Page 29 – answers for #1-5, 8
advertisement

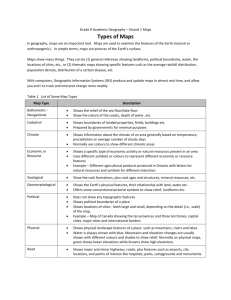
1. a) What is a map? Answers may vary, but should include the following concepts: Maps are a flat-surface representation of a part (or all) of Earth’s surface Maps use symbols (including colours) to show features on Earth’s surface b) Why are maps useful tools? Answers may vary, but should include: • Maps are useful tools for showing spatially related information c) How do maps help focus the reader’s attention on just a few specific things? …by presenting only a selected number of features that are found on Earth. (pages 22-25) Imago Mundi (c. 600 BCE) Babylonian map, the oldest known world map, 6th century BCE Hereford Mappa Mundi 1300 • Drawn on a single sheet of vellum • Measures 158 cm by 133 cm • The writing is in black ink, with additional red and gold, and blue or green for water (with the Red Sea coloured red) • Captions convey a mass of information on Biblical subjects and general history, in addition to geography http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hetq6CDfUUE&list=PLna7IMjegItQRjosiVkFrd5OJrZPfxIfU 2. What are general-purpose maps used for? GPMs show a wide variety of information: • They are designed to provide a broad understanding of an area • They are used for every day purposes (ex. finding the location of a park on a city map, planning a canoe trip in a large provincial park) 3. a) What is the purpose of thematic maps? TMs are used to display very specific information. Examples: • Maps that show the location of secondary schools in a district • Maps that show routes of school buses in a rural area b) Why are thematic maps useful? TMs are useful because: They are easy to understand Why are they easy to understand? …because there is a limited amount of information on the map c) Find 3 examples of thematic maps in your textbook • Page 147 (Figure 13-3) Air masses and ocean currents • Page 407 (Figure 30-3) Road and railway accessibility • Page 496 (Figure 37-8) Effects of global warming on vegetation regions 4. What is the purpose of a topographic map? Topographic maps are large-scale maps that show: • The natural and human features of a small area in detail 5. Construct a chart to compare large-scale and small-scale maps. Large-scale Maps Definition Typical Scales Purpose Small-scale Maps 5. Construct a chart to compare large-scale and small-scale maps. Large-scale Maps Small-scale Maps Definition Maps with a large amount of detail of a small area Maps that show less detail of a larger area Typical Scales 1: 50 000 or less Greater than 1:50 000 Purpose Residential planning, recreational activities, military purposes To show political, physical, and economic information 8.a) On a topographic map, what does the colour green indicate? (Fig. 2-6 – page 25) Green is used to show vegetation Forested areas are shaded green. Orchards are shown with a dense pattern of green dots. 8. b) In which direction does Indian Brook flow? It flows northward. There are clues on the map that tell you this: • Contour lines that the brook crosses get lower northward • Contour lines have V-shapes pointing southward (upstream) • Indian Brook drains into Georgian Bay (not the other way around) 8. c) What features are found at the following letters? A – Marshland B – Forested area C – Orchard D – Sewage treatment pond E – Marina F – Spot elevation along the highway 8. d) Is a legend necessary for a topographic map? An attempt has been made to make symbols understandable without reference to a legend on a topographic map. Some symbols are obvious: golf course / highway. BUT… Many symbols are not obvious and a legend must be consulted. To do now: #6-7 on page (homework check tomorrow) and… Review key terms for tomorrow’s Chapter quiz