The Rebuilding Years - Anderson School District One

The Rebuilding Years
Chapter 15
The Condensed version
Lincoln’s Plan
Overall Purpose: to help end the war faster
Political purpose: to restore Southern states’ full political union with other states
He required that state governments create significant social change by recognizing the end of slavery
Lincoln’s Plan
Main parts:
Remove the government officials of the
Confederate States of America and replace them with officials loyal to the Union
Punish high ranking Confederates by removing their right to vote
Confederates who took oath to constitution and
Union laws would receive a pardon and get their land back
State would be readmitted when 10% of men took oath of allegiance to Union. State had to write new constitution and elect new officials
Johnson’s Plan
Not much different than Lincoln’s
Purpose: to humiliate Southern elite
Main parts
State would be readmitted when 10% of men took oath of allegiance to Union. State had to write new constitution and elect new officials
Southern elite had to request a pardon from the president
Approve the 13 th amendment
Nullify the Ordinance of secession
South had to repay people and institutions that helped finance the Confederacy
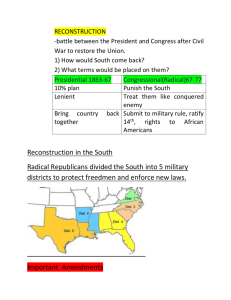
Radical Republican Plan
Overall Purpose: to make the South pay dearly for the Civil War
Political purpose: to protect the rights of freedmen and protect the power of the Republicans
Radical Republican Plan
Main parts:
The Confederacy would be split into five military districts, under the command of a military governor
New legislatures had to approve the 14 th amendment
Voting rights (suffrage) were given to black males and taken away from white males who participated in the war.
No person who participated in the war could hold a public office
State constitutions had to be approved by
Congress
Amendments
13 th : freed the slaves
14 th : gave citizenship to all people born in the United States
15 th : gave black males the right to vote
Freedmen
Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and
Abandoned Lands was created to help people who need assistance after the war (food, clothing, shelter, medical care, and education)
Known as the Freedmen’s Bureau, it helped freed slaves find jobs, and establish courts to protect illiterate workers
Freedmen
Bureau originally promised land to freedmen that was abandoned or taken from white farmers.
Congress gave the land back to white farmers, but the anger that the whites had against the freedmen continued
Freedmen
African Americans enjoyed new freedoms but not for long
Southern whites tried to regain control with laws like the Black Codes and with vigilante groups like the KKK
Economic problems
South had economic problems after the end of slavery
They had to rebuild the state
(buildings, houses, railroads) with no federal help
African American farmers now caused competition for white farmers
Sharecropping
Plantation owners were stuck with large plots of land, tools, and no one to work for them
Freedmen were willing to work, but had no land and no tools
Sharecropping allowed freedmen to use the tools and live in the old plantation slave houses, and use the land
Plantation owners would get part of the crop grown by the sharecroppers
Sharecropping
Sharecroppers were economically dependent upon land owner
In bad years sharecroppers could borrow a loan from the land owner, in the form of a lien, to buy supplies for the next year
The liens placed freedmen in a cycle of debt
Northern Immigration
To help out with the education and lives of freedmen, many northerners moved to South
Carolina to establish schools
They were mistaken as carpetbaggers and were not accepted by Southern white society
Carpetbaggers and Scalawags
Carpetbaggers were Northerners who moved to the South to make an economic gain
Land and businesses were cheap and there was little competition
Scalawags were Southerners that supported the carpetbaggers to get the social, economic, and political benefits from them
Women
Women suffered alongside their husbands with the loss of farms and houses
Elite white women had to take on household jobs that slaves had once done
Women whose husbands had been injured in the war had to take on a more physical role around the house and farm
Former slaves, carpetbaggers, and scalawags pushed for more rights for women
South Carolina’s New Constitution
Under the Reconstruction Policy’s
South Carolina had to write a new constitution
State representation was based on population alone, not on wealth and population as it had been previously
African Americans gained positions in offices of government and even sent six members to the United States
House of Representatives
Political Corruption
Corruption became a problem, because of the poor economy many people were willing to take bribes
South Carolina wanted new schools, but complained about them when taxes were raised to pay for them
The Hamburg Massacre of 1876 took place in Aiken county when six Africa
American militia members were killed by a white mob
This showed the whites trying to “redeem” their superiority
Election of 1876
Tired of the corrupt Republicans, white Democrats, known as “Red
Shirts” used violence, intimidation, and fraud to win the 1876 election
President Grant sent troops to help ensure a fair election
There were questions about the winners of the governor, as well as
General Assembly
Election of 1876
Neither side wanted to back down, and both Democrats and Republicans set up their own government in South Carolina
White taxpayers refused to support the
Republican government
Voting problems also took place on a nation level
Congress let go of their focus to protect the freedmen as they tried to fight corruption
Election of 1876
A compromise between Democrats and
Republicans was reached
Democrats in SC would accept the
Republican President Hayes
President Hayes would remove federal troops from South Carolina
Democrat and former Confederate General
Wade Hampton became governor of SC
African Americans no longer had federal troops to help protect them from the violence in SC