Standards US.22 Assess the causes of American imperialism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including the desire for raw materials and new markets, yellow journalism, and the desire to spread American democratic and moral ideals. US. 24 Describe the consequences of American imperialism of the period, including the following events: (E, G, H, P) · annexation of Hawaii · Spanish-American War (Teller, Platt, and Foraker Acts) · Philippine Insurrection · Roosevelt Corollary · Panama Canal What is Imperialism? Stronger nations attempt to build on their empire by dominating weaker nations Believed that the more territory around the world you controlled the more secure your nation would be (military and economics) Causes of Imperialism General Causes 1.Need for Raw Materials, Extractive Economieseconomies that extract resources from other areas of the world 2.Need for new markets to sell your products 3.Missionaries- teach non-Europeans how to be civilized,(“White Man’s Burden”) Effects of Imperialism 1. New Markets (Economic Growth) 2. Stronger Military (Military Occupation) 3. Unpopular Abroad Assignment Make a multiflow cart showing the causes and effects of Imperialism America’s First Steps Towards World Power 1. Admiral Perry opens up Japan- sailed a fleet of warships into Tokyo Bay and convinced Japan to end its isolationism and sign trade agreement with America 2. Purchase of Alaska from Russia- purchased by Secretary of State William Seward for $7.2 million called “Seward’s Folly” and “Seward’s Icebox” but a few years later both gold and oil was discovered there 3. Annexation of Hawaii- American sugar and pineapple growers led by Samuel Dole overthrow the Hawaiian Queen Liliuokalani and had the US annex the island Today’s Standards US.22 Assess the causes of American imperialism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including the desire for raw materials and new markets, yellow journalism, and the desire to spread American democratic and moral ideals. US. 24 Describe the consequences of American imperialism of the period, including the following events: (E, G, H, P) · annexation of Hawaii · Spanish-American War (Teller, Platt, and Foraker Acts) · Philippine Insurrection · Roosevelt Corollary · Panama Canal Yellow Journalism Sensational news coverage by emphasizing crime and scandal Mostly used by William Randolph Hearst and Joseph Pulitzer Lead to an increase in newspaper sales Hearst decides US needs to be in a war so he can sell more newspapers Spanish America War Background • Who? •Spain vs. America Where? •Philippines, Cuba (Spain’s Colonies) 11 Background: USA Cuba The Philippines 12 Causes of Spanish American War 1. Cuban rebels start revolution against Spain for independence 2. Hearst and other yellow journalists spread stories about cruelty of Spanish soldiers 3. Hearst published supposed letter from Spain’s ambassador to US that called President McKinley weak and stupid 4. USS Maine Explosion “You furnish the pictures, I’ll furnish the war” William Randolph Hearst Assignment With a partner read the Who Sunk the Maine document. For each section answer the following questions 1. Who wrote or spoke the material? 2. What qualifications did that person have for making a judgment? 3. What information did the person have about the situation? 4. What stake might that person have in the outcome of the investigation? When you finish reading all of the sections answer this questions 1. Who or what do you think sank the Maine ? Why? Effects of Spanish American War Spanish American War ended in December 1898 with signing of Treaty of Paris 1. US becomes a world power 2. America gains all of Spain’s former colonies including The Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam 3. Cuba wins independence, Teller Amendment stated that U.S. could not annex Cuba 4. Platt Amendment- US gets control of Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, Cuba had to sign special trade deals with USA before troops would leave Review Questions Use your notes and Chapter 5 of your textbook to answer the following questions 1. What were two causes of American Imperialism? What were two effects of American Imperialism? 2. Define yellow journalism. 3. What were two causes of the Spanish American War? 4. What territories did America gain from Spain after the Spanish American War? Today’s Standards US. 24 Describe the consequences of American imperialism of the period, including the following events: (E, G, H, P) · annexation of Hawaii · Spanish-American War (Teller, Platt, and Foraker Acts) · Philippine Insurrection · Roosevelt Corollary · Panama Canal US and Latin American US after the Spanish American War looked to take a greater role of power in Central and South America Considered them part of our “Sphere of Influence” Roosevelt used “Big Stick Diplomacy” when dealing with Latin America Believed that America needed a large army to backup its demands of Latin America nations Panama Canal Roosevelt believed US needed a canal through the Isthmus of Panama to allow the US Navy to travel from one side of the country to the other quickly Columbia refused to allow the US to build a canal on their land Roosevelt backed a revolution that created the nation of Panama in return for the right to build the canal Panama Canal Took 35,000 workers 6 years to construct the canal 5,ooo workers died from diseases and construction accidents (especially Malaria) Cut the travel distance for a ship going from New York to San Francisco by 8,000 miles US gave control of the canal back to Panama on January 1, 2000 Assignment Get in your assigned group and complete the Cartoon Analysis Worksheet for your selected Imperialism Cartoon Your group will explain your cartoon and its meaning to the class The Great War (WWI) Today’s Standards US.26 Explain the causes of World War I in 1914 and the reasons for the initial declaration of United States’ neutrality. US.28 Identify and explain the impact of the following events and people during World War I: • Impact of trench warfare • Use of new weapons and technologies Causes of World War 1 1. Nationalism- extreme belief in the superiority of your country 2. Tension among ethnic groups in multicultural nations 3. Imperialism led to an Arms Race among European nations 4. Alliance linked nations and their defense together 5. Assassination of Austrian Archduke Francis Ferdinand and his wife by Serbian nationals led to a series of events that caused the alliances to take effect Assignment Make a bubble map showing the causes of WWI The Allies (Triple Entente) 1. Great Britain 2. France 3. Russia The Central Powers 1. Germany 2. Austria-Hungary 3. Ottoman Empire Introduction to Modern Warfare Both sides dug trenches and used them to stage their attacks New weapons (tanks, machine guns, chemical weapons) led to huge increase in the casualty totals in each battle Western Front- 450 miles of trenches between France, Belgium, and Germany (deadliest spot in the war) Trench Warfare Trench Warfare Trench Warfare Stalemate Trench warfare led to a stalemate (no advantage for either side) because the defensive weapons were better than the offensive weapons One side would gain a few feet of territory and than lose it a few days later Soldiers developed conditions like trench foot as a result of standing in muddy ground full of bacteria “No Man’s Land” area between the trench where most of the solders died when they had to “go over the top” (2 million died in first few months of the war) Trench Foot Assignment On the map handed out Use map on page195 to locate and label the following countries 1. Great Britain 2. France 3. Germany 4. Russia 5. Italy 6. Serbia 7. Austria-Hungry 8. Ottoman Empire Also label each country as either Allied or Central Power Today’s Standards US.26 Explain the causes of World War I in 1914 and the reasons for the initial declaration of United States’ neutrality. US.27 Justify with supporting detail from text, the reasons for American entry into World War I, including the use of unrestricted submarine warfare by the Germans, the Zimmerman Note, the defense of democracy, and economic motivations. US. 28 Identify and explain the impact of the following events and people during World War I: • Alvin C. York US.30 Analyze the political, economic, and social ramifications of World War I on the home front, including the role played by women and minorities, voluntary rationing, the Creel Committee, opposition by conscientious objectors, and the case of Schenck v. United States. Three Groups of American Opinion about the War 1. Isolationists- War was not America’s problem, and America should not become involved 2. Interventionists- War did affect the nation’s interests and America should join the Allies 3. Internationalists- “middle ground” US should help the Allies but not fight in the war US Pushed Towards War Several events led to US involvement in WW1 1. US Banks had loaned millions of dollars to the Allies 2. Unconditional Submarine warfare by Germany on US merchant ships 3. German U-boat sinks the passenger liner the Lusitania killing 128 Americans 4. British agents intercept the Zimmerman Telegram in which Germany asked Mexico to attack the US in return for their former land in the western US 5. USA declares war on Germany after the Zimmerman Telegram Assignment Put the following events in order using a flow map The United States Enter World War I World War I begins The assassination of Archduke Francis Ferdinand and his wife by Serbian rebels Germany sends Mexico the Zimmerman telegram The Sinking of the Lusitania by German U-boats Building an Army Selective Service Act- draft of young men for military service By end of war 24 million had registered and 2.8 had been drafted into service Many Americans resisted draft (12 percent of draftees refused to report for service) Conscientious Objectors- people whose religious or moral views do not allow them to fight in a war Schenck v. United States- Supreme Court case over the distribution of antidraft pamphlets, distributors charged under espionage act Court ruled that first amendment did not apply because the actions represented a crime and a “clear and present danger” to the nation Alvin C York From Pall Mall, TN Originally was a Conscientious Objector Won the Congressional Medal of Honor for his actions in the Battle of Argonne Forrest Along with 16 other Americans captured 32 German machine guns, killed 28 Germans, and captured 132 Germans Today’s Standards US.30 Analyze the political, economic, and social ramifications of World War I on the home front, including the role played by women and minorities, voluntary rationing, the Creel Committee, opposition by conscientious objectors, and the case of Schenck v. United States. US. 28 Identify and explain the impact of the following events and people during World War I: • Major turning points • Herbert Hoover • John J. Pershing and the American Expeditionary Force • Doughboys The Home Front The war had the following effects on the home front 1. War Industries Board- organized industries and farmers in the production and distribution of war supplies (ex. weapons and food) 2. Propaganda Posters used by government to encourage compliance with war effort and recruit volunteer soldiers (Creel Committee on Public Information) 3. Women replaced men in factories 4. Great Migration- African Americans moved from the south to the north to find work in factories (stayed in north after the war) 5. Rationing of goods at home like rubber and sugar 6. Selling of War Bonds to help pay for the war Today’s Standards US.29 Analyze the aims and negotiating roles of world leaders, including Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points, and the causes and effects of the United States’ rejection of the League of Nations on world politics. End of the War USA only engaged in major combat in the war for eight months (March 1918November 1918) War ended when the Germans surrendered on a railway car in Compiegne, France on November 11, 1918 Wilson’s 14 Points President Wilson wanted a Peace Treaty based on 14 key points some of the key ones were: 1. No secret alliances among nations 2. Absolute freedom of navigation upon the seas 3. The end of colonies around the world 4. Self-determination for all ethnic groups on what nation they should belong to 5. League of Nations to peacefully settle disputes and avoid future wars Treaty of Versailles 1.Germany had to pay reparations (money for losses during the war) to all allied nations 2.Creation of several new countries from land formerly held by Germany, Russia, AustriaHungary, and the Ottoman Empire 3.Allies only agreed to one of President Wilson’s suggestions (to create the League of Nations) Europe Before WW1 Europe After WWI America Rejects the League of Nations Isolationists led by Republicans led by Henry Cabot Lodge thought the League of Nations would entangle America in European problems and opposed the treaty (isolationists) America eventually signed a separate treaty with Germany and never joined the League of Nations (League of Nations weaken because of this)