Fire Safety
advertisement

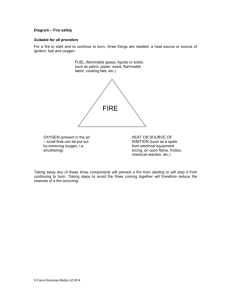
Fire Safety Fire risk assessment Colin de Jongh Health and Safety Manager Regulatory Reform Order (Fire Safety) Enacted 1st October 2006 Fire certificates cease to have effect New duty holder “Responsible Person” Must carry out a fire risk assessment Responsible Person The person who has to any extent the control of : A workplace – the employer, managers, supervisors etc. The premises – owner, occupier or agent Responsible Person Must appoint competent person(s) to assist with fire safety measures Take general fire precautions to ensure safety of employees and other relevant persons Does not apply to domestic premises, ships at sea, vehicles, fields or woods, mines etc. Does apply to external events. General Fire Precautions Reduce the risk and spread of fire Ensure means of escape at all times Fire fighting measures on premises Fire detection and warnings of Action in the case of fire Training and instruction Measures to mitigate the effects Any questions? Main causation of fires (12 months Jan 05 to Dec 05) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Deliberate ignition - 53 Electrical - 34 Cooking - 13 Friction, heat and sparks - 12 Smoking materials - 11 Naked light - 4 >£250K Organisations (12 months Jan 05 to Dec 05) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Dwellings - 27 Local/national government – 25 Hospitality & food and drink industry - 13 Retail – 12 Chemical Industry - 11 Education - 9 >£250K Fire safety risk assessment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify the fire hazards Identify the people at risk Evaluate, remove or reduce, and protect from risk Record, plan, inform, instruct, and train Review Any questions? 1. Identify the fire hazards Identify: Sources of ignition Sources of fuel Sources of oxygen The fire triangle Sources of ignition ARSON Smokers materials Naked flames Electrical, gas, portable heating equipment Hot processes- paint stripping, welding Lighting equipment Sources of fuel Flammable liquid based products Packaging materials Waste products Stationary Soft furnishings and furniture Some construction materials Sources of Oxygen The air around us Air conditioning Some chemicals Oxygen supplies – cylinder storage Pyrotechnics Any questions? 2. Identify the people at risk Employees especially those who work alone Vulnerable people Contractors Young people Other people in the immediate vicinity Fire fighters 3. Evaluate, remove, reduce, and protect from risk Evaluate the risk of a fire occurring: Accidentally By act or omission Deliberately 3. Evaluate, remove, reduce, and protect from risk Evaluate the risk to people Fire is spread by: Convection Conduction Radiation Contact or direct heat Smoke movement through a building Why do we close fire doors? Why we do close fire doors Evaluating the risks to people Consider: Fires on lower floors can affect escape routes for those on upper floors Fires developing in unoccupied spaces which people have to pass Spread of fire or smoke via vertical shafts and service or ventilation ducts Fires in service rooms affecting hazardous materials Remove or reduce the hazards - sources of ignition Replace potential sources of ignition with an alternative Replace naked flame and radiant heaters with fixed convector heaters or central heating Separate ignition sources and fuels Check areas after hot work has taken place Take precautions to avoid arson Remove or reduce the hazards - sources of fuel Ensure flammable materials, liquids and gases are kept to a minimum and stored properly Do not keep flammable solids, liquids and gases together Remove combustible waste daily Store waste materials securely away from buildings. Remove or reduce the hazards – sources of oxygen Close all doors, windows and other openings when not required for ventilation Shut down inessential ventilation systems Do not store oxidising materials next to heat sources or flammable materials Control use of oxygen cylinders Remove or reduce the hazards – to people Ensure that any risks remaining to people are controlled Provide systems to warn people and allow them to escape in the event of fire Provide adequate exits for the number of people present Fire detection and warning systems System will depend on the size and layout of the building It should provide adequate warning in the event of a fire Automatic or manual? You may/will need special arrangements for people with disabilities Fire-fighting equipment and facilities Can reduce the risk of a small fire (waste paper bin) developing into a larger one Controlling a fire in the early stages can reduce the risk to people There should be enough portable extinguishers suitable for the risk They should be sited throughout the premises at suitable locations Fire-fighting equipment and facilities Co2 Foam Powder Water Fire-fighting equipment and facilities Class A fire – rule of thumb one water extinguisher for every 200m² minimum 2 per floor Additional risks – appropriate type & number of extinguishers. See BS 5306-8 Other facilities Can include: Access for fire engines and fire-fighters Fire-fighting shafts and lifts Fire suppression systems – sprinklers Smoke-control systems Dry or wet rising mains and fire-fighters inlets Information and communication systems Fire-fighters switches Escape routes Escape routes should be: Suitable Easily, safely and immediately usable at all times Adequate for the number of people Free from any obstructions, slip or trips hazards Available for access by the emergency services Escape routes Suitable: Fire resistant construction Escape routes should not go through other occupiers premises Doors should open in the direction of travel Be fitted with vision panels if over 60 people Emergency evacuation of persons with mobility impairment Do not use lifts unless alternative power supplies and protected from smoke Take to refuge and wait for assistance or begin staged evacuation – provide communications. You must have plans to evacuate without assistance Consider use of evacuation chairs Provide buddy system for those with visual impairment Visual alarms in cases of hearing impairment Emergency escape lighting Provided on all escape routes to assist in evacuation and should cover: Exit doors and escape routes Intersections of corridors Outside each final exit and external escape routes and stairways Changes in level Fire equipment and alarm call points Signs and notices Comply with British or European standards Not mixed Be fire resistant British Standard European Standard Installation, testing & maintenance Installed by competent persons Maintained in line with manufacturers guidance Tested weekly Inspected quarterly Records kept for inspection Any questions? 4. Record, plan, inform, instruct & train Fire risk assessment – recorded available for inspection Actions prioritised and implemented Evacuation plans developed, implemented and tested – at least twice annually or once per term Employee groups informed of results Employees, visitors, contractors given adequate training and instruction 5. Review Review risk assessments, plans etc: When changes occur – changes to work processes, alterations to the building or work patterns Introduction of new equipment, hazardous substances, significant increase in people At least annually We don’t want to end up like this Or this Any questions?