Food Chain/Web Session 2 - Saint Mary Catholic School
advertisement

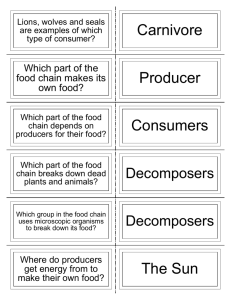
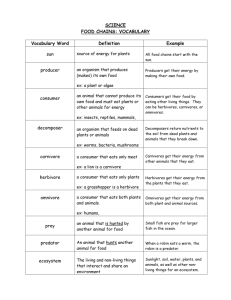
Food Chains and Food Webs What is a food chain? • A food chain is “a sequence of organisms, each of which uses the next, lower member of the sequence as a food source1” Important facts about food chains • In a food chain each organism obtains energy from the one at the level below. • Plants are called producers because they create their own food through photosynthesis3 • Animals are consumers because they cannot create their own food, they must eat plants or other animals to get the energy that they need. The Producers Producers are the beginning of a simple food chain. Producers are plants and vegetables. The Producers All energy comes from the Sun and plants are the ones who make food with that energy. They use the process of photosynthesis. Plants also make loads of other nutrients for other organisms to eat. Primary Producers • Primary producers are “organisms capable of producing their own food4” • We can also say that they are photosynthetic, use light energy. • Examples of primary producers include algae, phytoplankton, and large plants. • Primary producers are eaten by primary consumers (herbivores) Primary Producers of Common Marshes Marsh Mallow Cattails http://www.nicerweb.com/doc/class/pix/PRAIRIE/2005_07_18/Typha_angustifolia.jpg http://www.ncdot.org/doh/Operations/dp_chief_eng/roadside/wildflowerbook/graphics/images/page14a.jpg Marsh Fern Blue Flag Iris http://www.ontariowildflower.com/images/blueflag2.jpg http://wisplants.uwsp.edu/scripts/detail.asp?SpCode=THEPALvPUB The Consumers Consumers are the next link in a food chain. There are three levels of consumers. •Primary consumers (1st Order) –Worms, insects, squirrels, mice: all eat plants (HERBIVORES) ex: squirrel eats acorns •Secondary consumers (2nd Order) –Eat the primary consumers (CARNIVORES) example: cat eats squirrel •Tertiary consumers (3rd order) –Eat the primary and secondary consumers (CARNIVORES) ex: wolf eats cat and squirrel Other Ways to Classify Consumers 1. Primary Consumers: Herbivores. 2. Secondary Consumers: Carnivores that eat herbivores. 3. Tertiary Consumers: Carnivores that eat other carnivores. Four types of consumer • Herbivores: animals that eat only plants3 • Carnivores: animals that eat only other animals3. • Omnivores: animals that eat animals and plants3. • Detritivores: Animals that eat dead materials and organic wastes Primary Consumers in Marshes Muskrat (eats mostly Cattails) http://wdfw.wa.gov/wlm/living/graphics/muskrat1.jpg http://www.advancedwildlifecontrolllc.com/images/muskrat.jpg Primary Consumers in Marshes • Wood Duck eats seeds like those of the Swamp Marsh Mallow and Blue Flag Iris http://dsf.chesco.org/ccparks/lib/ccparks/wood_duck_pair.jpg Primary Consumers in Marshes • Glassy-winged Toothpick Grasshopper – eats leaves of plants like cattail and pickerelweed http://bugguide.net/node/view/41662 Secondary Consumers • Black Rat Snake eats eggs of animals like wood duck http://www.bio.davidson.edu/projects/tate/Terms.htm Secondary Consumers • Swamp Sparrow eats seeds but also insects like the toothpick grasshopper http://www.jeaniron.ca/2007/SwampSparrow6645.jpg Tertiary Consumers • Eat other animals in marsh including snake and sparrow Osprey www.montereybay.com www.audubon.org Omnivore • Racoon eats seeds, fruits, insects, worms, fish, and frogs… and pretty much anything else they can get their paws on! http://abouttitusville.com/BobPaty/Animals/images/Racoon.jpg Detritivore • Worms are common detritivores in many ecosystems including marshes The Decomposers The last links in the chain are the decomposers. (They break things down) Like bacteria, mold, fungi, mushrooms •If you die, they eat you. •If you poop, they eat that. •If you lose a leaf, they eat it. Whenever something that was alive dies, the decomposers get it. Decomposers break down nutrients in the dead "stuff" and return it to the soil. The producers can then use the nutrients and elements once it's in the soil. The decomposers complete the system, returning essential molecules to the producers. What is a food web? A food web is “an interlocking pattern of food chains2”