inter american university of puerto rico
advertisement

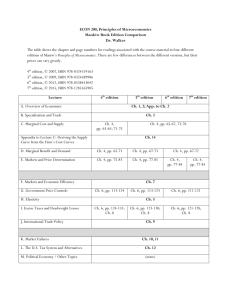
INTER AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO BAYAMON CAMPUS SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ENGR1100 – Introduction to Engineering Required Catalog Description: The history and development of engineering as a profession is explained. Social and professional responsibilities of an engineer and their function in society shall be discussed. Discussion of ethics and the study of real cases considered. Study of traditional and modern engineering tools shall take place. Career opportunities and options are explored as well as job placement strategies. Pre-requisite(s): First-year students Textbook: Wright, P. H., Introduction to Engineering, Third Edition, J. Wiley & Sons, NY, 2000. Suggested References: Eide, A.R., Jenison, R., Lane, M., and Larry L. N., Introduction to Engineering Design and Problem Solving, Second Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN 0072402210. Eide, A.R., Jenison, R., Lane, M., and Larry L. N., Introduction Fundamentals and Problem Solving, Forth Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2002. ISBN: 0072430273. Holtzapple and Reece, Foundations of Engineering, Second Edition. McGraw-Hill Inter, 2003. ISBN: 0072480823. Kemper and Sanders, Engineers and their Profession, Fifth Edition. Oxford Press, NY, 2001. ISBN: 0195105826. Course Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe the history and development of engineering as a profession Explain the engineering curriculum and know the facilities of the School of Engineering. Describe the different sub disciplines of engineering. Explain the current Code of Ethics ruling the practice of engineering, which will include discussing case studies 5. Apply the basics steps of the iterative engineering design process 6. Explain the tools used in engineering, including communication Topics Covered 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Lecture Topic* History of engineering Definition of Engineering The Engineer as a professional Creative, learning process & thinking Engineering approach on problem solving: steps Communication in engineering Calculations for engineering Computerized applications Case studies Projects *Schedule is subject to change Class-meeting Schedule: Three credit hours. Forty five-hour lecture per term. Hours 4.0 4.0 5.0 3.0 8.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 4.0 4.0 Evaluation Strategies Final grades shall be based on following distribution: Exams (Two partial exams) (40%) Homework & Quizzes and class attendance (20%) Projects In class (20%) Final Project (20%) Grading Policy Grades are reported according to the following standard grading system: A (90-100), B (80-89), C (70-79), D (60-69), F (0-59) Contribution of Course to Meeting Professional Component Three credit hours of engineering science and no credit hours of engineering design. Relationship of Course to Program Outcomes** a b c d e f g h i j k √ √ **The letter corresponds to the Program Outcomes of industrial engineering. Accommodations for Disabilities Students who require special services or assistance in carrying out academic duties must notify the Coordinator of Students with Disabilities at the Dean of Students Office at the beginning of the semester , or as soon as they become aware of their need(s). Academic fraud Dishonest conduct, fraud, plagiarism, or any other inadequate behavior regarding academic work are considered major infractions according to the Student Regulations Manual (Reglamento General de Estudiantes). Penalties for major infractions, according to the Manual, may include suspension from the University for set period of more than a year or permanent expulsion, among other disciplinary measures. Prepared by: Reinaldo Cintrón, PhD, PE Revised by: Heriberto Barriera, PhD Revised by: Catherine Aguilar, MEIE Date: 02/10/06 Date: 09/16/08 Date: 02/25/09