Measurement Student Notes
advertisement

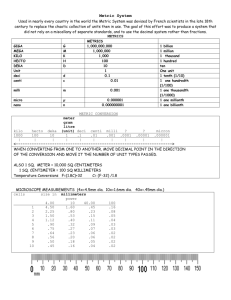
Unit 1: Measurement Matter Everything is made of _________ Matter is described as anything that has volume and mass. ______________ is the amount of space an object takes up. ___________ is the amount of matter in an object. Mass The unit for mass is the ______________ (kg). Mass is different from weight. Your weight factors in the effect of gravity. How do we measure Volume? * Volume = amount of space an object takes up 1.Direct measurement (using a metric ruler) 2.Water displacement 1.Direct Measurement For a Solid _____________ Object (rectangular prism): Volume = ____________________________ Volume Unit = _________ ** 1ml = 1cm^3 Volume Example Volume = LxWxH Volume = 7 x 4 x 2 = 56cm Problems 1. Problems 2. Problems 3. 2. Liquid Volume & Water Displacement Method Liquid Volume - Use a _____________________ cylinder - Remember: 1mL = 1cm^3 Water Displacement Method - Used for objects with an ___________ shape - Anything other than a square or rectangle TedED Video 1. Why couldn’t Archimedes find the volume of the crown by measuring it with a ruler? ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ Water Displacement - Essentially, however much water is __________________ (pushed out of the way) by the object= ______________ of the object. Example: Before Rock = ________ mL After Rock = ________ mL Rock Volume = ____ Example: Before Rock = _______ mL After Rock = _______ mL Rock Volume = ____ 1. With Object: ________ mL 2. With Object:________ mL W/out Object: ________ mL W/out Object: ________ mL Volume: ________ mL Volume: ________ mL The Metric System Metric Conversion Chart Metric Scale Basic Units Include: Meters Liters Grams Watts Newtons Kilo Hecto Deca Base Deci Centi Milli 1000 100 10 Base 0.1 0.01 0.00 Kilo Hecto Deca Base Deci Centi Milli K____________ H____________ D____________ B____________ D____________ C____________ M____________ K H Da B D C M Let’s look at a metric ruler. 1. How many meters are in a meter? _______ 2. How many decimeters are in a meter? ____ 3. How many centimeters are in a meter?____ 4. How many millimeters are in a meter?_____ K H Da B D C M Let’s look at a metric ruler in the other direction. 5. How many meters are needed to make a decameter? ___________ 6. How many meters are needed to make a hectometer? __________ 7. How many meters are needed to make a kilometer? ___________ Check 4 Understanding For the following units, state if they are smaller or larger than a meter. a. centi _____________________ b. hecto _____________________ c. deca _____________________ d. deci _____________________ K H Da B D C M 47424.6 mL = __________ Hl -Put your finger on the units that you are given (which are mL) on the scale above. -Move your finger left to hL, and count the number of places you have moved. -Move the decimal the name number of places in the same direction. K H Da B D C M 6.7234 kL = ____________ L (base unit) -Put your finger on the units that you are given (which are kL) on the scale above. -Move your finger right to B, and count the number of places you have moved. (Three to the right). -Move the decimal the name number of places in the same direction. Why does an object float on water? Density - Density = ratio of the mass to volume of a substance at a given temperature ** Basically, how _______________ ________________the molecules are within that substance. Density Unit = _______________for both liquids and solids Which is more dense? Formula for Density Density = __________ Part I: Find the Unknown Quantity A.D= ? V= 100mL M= 50ML Part I: Find the Unknown Quantity B. D= ? V= 950mL M= 95g Part I: Find the Unknown Quantity C) D= ? V= 40cm^3 M= 20 g Part I: Find the Unknown Quantity D) D= ? V= 90cm^3 M= 30g Part II: Conversion REMEMBER: Mass is always in __________. Volume is always in ________or ___________. D is always in g/mL or g/cm^3 ** You may need to convert back to g or mL. Part II: Converting Before Solving A.D= ? B.V= 1.2L (Convert L to mL 1st) M= 28,800g B. D= ? V= 100mL M= 1.5kg (Convert kg to g 1st) D=M/V D= D= M/V D= Part II: Converting Before Solving C. D= ? V= 0.52 L M= 500 mg What do we need to do 1st? Temperature Temperature: Measure of the _______________ kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter (different from heat) ______________ Energy: Energy of motion Three Units of Temperature 1._______________ (℉) 2._______________ (℃) - Based on ____________________ 3. _______________ (K) Kelvin (K) - Considered international scientific scale for temperature - Notice → no degree symbol - Freezing point of water: _______K - Boiling point of water: ________K Absolute Zero Absolute Zero _______ (-459.67℉) - Hypothetical temperature atoms reach minimum ________________ Fill in the table. ** 9/5 = 1.8 ** 5/9= .556 Conversion Formulas C to F ℉ = (9/5 x C) + 32 F to C ℃ = 5/9 x (F -32) C to K K = ℃ + 273 K to C ℃ = K -273 Fill in the table using the formulas. Temperature Scales Fahrenheit ℉ Celsius ℃ Water Boils Body Temperature 212 37 Room Temperature Water Freezes Kelvin K 293 0 Practice 1. “The weather forecaster predicts that today’s high will be 70° .” -Which scale is being used? _____________ -On the Celsius scale? __________________ -On the Kelvin scale? __________________ Practice 2. “It was so cold yesterday that the temperature only reached 275!” -Which scale is being used? ___________ -On the Celsius scale? ________________ -On the Fahrenheit scale? _______________ Practice 3. “Today’s temperature of 42° in Chicago set a record high for the month of August.” -Which scale is being used? ___________ -On the Kelvin scale? ________________ -On the Fahrenheit scale? _____________