What is Electrical Engineering
advertisement

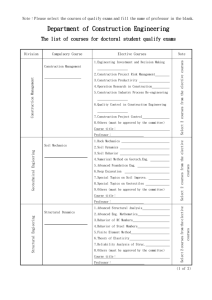
electrical and computer engineering electrical engineering Electrical Engineering involves the design of devices and systems that employ the flow of electrons to achieve useful purposes. It encompasses electrical power generation & distribution, electronics, wired & wireless communications, optoelectronics, signal processing, robotics, computers, radar, ultrasonics, and many other technologies. Electrical engineering includes two fields which are not present in the computer and biomedical programs—they are power generation and distribution, and electromagnetics. The power field deals with the design of high capacity power generation equipment in the most efficient manner possible. Power distribution deals with all the issues of monitoring, transmitting and protecting power from the generating station to the home. Electromagnetics is the study of electric and magnetic fields. Knowledge of this area is critical in the design of radios, TVs, cell phones, communications equipment, radar and many others. It deals with the transmission, amplification and processing of very high frequency signals (such as cell phone frequencies at 2.4 Ghz). The field of electromagnetics also deals with the design of antennas. Knowledge of electromagnetics allows a designer to make an antenna that will receive a much higher signal level with less interference. what's special about this program at mac? The department offers a personalized environment where students are able to meet one-on-one with their professors, many of whom are world-renowned leaders in their field. McMaster's facilities include specialized laboratories in a variety of specialized research fields. In addition, McMaster offers, programs in Engineering Management and Society, and offers the possibility of a 16-month internship in industry. Graduates are eligible to apply to an M.Eng. program that requires only one year of additional study beyond the Bachelor’s level. electrical engineering program In second year, EEs take an extra course in calculus. This is necessary background for an advanced electromagnetics course in third year. In third year, EEs take an extra course in electrical motors and generators, as well as an additional course in electromagnetics. The fourth year curriculum in EE consists almost entirely of technical elective courses. That means you get to choose the courses you want to take. This way, students specialize in areas they find most interesting. There is a wide variety of elective courses available. Basically, they include advanced courses in virtually all the topics covered in years II and III. The ECE program consists of the following topics (highlights indicate the program’s distinguishing courses): Circuits analysis Electronics Programming Digital logic Linear systems Applied math Electromagnetics Communications (radios, modems) Power conversion (motors, generators) Power systems Control theory what do graduates do? Electrical Engineering provides an extremely broad background which prepares students for a variety of opportunities in the workplace. Potential fields include: telecommunications design power systems electronics internet satellite communications marketing e-commerce in banking industry software systems automotive automation steel making aerospace manufacturing IC development http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 video and audio processing robotics radar power distribution power generation instrumentation food processing electrical and computer engineering ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING CURRICULUM LEVEL lI Circuits I Circuits II Programming I Electronics I Differential Equations Programming II Digital Logic Calculus Electromagnetics LEVEL III Motors and Generators Communications Systems I (Radios, etc.) Electronics II Linear Systems II (Control Theory) Probability Theory Numerical Methods Linear Systems I Electromagnetics II Microprocessors LEVEL IV 7 Technical Electives Capstone Design Project Complementary Studies http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering biomedical engineering Biomeds deal at the interface between electrical engineering and medicine. As such, they need a stronger background in the life sciences, namely biology, chemistry and anatomy and physiology. These are topics that the electricals and computers do not need. The BME program has several noteworthy features: Graduates have all the necessary background to apply immediately to medical school The program is fully PEO accredited (i.e., our graduates are eligible to apply for P.Eng (professional engineer) status as a biomedical engineer. (This is the first such program in Canada). Graduates are eligible to apply to an M.Eng. program that requires only one year of additional study beyond the Bachelor’s level. what's special about this program at mac? McMaster's new Electrical and Biomedical Engineering program is a unique four-year undergraduate program that combines a full Electrical Engineering degree with key courses in the Biological Sciences. By the end of the third year, students in the program will have completed all of the pre-medicine courses required by the MCA T and for entrance into Medicine at most Canadian and American medical schools. At the end of the fourth year, students may opt to continue for a fifth year and receive a Master's degree. The Biomedical program offers the possibility of a 16-month internship in industry. biomedical engineering program The biomedical program is heavier than either the computer or electrical engineering programs. They generally take one extra course per term. In the second year, the biomeds take an extra course in both biology and chemistry. In the third year, they take two additional courses in organic chemistry, one in biological materials, one in cellular bioelectricity, and two anatomy and physiology courses. In one of these anatomy courses, you will dissect a cadaver! In fourth year, you will take courses in biological systems, biomedical instrumentation, medical robotics (e.g. for telerobotic surgery) and medical imaging, using devices such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The Biomedical program consists of the following topics (highlights indicate the program’s distinguishing courses): Circuit analysis Electronics Programming Digital logic Linear systems Applied math Electromagnetics Communications Control theory Biology Cellular systems Chemistry and organic chemistry Medical imaging Biomedical instrumentation what do graduates do? Graduates from the program may choose to pursue careers as Electrical Engineers, or may choose to enter the field of Biomedical Engineering. Some graduates may also choose to apply for entrance to medical schools. Potential fields include: health and medicine straight electrical engineering robotics telemedicine instrumentation industrial: biosensors comp-assisted minimal access surgery telerobotic surgery imaging http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 computer tomography magnetic resonance imaging pharmaceuticals electrical and computer engineering ELECTRICAL AND BIOMEDICAL CURRICULUM LEVEL lI Circuits I Circuits II Programming I Electronics I Differential Equations Programming II Introduction to Biology Calculus Introduction to Chemistry LEVEL III Digital Logic Linear Systems II Biological Materials Cell Biology Organic Chemistry I Electromagnetics I Linear Systems I Organic Chemistry II Anatomy I Anatomy II Electronics II Microprocessors LEVEL IV Probability Theory Communications I Linear Systems II (Discrete Time) Medical Imaging Biological Systems 2 Complementary Studies Bio Capstone Design Project Bio Capstone Design Project http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering computer engineering Computer Engineering involves the use of scientific discoveries and practical knowledge in digital circuit technology to create devices and systems that can be used to benefit the public. It encompasses computer hardware, software, electronics, digital communications, multimedia, signal processing, robotics, and other related technologies. Computer Engineers apply structured engineering design principles & methodologies to solve problems and develop products. Computer Engineers focus on the computer hardware and its interaction with the software. The specialty of the computer engineer is computer hardware. (Computer hardware is the term used for all the physical electronics and devices that comprise a computer.) what's special about this program at mac? Like other engineering programs at McMaster, this program will teach you the fundamental principles and will not focus on technologies that may quickly become obsolete. Students will find that, once they have completed the program, they easily learn to use whatever tools and techniques are current at the time. There is a focus on computer system design, i.e., hardware and software, which is attractive to industry. In addition, McMaster offers, programs in Engineering Management and Society, and offers the possibility of a 16-month internship in industry. Graduates are eligible to apply to an M.Eng. program that requires only one year of additional study beyond the Bachelor’s level. computer engineering program The second year gives a basic introduction into computer engineering. In third year, you start to specialize in computeroriented courses. You will take a course in computer hardware design. This course shows you how to design very complex computer hardware using so-called “programmable logic devices” (PLDs). PLDs consist of a large collection of AND and OR gates that may be configured in any way that the designer specifies. In labs you will use PLDs, to design digital systems such as an MP3 player or any form of peripheral computer equipment. You will also take a course in computer architecture. This subject deals with the design of high-performance computers at the minimum possible cost. You will learn what makes computers faster and easier to use. In the fourth year, you specialize more strongly in computers. There are additional courses in computer hardware design and computer architecture. There are courses in computer networks, internet communications and operating systems. You will also tale a technical elective, which is a course of your choosing. The Computer Engineering program consists of the following topics (highlights indicate the program’s distinguishing courses): Circuit analysis Electronics Programming Digital logic Linear systems Applied math Electromagnetics Computer hardware Software development/operating systems Computer architecture Communications Control theory Computer communication what do graduates do? Computer Engineers are currently in demand in Canada. Graduates find employment in areas such as: automotive software and computer communications development telecommunications robotics automation police forces telemedicine food processing military services power distribution and generation steel making electronics manufacturing instrumentation insurance IC development financial services video and audio processing robotics http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering COMPUTER ENGINEERING CURRICULUM LEVEL lI Circuits I Circuits II Programming I Electronics I Differential Equations Programming II Digital Logic Microprocessors Electromagnetics I LEVEL III Computer Hardware I Communication Systems I Electronics II Linear Systems II Software Development Numerical Methods Probability Theory Computer Hardware II (Comp. Architecture) Linear Systems I LEVEL III Computer Communications I Computer Communications II Computers III (Architecture) Operating Systems Technical Elective Complementary Studies Capstone Design Project Computer Hardware III Capstone Design Project http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering electrical or computer engineering and management what is computer or electrical engineering & management? The Computer or Electrical Engineering and Management program combines a regular four-year program in a specific engineering discipline with the core business courses of a four-year business program to make a five-year combined degree program. This program is the only discipline-specific, accredited, undergraduate Engineering and Management program in Canada. The program was first accredited in 1975 and takes five years to complete. At this time there are over 1,300 Engineering and Management graduates. Elements of the program include courses required by the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, courses required by the Business Faculty and courses required by the Engineering & Management department. Students must take Economics in their first year. Students apply to enter the Management program at the end of their first year when they make their discipline choices. A maximum of 136 students are allowed to enter the Management program in Level 2. why do students take engineering & mgmt? Some want a more well-rounded education that includes business as well as engineering. Some recognize that they will need business skills to fulfill their career goals. Some want to gain an extra competitive edge in the job market. Others just want to keep their career options open. how hard is it? The program is no harder or easier than the other engineering programs. It does require the development of different skills, however. Our graduates have business awareness skills, an ability to write well, an ability to speak well, and the ability to relate to people. All this is in addition to the skills related to their chosen discipline. what are the advantages? A major advantage of the program is that it provides skills not available to graduates in any other program in Canada. It gives graduates an extra competitive edge in getting a job. For example, the employment rate for Engineering and Management graduates has always been higher than for graduates in traditional engineering disciplines. Also, graduates in the Engineering and Management program command higher salaries than for graduates in the traditional programs. The program gives graduates a competitive edge in management as well, enabling them to fast-track their way to the top. what do graduates do? In addition to a career as a Professional Engineer, a graduate of Computer or Electrical Engineering & Management can become a(n) engineering project manager, accountant, production manager, engineering financial analyst, engineering marketing specialist, industrial relations specialist. Some graduates start their own companies. Graduates have also gone on to do higher degrees in Engineering and Business, some obtaining Ph.D.s in either profession. http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering COMPUTER ENGINEERING & MANAGEMENT* LEVEL l Course Description Course Description CHEM 1E03 General Chemistry for Engineering I MATH 1NN3 Calculus for Engineering II ENG 1C03 Engineering Design and Graphics PHYS 1D03 Introductory Mechanics ENG 1D04 Engineering Computation PHYS 1E03 Waves, Electricity and Magnetic Fields ENG 1P03 Intro to Professional Engineering ELECTIVE Complementary Studies Elective MATLS 1M03 Structure and Properties of Materials ELECTIVE Complementary Studies Elective MATH 1H03 Linear Algebra for Engineering ENG 1AOO Safety Training MATH 1N03 Calculus for Engineering I LEVEL II COMM 2AA3 Financial Accounting I ELEC ENG 2CJ4 Circuits and Systems COMP ENG 2SH4 Principles of Programming ELEC ENG 2FH3 Intro Engineering Electromagnetics ELEC ENG 2SI4 Data Struct., Algo. and Discrete Maths ENGMNGT 2AA2 Communication Skills ECON 1BBS Introductory Macroeconomics MATH 2P04 Differential Equations for End ECON 2XOS Applied Business Economics ELECTIVE Complementary Studies Elective ELEC ENG 2CI5 Introduction to Electrical End LEVEL III COMM 2AB3 Managerial Accounting I ELEC ENG 3TQ4 Probability and Random Processes COMM 2BA3 Organizational Behaviour COMP ENG 2DI4 Logic Design COMM 2FA3 Introduction to Finance COMP ENG 2DP4 MicroProcessor Systems COMM 2MA3 Introduction to Marketing ENGMNGT 3AA1 Project Mgmt. and Teamwork Skills ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronics Devices and Circuits I MATH 3KO3 Engineering Math III (complex Var.) ELEC ENG 3TP4 Signal and Systems LEVEL IV ELEC ENG 3EJ4 Electronic Devices and Circuits II COMM 3FAS Managerial Finance ELEC ENG 3TR4 Communications Systems COMM 3MC3 Applied Marketing Mgmt. COMP ENG 3DQ4 Digital Systems and Design STATS SY03 Statistical Analysis for Engineers COMP ENG 3DR4 Computer Organization ENGMGNT 4A01 Engineering and Mgmt. Report SFWR 3K04 Software Dev for Elect. Engineering ENG 4HO3/4AO3 Technology and Society COMM 3BC3 Human Resource Mgmt. COMM ELECTIVE LEVEL V COMM 4PA3 Business Policy COMP ENG 4DS4 Embedded Systems COMM 4QA3 Operations Modelling and Analysis COMP ENG 4OI5 Engineering Design COMP ENG 3SK3 Computer Aided Engineering SFWR ENG 3SH3 Operating System Concepts COMP ENG 4DK4 Computer Networks ENG MGMT 5BO3 Engineering and Mgmt. Projects COMP ENG 4DM4 Computer Architecture COMM ELECTIVE COMP ENG 4DN4 Advanced Internet Communications *The curriculum for Electrical Engineering & Management is not shown but has a similar structure http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering electrical or computer engineering and society what is computer or electrical engineering & society? The Engineering and Society program was created to provide students with a broader university education and to give them greater insight into the way engineering works in society. Graduates of this program learn about the complex issues of socially responsible engineering and can be expected to make this a life long commitment. The program is fashioned after the Engineering and Management program in that it spreads out the Engineering curriculum over five years, allowing room for another set of subjects. In the Engineering and Society program a set of focused electives and a series of required core courses are taken in addition to the basic engineering curriculum. This allows engineering students who have a strong interest in another subject (such as Music, French, or History) to take classes in that subject as well. Students apply for admission to the program near the end of their first year. The program takes up to 40 students a year. what skills do you learn? Since students in the program come from other engineering disciplines and take many courses from other faculties, they acquire an ability to interact effectively with others and to take a multi-dimensional approach to problem solving. Students develop their oral communication skills through the many group discussions and presentations (both individual and group) required in the core courses. Due to the nature of the material studied, written papers and assignments are common. Students develop a significant proficiency in written communication. The inquiry courses and inquiry approach in other core courses enable students to develop their research skills. This includes an ability to formulate relevant questions and to critically define and assess problems. what is special about the program? Some students are attracted to the greater interaction with fellow classmates offered by the style of learning in the core courses. For others, it is the opportunity to add flavor and variety to their required technical courses. The focused electives enable students to develop their interests outside of engineering. The four-year programs also allow for a few electives, but not many. Students in the Society program are able to explore another area of study in much more depth. By the time students are in their final year, they have learned what it takes to be a responsible engineer and to appreciate the broad base of knowledge the core courses offer. The small size of the program results in a sense of community and trust among colleagues. It is also quite easy to get to know your professors. what do graduates do? Computer and Electrical Engineers are currently in demand in Canada. Graduates find employment in areas such as environmental consulting, public industry research, conservation authorities, federal, provincial and municipal government, resource industries, colleges and universities and communications or start their own company. http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & SOCIETY CURRICULUM LEVEL l Course Description Course Description CHEM 1E03 General Chemistry for Engineering I MATH 1NN3 Calculus for Engineering II ENG 1C03 Engineering Design and Graphics PHYS 1D03 Introductory Mechanics ENG 1D04 Engineering Computation PHYS 1E03 Waves, Electricity and Magnetic Fields ENG 1P03 Intro to Professional Engineering ELECTIVE Complementary Studies Elective MATLS 1M03 Structure and Properties of Materials ELECTIVE Complementary Studies Elective MATH 1H03 Linear Algebra for Engineering ENG 1AOO Safety Training MATH 1N03 Calculus for Engineering I LEVEL II COMP ENG 2DI4 Logic Design MATH 2QO4 Advanced Calculus for Engineering COMP ENG 2SH4 Programming ENGSOC 2XO3 Inquiry in an Engineering Context I COMP ENG 2SI4 Data Structures and Algorithms ENGSOC 2YO3 Case Studies in History and Tech. ELEC ENG 2CI5 Introduction to Elec. Eng. ELECTIVE Focus elective ELEC ENG 2CJ4 Circuits & Systems MATH 2PO4 Differential Equations for Eng. LEVEL III COMP ENG 2DP4 Microprocessor Systems SFWR 3M04 Software Dev for Electrical Eng COMP ENG 3SK3 Computer Aided Engineering ENGSOC 3Y03 Culture of Tech. ELEC ENG 2EI5 Electronics Devices and Circuits I ENGSOC 3Z03 Preventive Engineering ELEC ENG 2FH3 Intro Engineering Electromagnetics ELECTIVE Focus Elective ELEC ENG 3TQ4 Probability and Random Processes ELECTIVE Optional Focus Elective MATH 3K03 Engineering Math III (complex Var.) ELECTIVE Optional Focus Elective LEVEL IV ELEC ENG 3EJ4 Electronic Devices and Circuits II ENG 4B03 Economics for Engineers ELEC ENG 3FK4 Advanced Electromagnetics ENGSOC 3X03 Inquiry in an Engineering Context II ELEC ENG 3PI4 Power Devices and Systems ELECTIVE Focus Elective ELEC ENG 3TP4 Signal and Systems ELECTIVE Focus Elective ELEC ENG 3TR4 Communications Systems ELECTIVE Focus Elective LEVEL V ELEC ENG 40I5 Engineering Design ELECTIVE Focus Elective ELECTIVE ECE Directed Technical Elective ELECTIVE Focus Elective ELECTIVE ECE Directed Technical Elective ENGSOC 4X03 Inquiry in an Engineering Context III ELECTIVE ECE Directed Technical Elective ENGSOC 4Z03 Social Control of Tech. ELECTIVE ECE Directed Technical Elective ELECTIVE Eng. And Soc. Focus Elective *The curriculum for Computer Engineering & Society is not shown but has a similar structure http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering TECHNICAL ELECTIVES Electrical Engineering Course Description Term COE 3DQ4 Digital Systems Design 1 COE 3DR4 Computer Organization 2 COE 4DK4 Computer Engineering Networks 1 COE 4DM4 Computer Architecture 1 COE 4DN4 Advanced Internet Communications 2 COE 4DS4 Embedded Systems 2 COE 4EK3 Microelectronics 1 COE 4TL4 Digital Signal Processing 1 EE 4BD4 Biomedical Instrumentation 2 EE 4BF3 Medical Image Processing 2 EE 4CL4 Control System Design 2 EE 4EM3 Photonic Device And Systems Engineering 2 EE 4FJ4 Microwave Engineering 2 EE 40J3 Research Project 1 and 2 EE 4PK4 Power Electronics 2 EE 4PL4 Energy Systems And Management 1 EE 4TK4 Digital Communications Systems 2 ME 4H03 Mechatronics 2 http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009 electrical and computer engineering TECHNICAL ELECTIVES Computer Engineering Course Description Term COE 4EK3 Microelectronics 1 COE 40J3 Research Project 1 and 2 COE 4TL4 Digital Signal Processing 1 COE 4TN3 Image Processing 2 EE 3FK4 Electromagnetics II 2 EE 3PI4 Power Devices And Systems 1 EE 4BD4 Biomedical Instrumentation 2 EE 4BF3 Medical Image Processing 2 EE 4CL4 Control System Design 2 EE 4EM3 Photonic Device And Systems Engineering 2 EE 4FJ4 Microwave Engineering 2 EE 4PK4 Power Electronics 2 EE 4PL4 Energy Systems And Management 1 EE 4TK4 Digital Communications Systems 2 http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/ As of 3/16/2009